Abstract
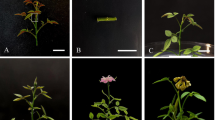
Water loss through inflorescences may place extreme demands on plant water status in arid environments. Here we examine how corolla size, a trait known to influence pollination success, affects the water cost of flowering in the alpine skypilot, Polemonium viscosum. In a potometry experiment, water uptake rates of inflorescences were monitored during bud expansion and anthesis. Corolla volume of fully expanded flowers predicted water uptake during bud expansion (R 2=0.61, P=0.0375) and corolla surface area predicted water uptake during anthesis (R 2=0.59, P=0.044). To probe mechanisms underlying the relationship between corolla size and water uptake, cell dimensions and densities were measured in several regions of fully expanded corollas. Corolla length was positively correlated with cell length in the middle of the corolla tube and cell diameter in the corolla lobe (Pearson's r from 0.26–0.33, n=86, P ≤ 0.05). Cell density was negatively correlated with cell dimensions in the upper corolla tube and lobe (Pearson's r from –0.39 to –0.42, P ≤ 0.0015). These findings suggest that more water may be required to maintain turgor in large corollas in part because their tissues have lower cell wall densities. The carbon cost of water use by flowers was assessed in krummholz and tundra habitats for P. viscosum flowering, respectively, during dry and wet portions of the growing season. For plants in full flower, average leaf water potentials were significantly more negative (P=0.0079) at mid-day in the krummholz (June) than in the tundra (July), but were similar before dawn (P=0.631). Photosynthetic rate at the time of flowering declined significantly with increasing corolla size in the krummholz (P=0.0376), but was unrelated to corolla size on the tundra (P>0.72). Plants losing water through large corollas may close leaf stomata to maintain turgor. If photosynthesis limits growth in this perennial species, then the water cost of producing large flowers should exacerbate the cost of reproduction under dry conditions. Such factors could select for flowers with smaller corollas in the krummholz, countering pollinator-mediated selection and helping maintain genetic variation in corolla size components of P. viscosum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 May 1998 / Accepted: 2 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galen, C., Sherry, R. & Carroll, A. Are flowers physiological sinks or faucets? Costs and correlates of water use by flowers of Polemonium viscosum . Oecologia 118, 461–470 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050749
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050749