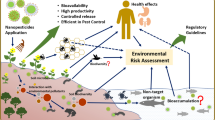
Abstract
Insects feed on plants and cause the growth of plants to be restricted. Moreover, the application of traditional pesticides causes harmful effects on non-target organisms and poses serious threats to the environment. The use of conventional pesticides has negative impacts on creatures that are not the intended targets. It also presents significant risks to the surrounding ecosystem. Insects that are exposed to these chemicals eventually develop resistance to them. This review could benefit researcher for future development of nanopesticides research. This is because a holistic approach has been taken to describe the multidimensional properties of nanopesticides, health and environmental concerns and its possible harmful effects on non-target organisms and physiochemical entities. The assessment of effects of the nanopesticides is also being discussed through the drosophotoxicology. The future outlooks have been suggested to take a critical analysis before commercialization or formulation of the nanopesticides.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on the request.
Abbreviations
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
- nm:
-
Nanometer
- IPMS:
-
Integrated Pest Management Strategies
- CDS:
-
Controlled Delivery System
- EC:
-
Emulsion Concentrate
- O/W:
-
Oil in Water
- W/W:
-
Water in Water
- TEM:
-
Transmission Electron Micrograph
- ATR-FTIR:
-
Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene Glycol
- SLN:
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticle
- PE:
-
Pickering Emulsion
- AcI:
-
Active Ingredient
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- EPA:
-
Environment Protection Act
- USDA:
-
United States Department of Agriculture
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- OECD:
-
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
References
Singh SB (2014) Nanotechnology in agri-food production: An overview. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 7(2):31–53. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSA.S39406
E. Birch AN, Begg GS, Squire GR. How agro-ecological research helps to address food security issues under new IPM and pesticide reduction policies for global crop production systems. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(10):3251–3261. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err064
Dhaliwal G, Jindal V, Dhawan A (2010) Insect pest problems and crop losses: changing trends. Indian J Ecol 37(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.25753.47201
Brunner J, Talbott K, Elkin C. Logging Burma’s Frontier Forests: Resources and the Regime. World Resousces Inst. Published online 1998:62.
Aspelin AL, Grube AH. Pesticides Industry Sales and Usage: 1994 and 1995 Market Estimates. Off Pestic Programs, US Environ Prot Agency. 1997;(August):39.
Ippolito A, Kattwinkel M, Rasmussen JJ, Schäfer RB, Fornaroli R, Liess M (2015) Modeling global distribution of agricultural insecticides in surface waters. Environ Pollut 198:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.12.016
Wilson C. Cost and policy implications of agricultural pollution, with special reference to pesticides. Dep Econ. 1999;PhD:233.
Ruiz-Suárez N, Boada LD, Henríquez-Hernández LA et al (2015) Continued implication of the banned pesticides carbofuran and aldicarb in the poisoning of domestic and wild animals of the Canary Islands (Spain). Sci Total Environ 505:1093–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.093
Zhang Y, Chen W, Jing M et al (2019) Self-assembled mixed micelle loaded with natural pyrethrins as an intelligent nano-insecticide with a novel temperature-responsive release mode. Chem Eng J 361:1381–1391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.132
Parween T, Jan S, Mahmooduzzafar S, Fatma T, Siddiqui ZH (2016) Selective effect of pesticides on plant—a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56(1):160–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2013.787969
Iavicoli I, Leso V, Beezhold DH, Shvedova AA (2017) Nanotechnology in agriculture: opportunities, toxicological implications, and occupational risks. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 329:96–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.05.025
Anton N, Vandamme TF (2011) Nano-emulsions and micro-emulsions: Clarifications of the critical differences. Pharm Res 28(5):978–985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0309-1
Senior JH (2008) Nanoparticulate drug delivery systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34(1):116. https://doi.org/10.1080/03639040701877119
Torchilin V (2006) Introduction. Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery: Needs and Requirements. Nanoparticulates as Drug Carriers, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1142/9781860949074_0001
Elibol OH, Morisette D, Akin D, Denton JP, Bashir R (2003) Integrated nanoscale silicon sensors using top-down fabrication. Appl Phys Lett 83(22):4613–4615. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1630853
Soloviev M (2007) Nanobiotechnology today: focus on nanoparticles. J Nanobiotechnol 5(11):3–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-5-11
Kah M, Beulke S, Tiede K, Hofmann T (2013) Nanopesticides: State of knowledge, environmental fate, and exposure modeling. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43(16):1823–1867. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2012.671750
Kah M, Hofmann T (2014) Nanopesticide research: Current trends and future priorities. Environ Int 63:224–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.11.015
Kalpana Sastry R, Anshul S, Rao NH (2013) Nanotechnology in food processing sector—an assessment of emerging trends. J Food Sci Technol 50(5):831–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0873-y
Wibowo D, Zhao CX, Peters BC, Middelberg APJ (2014) Sustained release of fipronil insecticide in Vitro and in Vivo from biocompatible silica nanocapsules. J Agric Food Chem 62(52):12504–12511. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf504455x
Nishisaka C, Grillo R, Sanches G, Fraceto L, Lima R (2014) Analysis of the effects of pesticides and nanopesticides on the environment. BMC Proc 8(S4):6561. https://doi.org/10.1186/1753-6561-8-s4-p100
Kapinder, Dangi K, Verma AK. Efficient & eco-friendly smart nano-pesticides: Emerging prospects for agriculture. Mater Today Proc. 2021;45:3819–3824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.211
Huang B, Chen F, Shen Y et al (2018) Advances in targeted pesticides with environmentally responsive controlled release by nanotechnology. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020102
Xu Z, Tang T, Lin Q et al (2022) Environmental risks and the potential benefits of nanopesticides: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20(3):2097–2108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01338-0
Coa F, Bortolozzo L, Petry R et al (2020). Environmental toxicity of nanopesticides against non-target organisms: the State of the Art. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44873-8_8
Yan S, Cheng WY, Han ZH et al (2020) Nanometerization of thiamethoxam by a cationic star polymer nanocarrier efficiently enhances the contact and plant-uptake dependent stomach toxicity against green peach aphids. Pest Manag Sci 77(4):1954–1962. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6223
Zhao X, Zhu Y, Zhang C, Lei J, Ma Y, Du F (2017) Positive charge pesticide nanoemulsions prepared by the phase inversion composition method with ionic liquids. RSC Adv 7(77):48586–48596. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra08653a
Abdollahdokht D, Gao Y, Faramarz S et al (2022) Conventional agrochemicals towards nano-biopesticides: an overview on recent advances. Chem Biol Technol Agric 9:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-021-00281-0
Margulis-Goshen K, Magdassi S. Nanotechnology: an advanced approach to the development of potent insecticides bt - advanced technologies for managing insect pests. In: Ishaaya I, Palli SR, Horowitz AR, eds. Springer, Netherlands; 2013:295–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4497-4_15
Shahid M, Naeem-Ullah U, Khan W, Saeed DS, Razzaq K (2021) Application of nanotechnology for insect pests management: a review. J Innov Sci 7(1):28–39. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.jis/2021/7.1.28.39
Keshavarz MH, Shirazi Z, Eskandari P (2022) A simple assessment of toxicity towards Chlorella vulgaris of organic aromatic compounds in environmental protection. Process Saf Environ Prot 163:669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.05.074
Divya K, Divyasree R, Vamsidhar M et al (2021) Emulsion, micro emulsion and nano emulsion: a review. Published Online. https://doi.org/10.20959/wjpps20214-18643
Mujahid A, Dickert FL. (2016) 5 - Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Principle, Design, and Enzyme-Like Catalysis. In: Li S, Cao S, Piletsky SA, Turner APFBTMIC, eds. Elsevier, Amsterdam. 2016:79–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801301-4.00005-0
Khan MM, Cho MH (2018) Positively charged gold nanoparticles for hydrogen peroxide detection. Bionanoscience 8(2):537–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0503-x
Chan WCW, Nie S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science (80- ). 1998;281(5385):2016–2018. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.281.5385.2016
De JWH, Paul JB (2008) Drug delivery and nanoparticles: applications and hazards. Int J Nanomedicine 3(2):133–149. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s596
Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil SE. Immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Nanosci Technol A Collect Rev from Nat Journals. 2009:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814287005_0029
Chin CP, Wu HS, Wang SS (2011) New approach to pesticide delivery using nanosuspensions: research and applications. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(12):7637–7643. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie2001007
Elek N, Hoffman R, Raviv U, Resh R, Ishaaya I, Magdassi S (2010) Novaluron nanoparticles: formation and potential use in controlling agricultural insect pests. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 372(1–3):66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.09.034
Bhagat D, Samanta SK, Bhattacharya S (2013) Efficient management of fruit pests by pheromone nanogels. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01294
Boehm AL, Martinon I, Zerrouk R, Rump E, Fessi H (2003) Nanoprecipitation technique for the encapsulation of agrochemical active ingredients. J Microencapsul 20(4):433–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/0265204021000058410
Israelachvili J. The science and applications of emulsions - an overview. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp. 1994;91(C):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-7757(94)02743-9
Gutiérrez JM, González C, Maestro A, Solè I, Pey CM, Nolla J (2008) Nano-emulsions: New applications and optimization of their preparation. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 13(4):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2008.01.005
Review B (1996) Lat Am Perspect 23(4):50
Katagi T (2008) Surfactant effects on environmental behavior of pesticides. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 194:71–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-74816-0_4
Mason TG, Wilking JN, Meleson K, Chang CB, Graves SM (2006) Nanoemulsions: formation, structure, and physical properties. J Phys Condens Matter. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/18/41/R01
Song S, Liu X, Jiang J, Qian Y, Zhang N, Wu Q (2009) Stability of triazophos in self-nanoemulsifying pesticide delivery system. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 350(1–3):57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.08.034
McClements DJ (2012) Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: Terminology, differences, and similarities. Soft Matter 8(6):1719–1729. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2sm06903b
Anton N, Benoit JP, Saulnier P (2008) Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates—a review. J Control Release 128(3):185–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.02.007
Balaji APB, Sastry TP, Manigandan S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2017) Environmental benignity of a pesticide in soft colloidal hydrodispersive nanometric form with improved toxic precision towards the target organisms than non-target organisms. Sci Total Environ 579:190–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.240
Feng J, Shi Y, Yu Q, Sun C, Yang G (2016) Effect of emulsifying process on stability of pesticide nanoemulsions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 497:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.03.024
Nenaah GE, Ibrahim SIA, Al-Assiuty BA (2015) Chemical composition, insecticidal activity and persistence of three Asteraceae essential oils and their nanoemulsions against Callosobruchus maculatus (F.). J Stored Prod Res 61:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2014.12.007
Balaji APB, Mishra P, Suresh Kumar RS, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2015) Nanoformulation of poly(ethylene glycol) polymerized organic insect repellent by PIT emulsification method and its application for Japanese encephalitis vector control. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 128:370–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.02.034
Pant M, Dubey S, Patanjali PK, Naik SN, Sharma S (2014) Insecticidal activity of eucalyptus oil nanoemulsion with karanja and jatropha aqueous filtrates. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 91:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.11.019
Zhang X, Liu J, Fan Z (2013) Stability of etofenprox in water emulsion induced by block copolymer and surfactant. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 422:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.01.046
Lim CJ, Basri M, Omar D, Abdul Rahman MB, Salleh AB, Raja Abdul Rahman RNZ. Green nanoemulsion-laden glyphosate isopropylamine formulation in suppressing creeping foxglove (A. gangetica), slender button weed (D. ocimifolia) and buffalo grass (P. conjugatum). Pest Manag Sci. 2013;69(1):104–111. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3371
Chaw Jiang L, Basri M, Omar D, et al. Green nano-emulsion intervention for water-soluble glyphosate isopropylamine (IPA) formulations in controlling Eleusine indica (E. indica). Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2012;102(1):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2011.10.004
Liu Y, Wei F, Wang Y, Zhu G (2011) Studies on the formation of bifenthrin oil-in-water nano-emulsions prepared with mixed surfactants. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 389(1–3):90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.08.045
Zhang X, Liu J (2011) Effect of arabic gum and xanthan gum on the stability of pesticide in water emulsion. J Agric Food Chem 59(4):1308–1315. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf1034459
Sakulku U, Nuchuchua O, Uawongyart N, Puttipipatkhachorn S, Soottitantawat A, Ruktanonchai U (2009) Characterization and mosquito repellent activity of citronella oil nanoemulsion. Int J Pharm 372(1–2):105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.12.029
Wang L, Li X, Zhang G, Dong J, Eastoe J (2007) Oil-in-water nanoemulsions for pesticide formulations. J Colloid Interface Sci 314(1):230–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.04.079
Acosta E (2009) Bioavailability of nanoparticles in nutrient and nutraceutical delivery. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 14(1):3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2008.01.002
Müller RH, Junghanns JUAH. Drug nanocrystals/nanosuspensions for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Nanoparticulates as Drug Carriers 2006:307–328. https://doi.org/10.1142/9781860949074_0014
Hancock BC, Parks M (2000) What is the true solubility advantage of amorphous Pharmaceuticals? Pharm Res 17(4):397–404. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007516718048
Zhang H, Wang D, Butler R et al (2008) Formation and enhanced biocidal activity of water-dispersable organic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 3(8):506–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.188
Ciolkosz D, Albright L (1999) Project Final. Report 44(212966):1–62
Al Annu, Ort Rep, Isi D. S U S Tain in G Growth. Published online 2000:195–205.
Duke SO, Powles SB (2008) Glyphosate: a once-in-a-century herbicide. Pest Management Science 64(4):319–325. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1518
Shakil NA, Singh MK, Pandey A et al (2010) Development of poly(ethylene glycol) based amphiphilic copolymers for controlled release delivery of carbofuran. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 47(3):241–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601320903527038
Kumar J, Shakil NA, Singh MK, Singh MK, Pandey A, Pandey RP (2010) Development of controlled release formulations of azadirachtin-A employing poly(ethylene glycol) based amphiphilic copolymers. J Environ Sci Health B 45(4):310–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601231003704457
Liu Y, Laks P, Heiden P. Controlled release of biocides in solid wood. I. Efficacy against brown rot wood decay fungus (Gloeophyllum trabeum). J Appl Polym Sci. 2002;86(3):596–607. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.10896
Liu Y, Laks P, Heiden P. Controlled release of biocides in solid wood. II. Efficacy against Trametes versicolor and Gloeophyllum trabeum wood decay fungi. J Appl Polym Sci. 2002;86(3):608–614. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.10897
Liu Y, Laks P, Heiden P. Controlled release of biocides in solid wood. III. Preparation and characterization of surfactant-free nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci. 2002;86(3):615–621. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.10898
Liu Y, Yan L, Heiden P, Laks P (2001) Use of nanoparticles for controlled release of biocides in solid wood. J Appl Polym Sci 79(3):458–465. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4628(20010118)79:3%3c458::AID-APP80%3e3.0.CO;2-H
Salma U, Chen N, Richter DL et al (2010) Amphiphilic core/shell nanoparticles to reduce biocide leaching from treated wood, 1 - leaching and biological efficacy. Macromol Mater Eng 295(5):442–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.200900250
Chang PR, Jian R, Zheng P, Yu J, Ma X (2010) Preparation and properties of glycerol plasticized-starch (GPS)/cellulose nanoparticle (CN) composites. Carbohydr Polym 79(2):301–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.08.007
Bhan S, Mohan L, Srivastava CN (2014) Relative larvicidal potentiality of nano-encapsulated Temephos and Imidacloprid against Culex quinquefasciatus. J Asia Pac Entomol 17(4):787–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2014.07.006
Roy A, Bajpai J, Bajpai AK (2009) Dynamics of controlled release of chlorpyrifos from swelling and eroding biopolymeric microspheres of calcium alginate and starch. Carbohydr Polym 76(2):222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.10.013
Kang MA, Seo MJ, Hwang IC et al (2012) Insecticidal activity and feeding behavior of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae, after treatment with nano types of pyrifluquinazon. J Asia Pac Entomol 15(4):533–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2012.05.015
Suresh Kumar RS, Shiny PJ, Anjali CH et al (2013) Distinctive effects of nano-sized permethrin in the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(4):2593–2602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1161-0
Frederiksen HK, Kristensen HG, Pedersen M (2003) Solid lipid microparticle formulations of the pyrethroid gamma-cyhalothrin - Incompatibility of the lipid and the pyrethroid and biological properties of the formulations. J Control Release 86(2–3):243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(02)00406-6
Lai F, Wissing SA, Müller RH, Fadda AM (2006) Artemisia arborescens L essential oil-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for potential agricultural application: preparation and characterization. AAPS PharmSciTech. https://doi.org/10.1208/pt070102
Bang SH, Yu YM, Hwang IC, Park HJ (2009) Formation of size-controlled nano carrier systems by self-assembly. J Microencapsul 26(8):722–733. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652040902726994
Hwang IC, Kim TH, Bang SH et al (2011) Insecticidal effect of controlled release formulations of etofenprox based on nano-bio technique. J Fac Agric Kyushu Univ 56(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.5109/19633
Nguyen HM, Hwang IC, Park JW, Park HJ (2012) Enhanced payload and photo-protection for pesticides using nanostructured lipid carriers with corn oil as liquid lipid. J Microencapsul 29(6):596–604. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2012.668960
Nguyen HM, Hwang IC, Park JW, Park HJ (2012) Photoprotection for deltamethrin using chitosan-coated beeswax solid lipid nanoparticles. Pest Manag Sci 68(7):1062–1068. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3268
Paula HCB, Sombra FM, Cavalcante RDF, Abreu FOMS, De Paula RCM (2011) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/cashew gum beads loaded with Lippia sidoides essential oil. Mater Sci Eng C 31(2):173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2010.08.013
Brunel F, El Gueddari NE, Moerschbacher BM (2013) Complexation of copper(II) with chitosan nanogels: toward control of microbial growth. Carbohydr Polym 92(2):1348–1356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.10.025
Persano L, Camposeo A, Tekmen C, Pisignano D (2013) Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nanofibers: a review. Macromol Mater Eng 298(5):504–520. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201200290
Xiang C, Taylor AG, Hinestroza JP, Frey MW (2013) Controlled release of nonionic compounds from poly(lactic acid)/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 127(1):79–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.36943
Adak T, Kumar J, Shakil NA, Walia S (2012) Development of controlled release formulations of imidacloprid employing novel nano-ranged amphiphilic polymers. J Environ Sci Heal - Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 47(3):217–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.634365
Sarkar DJ, Kumar J, Shakil NA, Walia S (2012) Release kinetics of controlled release formulations of thiamethoxam employing nano-ranged amphiphilic PEG and diacid based block polymers in soil. J Environ Sci Heal - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst Environ Eng 47(11):1701–1712. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.687294
Pankaj, Shakil NA, Kumar J, Singh MK, Singh K. Bioefficacy evaluation of controlled release formulations based on amphiphilic nano-polymer of carbofuran against Meloidogyne incognita infecting tomato. J Environ Sci Heal - Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes. 2012;47(6):520–528. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.665667
Kaushik P, Shakil NA, Kumar J, Singh MK, Singh MK, Yadav SK (2013) Development of controlled release formulations of thiram employing amphiphilic polymers and their bioefficacy evaluation in seed quality enhancement studies. J Environ Sci Heal - Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 48(8):677–685. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2013.778614
Loha KM, Shakil NA, Kumar J, Singh MK, Adak T, Jain S (2011) Release kinetics of β-cyfluthrin from its encapsulated formulations in water. J Environ Sci Heal - Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 46(3):201–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2011.540200
Choudhury SR, Pradhan S, Goswami A (2012) Preparation and characterisation of acephate nano-encapsulated complex. Nanosci Methods 1(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2010.533443
Hill LE, Gomes C, Taylor TM (2013) Characterization of beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes containing essential oils (trans-cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, cinnamon bark, and clove bud extracts) for antimicrobial delivery applications. LWT Food Sci Technol 51(1):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.11.011
Abreu FOMS, Oliveira EF, Paula HCB, De Paula RCM (2012) Chitosan/cashew gum nanogels for essential oil encapsulation. Carbohydr Polym 89(4):1277–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.048
Mustafa IF, Hussein MZ (2020) Synthesis and technology of nanoemulsion-based pesticide formulation. Nanomaterials 10(8):1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081608
Hazra DKPA (2019) Role of pesticide formulations for sustainable crop protection and environment management: A review. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 8(2):686–693
M. Surendhiran et al., MS et al. . Nano Emulsion Seed Invigouration for Improved Germination and Seedling Vigour in Maize. Int J Agric Sci Res. 2019;9(3):333–340. https://doi.org/10.24247/ijasrjun201946
Chen K, Yu G, He F et al (2017) A pH-responsive emulsion stabilized by alginate-grafted anisotropic silica and its application in the controlled release of λ-cyhalothrin. Carbohydr Polym 176:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.07.046
Hou R, Zhou J, Song Z et al (2023) pH-responsive λ-cyhalothrin nanopesticides for effective pest control and reduced toxicity to Harmonia axyridis. Carbohydr Polym 302:120373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120373
Osman Mohamed Ali E, Shakil NA, Rana VS, et al. Antifungal activity of nano emulsions of neem and citronella oils against phytopathogenic fungi, Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotium rolfsii. Ind Crops Prod. 2017;108(December 2016):379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.06.061
de Souza JF, da Silva PK, Alves TFR et al (2020) Structural comparison, physicochemical properties, and in vitro release profile of curcumin-loaded lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoparticle: Influence of hydrotrope as interface stabilizers. J Mol Liq 306:112861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112861
Bisset NB, Webster GR, Da DY, Boyd BJ (2019) Understanding the kinetic mixing between liquid crystalline nanoparticles and agrochemical actives. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 175:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.11.063
Bhowmik M, Gupta MK. Biology of Cabbage Butterfly Pieris Brassicae Linn. (Lepidoptera: Pieridae). Vol 6.; 2017. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.420
Bang SH, Hwang IC, Yu YM, Kwon HR, Kim DH, Park HJ (2011) Influence of chitosan coating on the liposomal surface on physicochemical properties and the release profile of nanocarrier systems. J Microencapsul 28(7):595–604. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2011.557748
Nowack B, Krug H, Height M. Erratum: 120 years of nanosilver history: Implications for policy makers (Environmental Science and Technology (2011) 45 (1177–1183). https://doi.org/10.1021/es103316q. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45(7):3189. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200435m
Jung JH, Kim SW, Min JS et al (2010) The effect of nano-silver liquid against the white rot of the green onion caused by Sclerotium cepivorum. Mycobiology 38(1):39. https://doi.org/10.4489/myco.2010.38.1.039
Jo YK, Kim BH, Jung G (2009) Antifungal activity of silver ions and nanoparticles on phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Dis 93(10):1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-93-10-1037
Lamsal K, Kim SW, Jung JH, Kim YS, Kim KS, Lee YS (2011) Inhibition effects of silver nanoparticles against powdery mildews on cucumber and pumpkin. Mycobiology 39(1):26–32. https://doi.org/10.4489/MYCO.2011.39.1.026
Lamsal K, Kim SW, Jung JH, Kim YS, Kim KS, Lee YS (2011) Application of silver nanoparticles for the control of Colletotrichum species in vitro and pepper anthracnose disease in field. Mycobiology 39(3):194–199. https://doi.org/10.5941/MYCO.2011.39.3.194
Abduz Zahir A, Bagavan A, Kamaraj C, Elango G, Abdul Rahuman A. Efficacy of plant-mediated synthesized silver nanoparticles against Sitophilus oryzae. J Biopestic. 2012;5(SUPPL.):95–102.
Suman TY, Elumalai D, Kaleena PK, Rajasree RSR (2013) GC-MS analysis of bioactive components and synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Ammannia baccifera aerial extract and its larvicidal activity against malaria and filariasis vectors. Ind Crops Prod 47:239–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.03.010
Ding Y, Xiao Z, Chen F et al (2023) A mesoporous silica nanocarrier pesticide delivery system for loading acetamiprid: effectively manage aphids and reduce plant pesticide residue. Sci Total Environ 863:160900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160900
Shah MA, Khan AA (2014) Use of diatomaceous earth for the management of stored-product pests. Int J Pest Manag 60(2):100–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670874.2014.918674
Stadler T, Buteler M, Weaver DK (2010) Novel use of nanostructured alumina as an insecticide. Pest Manag Sci 66(6):577–579. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1915
Stadler T, Buteler M, Weaver DK, Sofie S. Comparative toxicity of nanostructured alumina and a commercial inert dust for Sitophilus oryzae (L.) and Rhyzopertha dominica (F.) at varying ambient humidity levels. J Stored Prod Res. 2012;48:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2011.09.004
Buteler M, Sofie SW, Weaver DK, Driscoll D, Muretta J, Stadler T (2015) Development of nanoalumina dust as insecticide against Sitophilus oryzae and Rhyzopertha dominica. Int J Pest Manag 61(1):80–89. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670874.2014.1001008
Fauteux F, Rémus-Borel W, Menzies JG, Bélanger RR (2005) Silicon and plant disease resistance against pathogenic fungi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 249(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.06.034
Majeed Zargar S, Nazir M, Kumar Agrawal G, Kim DW, Rakwal R (2010) Silicon in Plant Tolerance Against Environmental Stressors: Towards Crop Improvement Using Omics Approaches. Curr Proteomics 7(2):135–143. https://doi.org/10.2174/157016410791330507
Nair R, Varghese SH, Nair BG, Maekawa T, Yoshida Y, Kumar DS (2010) Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci 179(3):154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.012
Barik TK, Sahu B, Swain V (2008) Nanosilica - From medicine to pest control. Parasitol Res 103(2):253–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-0975-7
Hae-Jun P et al (2006) A new composition of nanosized silica-silver for control of various plant diseases. Plant Pathol J. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.2006.22.3.295
Debnath N, Mitra S, Das S, Goswami A (2012) Synthesis of surface functionalized silica nanoparticles and their use as entomotoxic nanocides. Powder Technol 221:252–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.01.009
Rouhani M, Samih M (2013) Insecticidal effect of silica and silver nanoparticles on the cowpea seed beetle, Callosobruchus maculatus F. (Col.: Bruchidae). J Entomol Res 4:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0446-2
Jeer M. Chapter 17 - Recent developments in silica-nanoparticles mediated insect pest management in agricultural crops. In: Etesami H, Al Saeedi AH, El-Ramady H, Fujita M, Pessarakli M, Anwar Hossain M, eds. Silicon and Nano-Silicon in Environmental Stress Management and Crop Quality Improvement. Academic Press; 2022:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91225-9.00016-9
Faliagka S, Katsoulas N (2022) Silica coated insect proof screens for effective insect control in greenhouses. Biosyst Eng 215:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2022.01.003
Norman DJ, Chen J (2011) Effect of foliar application of titanium dioxide on bacterial blight of geranium and xanthomonas leaf spot of poinsettia 46(3):426–428. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.46.3.426
Paret, Mathews L et al (2013) Photocatalysis: effect of light-activated nanoscale formulations of TiO(2) on Xanthomonas perforans and control of bacterial spot of tomato. Phytopathology 103(3):228–236. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-08-12-0183-R
Paret ML, Palmateer AJ, Knox GW (2013) Evaluation of a light-activated nanoparticle formulation of Titanium Dioxide with Zinc for management of bacterial leaf spot on rosa ‘Noare’ 48(2):189–192. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.48.2.189
Mondal KK, Mani C (2011) Investigation of the antibacterial properties of nanocopper against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae, the incitant of pomegranate bacterial blight. Ann Microbiol 2012:889–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0382-7
Gogos A, Knauer K, Bucheli TD (2012) Nanomaterials in plant protection and fertilization: current state, foreseen applications, and research priorities. J Agric Food Chem 60(39):9781–9792. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf302154y
Khater H (2012) Ecosmart biorational insecticides: alternative insect control strategies. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/27852
Paper O (2009) Development of a controlled release neem capsule with a sodium alginate matrix, crosslinked by glutaraldehyde and coated with natural rubber 2009:609–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-009-0126-z
Jerobin J, Sureshkumar RS, Anjali CH, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2012) Biodegradable polymer based encapsulation of neem oil nanoemulsion for controlled release of Aza-A. Carbohydr Polym 90(4):1750–1756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.064
Forim MR et al (2013) Development of a new method to prepare nano-/microparticles loaded with extracts of azadirachta indica, their characterization and use in controlling plutella xylostella. J Agric Food Chem 61(38):9131–9139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf403187y
Tonielo J, Rossi M, Soares E et al (2014) Effects of different formulations of neem oil-based products on control Zabrotes subfasciatus ( Boheman, 1833) ( Coleoptera : Bruchidae ) on beans. J Stored Prod Res 56:49–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2013.10.004
Chen X jun, Xu H hong, Yang W, Liu S zi. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B : Biology Research on the effect of photoprotectants on photostabilization of rotenone. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2009;95(2):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2009.01.003
Isman MB (2005) Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu Rev Entomol 51(1):45–66. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.151146
Lao S bing, Zhang Z xiang, Xu H hong, Jiang G biao. Novel amphiphilic chitosan derivatives : Synthesis , characterization and micellar solubilization of rotenone. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;82(4):1136–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.06.044
Luiz J, Oliveira D, Vangelie E et al (2014) Application of nanotechnology for the encapsulation of botanical insecticides for sustainable agriculture : Prospects and promises. Biotechnol Adv 32(8):1550–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.10.010
Amiri A, Dugas R, Pichot AL, Bompeix G. International Journal of Food Microbiology In vitro and in vitro activity of eugenol oil ( Eugenia caryophylata ) against four important postharvest apple pathogens. 2008;126:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.04.022
Garg A, Singh S (2011) Colloids and Surfaces B : Biointerfaces Enhancement in antifungal activity of eugenol in immunosuppressed rats through lipid nanocarriers. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 87(2):280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.05.030
Sajomsang W, Nuchuchua O, Gonil P et al (2012) Water-soluble β-cyclodextrin grafted with chitosan and its inclusion complex as a mucoadhesive eugenol carrier. Carbohydr Polym Published online. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.060
Woranuch S, Yoksan R. Eugenol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles : I . Thermal stability improvement of eugenol through encapsulation. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;96(2):578–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.08.117
Balaguer MP, Gavara R (2012) Food Hydrocolloids Formation of zein nanoparticles by electrohydrodynamic atomization : Effect of the main processing variables and suitability for encapsulating the food coloring and active ingredient curcumin. Food Hydrocoll 28(1):82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.11.013
Bielska D, Karewicz A, Kamiński K et al (2013) Self-organized thermo-responsive hydroxypropyl cellulose nanoparticles for curcumin delivery. Eur Polym J 49(9):2485–2494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.02.012
Holmberg BA, Wang H, Norbeck JM, Yan Y (2003) Controlling size and yield of zeolite Y nanocrystals using tetramethylammonium bromide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 59(1):13–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(03)00271-3
Holmberg B, Wang H, Yan Y (2004) High silica zeolite Y nanocrystals by dealumination and direct synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 74:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2004.06.018
Li Q, Creaser D, Sterte J (2002) An Investigation of the Nucleation/Crystallization Kinetics of Nanosized Colloidal Faujasite Zeolites. Chem Mater 14(3):1319–1324. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm011242g
Madsen C, Madsen C, J. H. Jacobsen C. Nanosized zeolite crystals—convenient control of crystal size distribution by confined space synthesis. Chem Commun. 1999;(8):673–674. https://doi.org/10.1039/A901228A
Schmidt I, Madsen C, Jacobsen CJ (2000) Confined space synthesis. A novel route to nanosized zeolites. Inorg Chem 39(11):2279–2283. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic991280q
Jacobsen CJH, Madsen CG, Janssens TVW, Jakobsen HJ, Skibsted J (2000) Zeolites by confined space synthesis – characterization of the acid sites in nanosized ZSM-5 by ammonia desorption and 27Al/29Si-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 39:393–401. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:97617168
Kim SS, Shah J, Pinnavaia T (2003) Colloid-Imprinted Carbons as Templates for the Nanocasting Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite. Chem Mater - CHEM MATER 15(8) https://doi.org/10.1021/cm021762r
Martens RM, Verduijn JP. United States Patent (19). 2000;(19):6–11.
Mohr GD, City L, Verduijn JP et al (2000) United States Patent 19:19
City L, Verduijn JP. (12) United States Patent. 2004;(12).
Larlus O, Mintova S, Valtchev V, Jean B, Metzger TH, Bein T (2004) Silicalite-1/polymer films with low-k dielectric constants. Appl Surf Sci 226(1–3):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2003.11.062
Mitra A, Cao, WangWang, et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Pure-Silica-Zeolite BEA as Low Dielectric Constant Material for Microprocessors. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2004;43(12):2946–2949. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie034062k
Jennings B (2011) Drosophila – a versatile model in biology & medicine. Mater Today - MATER TODAY 14:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(11)70113-4
Rubin GM, Lewis EB (2000) A brief history of Drosophila’s contributions to genome research. Science 287(5461):2216–2218. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5461.2216
Rand MD (2010) Drosophotoxicology: the growing potential for Drosophila in neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32(1):74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2009.06.004
Hsu T, Schulz RA (2000) Sequence and functional properties of Ets genes in the model organism Drosophila. Oncogene 19(55):6409–6416. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204033
Posgai RT. Development of a Drosophila Melanogaster Model System for Nanoparticle Development of a Drosophila Melanogaster Model System for Nanoparticle. Grad Theses Diss. Published online 2012:574.
Posgai R, Ahamed M, Hussain SM, Rowe JJ, Nielsen MG (2009) Inhalation method for delivery of nanoparticles to the Drosophila respiratory system for toxicity testing. Sci Total Environ 408(2):439–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.008
Roeder T, Isermann K, Kallsen K, Uliczka K, Wagner C (2012) A Drosophila asthma model - what the fly tells us about inflammatory diseases of the lung. Adv Exp Med Biol 710:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-5638-5_5
Araj SEA, Salem NM, Ghabeish IH, Awwad AM. Toxicity of nanoparticles against Drosophila melanogaster (Diptera: Drosophilidae). J Nanomater. 2015;2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/758132
Demir E (2020) Drosophila as a model for assessing nanopesticide toxicity. Nanotoxicology 14(9):1271–1279. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2020.1815886
Demir E, Vales G, Kaya B, Creus A, Marcos R (2011) Genotoxic analysis of silver nanoparticles in Drosophila. Nanotoxicology 5(3):417–424. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2010.529176
Vecchio G, Galeone A, Brunetti V, et al. Concentration-dependent, size-independent toxicity of citrate capped AuNPs in drosophila melanogaster. PLoS One. 2012;7(1). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029980
Armstrong N, Ramamoorthy M, Lyon D, Jones K, Duttaroy A (2013) Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles Action on Insect Pigmentation Reveals Intervention of Copper Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 8(1):19–21. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053186
Pandey A, Chandra S, Chauhan LKS, Narayan G, Chowdhuri DK (2013) Cellular internalization and stress response of ingested amorphous silica nanoparticles in the midgut of Drosophila melanogaster. Biochim Biophys Acta - Gen Subj 1830(1):2256–2266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.10.001
Vales G, Demir E, Kaya B, Creus A, Marcos R (2013) Genotoxicity of cobalt nanoparticles and ions in Drosophila. Nanotoxicology 7(4):462–468. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2012.689882
Lloyd TE, Taylor JP (2010) Flightless flies: Drosophila models of neuromuscular disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1184:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05432.x
Perry T, Batterham P (2018) Harnessing model organisms to study insecticide resistance. Curr Opin Insect Sci 27:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2018.03.005
Douris V, Denecke S, Van Leeuwen T, Bass C, Nauen R, Vontas J (2020) Using CRISPR/Cas9 genome modification to understand the genetic basis of insecticide resistance: Drosophila and beyond. Pestic Biochem Physiol 167(April):104595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2020.104595
Ibrahim SS, Riveron JM, Bibby J et al (2015) Allelic Variation of Cytochrome P450s Drives Resistance to Bednet Insecticides in a Major Malaria Vector. PLoS Genet 11(10):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005618
Fenner K, Canonica S, Wackett LP, Elsner M. Evaluating pesticide degradation in the environment: Blind spots and emerging opportunities. Science (80- ). 2013;341(6147):752–758. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1236281
Hassellöv M, Readman JW, Ranville JF, Tiede K (2008) Nanoparticle analysis and characterization methodologies in environmental risk assessment of engineered nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology 17(5):344–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0225-x
Siddiqui M, Al-whaibi M, Mohammad F, Al-Khaishany M. Role of Nanoparticles in Plants. In: Nanotechnology and Plant Sciences: Nanoparticles and Their Impact on Plants. ; 2015:19–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14502-0_2
Aslani F, Bagheri S, Muhd Julkapli N, Juraimi AS, Hashemi FSG, Baghdadi A (2014) Effects of engineered nanomaterials on plants growth: an overview. ScientificWorldJournal 2014:641759. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/641759
Hermes PH et al (2020) Carbon nanotubes as plant growth regulators: prospects. In: Patra J, Fraceto L, Das G, Campos E (eds) Green Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences. Springer, Cham, pp 77–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39246-8_4
Zhang X, Xu Z, Wu M et al (2019) Potential environmental risks of nanopesticides: application of Cu(OH)(2) nanopesticides to soil mitigates the degradation of neonicotinoid thiacloprid. Environ Int 129:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.022
Zhao L, Huang Y, Adeleye AS, Keller AA (2017) Metabolomics reveals Cu(OH)(2) nanopesticide-activated anti-oxidative pathways and decreased beneficial antioxidants in spinach leaves. Environ Sci Technol 51(17):10184–10194. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02163
Nuruzzaman M, Rahman MM, Liu Y, Naidu R (2016) Nanoencapsulation, nano-guard for pesticides: a new window for safe application. J Agric Food Chem 64(7):1447–1483. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05214
Venugopal NVS, Sainadh NVS (2016) Novel polymeric nanoformulation of mancozeb—an eco-friendly nanomaterial. Int J Nanosci 15(4):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219581X16500162
Ocsoy I, Paret ML, Ocsoy MA et al (2013) Nanotechnology in plant disease management: DNA-directed silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide as an antibacterial against Xanthomonas perforans. ACS Nano 7(10):8972–8980. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4034794
Acknowledgements
MMK would like to acknowledge the FIC block grant (UBD/RSCH/1.4/FICBF(b)/2022/046) received from Universiti Brunei Darussalam, Brunei Darussalam.
Funding
Universiti Brunei Darussalam, UBD/RSCH/1.4/FICBF(b)/2022/046.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MFUR: Methodology, data curation and writing – original draft preparation. MMK: Supervision, conceptualization, funding acquisition and writing – review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, M.F.U., Khan, M.M. Application of nanopesticides and its toxicity evaluation through Drosophila model. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 47, 1–22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02932-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02932-y