Abstract
Background and study aims
Minimally invasive retroperitoneoscopic surgery (MIS) for psoas abscess (PA) in patients with thoracolumbar tuberculosis is not well-illustrated and has not reached the status of being fully clinically assessed when we review the English literatures. The aim of this study is to introduce and investigate on efficacy and feasibility of MIS (retroperitoneoscopic technique) for PA in patients with thoracolumbar tuberculosis.
Patients and methods
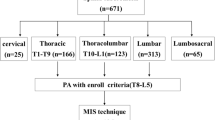
From January 2008 to 2013, 39 consecutive patients of the diagnosis of PA with thoracolumbar tuberculosis received the debridement of abscesses and cavity walls of abscesses by the retroperitoneoscopic technique (MIS) in combination with anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy. Medical records and follow-up data were retrospectively studied. CRP and ESR of every patient preoperatively and postoperatively were analyzed
Results
Immediate relief in clinical symptoms and signs, and amelioration in imaging and laboratory examinations were obviously observed in all the patients. The follow-up had proceeded for 12–48 (mean 23) months. No complication was observed during the follow-up postoperatively.
Conclusions
The retroperitoneoscopic technique for PA gain advantages in terms of shorter hospital stay, minimal invasiveness, absence of radiation, quicker recovery to daily life compared with percutaneous drainage, and anterior or posterior debridement surgery. Despite the technique not been fully clinically proved, it seems to be a recommended option as an effective diagnostic and therapeutic technique for PA, especially with massive or complicated PA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mynter H (1881) Acute psoitis. Buffalo Med Surg J 21:202–210
Santaella RO, Fishman EK, Lipsett PA (1995) Primary vs secondary iliopsoas abscess. Presentation, microbiology, and treatment. Arch Surg 130:1309–1313
Franco-Paredes C, Blumberg HM (2001) Psoas muscle abscess caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Staphylococcus aureus: case report and review. Am J med sci 321:415–417
Raviglione M, Marais B, Floyd K, Lonnroth K, Getahun H, Migliori GB, Harries AD, Nunn P, Lienhardt C, Graham S, Chakaya J, Weyer K, Cole S, Kaufmann SH, Zumla A (2012) Scaling up interventions to achieve global tuberculosis control: progress and new developments. Lancet 379:1902–1913
Chiang CY, Van Weezenbeek C, Mori T, Enarson DA (2013) Challenges to the global control of tuberculosis. Respirology 18:596–604
Pang X, Shen X, Wu P, Luo C, Xu Z, Wang X (2013) Thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis with psoas abscesses treated by one-stage posterior transforaminal lumbar debridement, interbody fusion, posterior instrumentation, and postural drainage. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133:765–772
Wu TL, Huang CH, Hwang DY, Lai JH, Su RY (1998) Primary pyogenic abscess of the psoas muscle. Int Orthop 22:41–43
Jin W, Wang Q, Wang Z, Geng G (2014) Complete debridement for treatment of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a clinical curative effect observation. The spine journal: official journal of the North American Spine Society 14:964–970
Pang X, Shen X, Wu P, Luo C, Xu Z, Wang X (2013) Thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis with psoas abscesses treated by one-stage posterior transforaminal lumbar debridement, interbody fusion, posterior instrumentation, and postural drainage. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133:765–772
Bresee JS, Edwards MS (1990) Psoas abscess in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 9:201–206
Procaccino JA, Lavery IC, Fazio VW, Oakley JR (1991) Psoas abscess: difficulties encountered. Dis Colon Rectum 34:784–789
Nussbaum ES, Rockswold GL, Bergman TA, Erickson DL, Seljeskog EL (1995) Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg 83:243–247
Atkin G, Qurashi K, Isla A (2005) Laparoscopic drainage of bilateral tuberculous psoas abscesses. Surg laparosc endosc percutan tech 15:380–382
Baier PK, Arampatzis G, Imdahl A, Hopt UT (2006) The iliopsoas abscess: aetiology, therapy, and outcome. Langenbeck’s arch surg/Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Chirurgie 391:411–417
Buyukbebeci O, Seckiner I, Karsli B, Karakurum G, Baskonus I, Bilge O, Kacira BK (2012) Retroperitoneoscopic drainage of complicated psoas abscesses in patients with tuberculous lumbar spondylitis. Eur Spine J 21:470–473
Katara AN, Shah RS, Bhandarkar DS, Unadkat RJ (2004) Retroperitoneoscopic drainage of a psoas abscess. J Pediatr Surg 39:e4–e5
Acknowledgments
This publication was founded in part by the Beijing science and technique star foundation (2010B80).
Disclosures
Xuesong Zhang, Zhifa Zhang, Yan Wang, Yonggang Zhang, Xin Ma, Jiaqi Wang, Ming Lu, Wenhao Hu, and Yao Wang have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xuesong Zhang and Zhifa Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. Minimally invasive retroperitoneoscopic surgery for psoas abscess with thoracolumbar tuberculosis. Surg Endosc 29, 2451–2455 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3913-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3913-z