Abstract
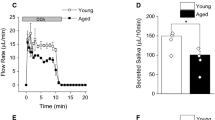
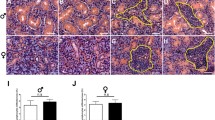
Prosaposin (PSAP), a potent neurotrophic factor, is found in neuronal and non-neuronal tissues and various biological fluids. Neuropathological conditions often alter PSAP production in neural tissues. However, little is known about its alterations in non-neural tissues, particularly in the salivary glands, which are natural reservoirs of various neurotrophic factors. In this study, we explored whether neurotoxic stimulation by kainic acid (KA), a glutamate analog, altered PSAP levels in the salivary system of rats. The results revealed that KA injection did not alter total saliva production. However, KA-induced neurotoxic stimulation significantly increased the PSAP level in the secreted saliva but decreased it in the serum. In addition, KA-induced elevated immunoreactivities of PSAP and its receptors have been observed in the granular convoluted tubule (GCT) cells of the submandibular gland (SMG), a major salivary secretory organ. Indeed, a large number of PSAP-expressing immunogold particles were observed in the secretory granules of the SMG. Furthermore, KA-induced overexpression of PSAP was co-localized with secretogranin in secretory acini (mostly in GCT cells) and the ductal system of the SMG, suggesting the release of excess PSAP from the salivary glands into the oral cavity. In conclusion, the salivary system produces more PSAP during neurotoxic conditions, which may play a protective role in maintaining the secretory function of the salivary glands and may work in distant organs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Grãos MM, Carvalho RF, Carvalho AP, Duarte CB (2005) Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ 12:1329–1343
Aloe L, Alleva E, Böhm A, Levi-Montalcini R (1986) Aggressive behavior induces release of nerve growth factor from mouse salivary gland into the bloodstream. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:6184–6187
Beutler E, Grabowski GA (2001) Gaucher disease. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Valle D, Sly WS (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGrawHill, New York, pp 3635–3668
Bradová V, Smíd F, Ulrich-Bott B, Roggendorf W, Paton BC, Harzer K (1993) Prosaposin deficiency: further characterization of the sphingolipid activator protein-deficient sibs. Multiple glycolipid elevations (including lactosylceramidosis), partial enzyme deficiencies and ultrastructure of the skin in this generalized sphingolipid storage disease. Hum Genet 92:143–152
Carro E, Bartolomé F, Bermejo-Pareja F, Villarejo-Galende A, Molina JA, Ortiz P, Calero M, Rabano A, Cantero JL, Orive G (2017) Early diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease based on salivary lactoferrin. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 8:131–138
Castagnola M, Scarano E, Passali GC, Messana I, Cabras T, Iavarone F, Di Cintio G, Fiorita A, De Corso E, Paludetti G (2017) Salivary biomarkers and proteomics: future diagnostic and clinical utilities. Biomarkers e proteomica salivari: prospettive future cliniche e diagnostiche. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 37:94–101
Chen J, Saito S, Kobayashi N, Sato K, Terashita T, Shimokawa T, Mominoki K, Miyawaki K, Sano A, Matsuda S (2008) Expression patterns in alternative splicing forms of prosaposin mRNA in the rat facial nerve nucleus after facial nerve transection. Neurosci Res 60:82–94
Cui Y, Zhang H, Zhu J, Liao Z, Wang S, Liu W (2022) Investigation of whole and glandular saliva as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis. Brain Sci 12:595
de Moraes JK, Wagner VP, Fonseca FP, Vargas PA, de Farias CB, Roesler R, Martins MD (2018) Uncovering the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tyrosine kinase receptor B signaling in head and neck malignancies. J Oral Pathol Med 47:221–227
Farah R, Haraty H, Salame Z, Fares Y, Ojcius DM, Said Sadier N (2018) Salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Biom J 41:63–87
Fauchais AL, Boumediene A, Lalloue F, Gondran G, Loustaud-Ratti V, Vidal E, Jauberteau MO (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor correlate with T-cell activation in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol 38:50–57
Giacobbo BL, Doorduin J, Klein HC, Dierckx RAJO, Bromberg E, de Vries EFJ (2019) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: focus on neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol 56:3295–3312
Gutierrez A, Corey-Bloom J, Thomas EA, Desplats P (2020) Evaluation of biochemical and epigenetic measures of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a biomarker in Huntington's disease patients. Front Mol Neurosci 12:335
Hineno T, Sano A, Kondoh K, Ueno S, Kakimoto Y, Yoshida K (1991) Secretion of sphingolipid hydrolase activator precursor, prosaposin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 176:668–674
Hiraiwa M, Soeda S, Kishimoto Y, O'Brien JS (1992) Binding and transport of gangliosides by prosaposin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:11254–11258
Hiraiwa M, O'Brien JS, Kishimoto Y, Galdzicka M, Fluharty AL, Ginns EI, Martin BM (1993) Isolation, characterization, and proteolysis of human prosaposin, the precursor of saposins (sphingolipid activator proteins). Arch Biochem Biophys 304:110–116
Humberto JSM, Pavanin JV, Rocha MJAD, Motta ACF (2018) Cytokines, cortisol, and nitric oxide as salivary biomarkers in oral lichen planus: a systematic review. Braz Oral Res 32:e82
Islam F, Khan MSI, Nabeka H, Saito S, Li X, Shimokawa T, Yamamiya K, Kobayashi N, Matsuda S (2018) Prosaposin and its receptors are differentially expressed in the salivary glands of male and female rats. Cell Tissue Res 373:439–457
Islam F, Khan MSI, Nabeka H, Shimokawa T, Yamamiya K, Matsuda S (2020) Age- and sex-associated changes in prosaposin and its receptors in the lacrimal glands of rats. Histol Histopathol 35:69–81
Jakaria M, Park SY, Haque ME, Karthivashan G, Kim IS, Ganesan P, Choi DK (2018) Neurotoxic agent-induced injury in neurodegenerative disease model: focus on involvement of glutamate receptors. Front Mol Neurosci 11:307
Kanai K, Nunoya T, Shibuya K, Nakamura T, Tajima M (1998) Variations in effectiveness of antigen retrieval pretreatments for diagnostic immunohistochemistry. Res Vet Sci 64:57–61
Kishimoto Y, Hiraiwa M, O’Brien JS (1992) Saposins: Structure, function, distribution, and molecular genetics. J Lipid Res 33:1255–1267
Kondoh K, Hineno T, Sano A, Kakimoto Y (1991) Isolation and characterization of prosaposin from human milk. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:286–292
Kunihiro J, Nabeka H, Wakisaka H, Unuma K, Khan MSI, Shimokawa T, Islam F, Doihara T, Yamamiya K, Saito S, Hamada F, Matsuda S (2020) Prosaposin and its receptors GRP37 and GPR37L1 show increased immunoreactivity in the facial nucleus following facial nerve transection. PLoS One 15:e0241315
Li X, Nabeka H, Saito S, Shimokawa T, Khan MSI, Yamamiya K, Shan F, Gao H, Li C, Matsuda S (2017) Expression of prosaposin and its receptors in the rat cerebellum after kainic acid injection. IBRO Rep 2:31–40
Li Y, Li F, Qin D, Chen H, Wang J, Wang J, Song S, Wang C, Wang Y, Liu S, Gao D, Wang ZH (2022) The role of brain derived neurotrophic factor in central nervous system. Front Aging Neurosci 14:986443
Liu Q, Tang Q, Jing X, Zhang J, Xia Y, Yan J, Xu Y, Li J, Li Y, He J, Mo L (2022) Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor protects against paracetamol -induced liver injury by inhibiting PERK-ATF4-CHOP signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 602:163–169
Loo JA, Yan W, Ramachandran P, Wong DT (2010) Comparative human salivary and plasma proteomes. J Dent Res 89:1016–1023
Mitre M, Mariga A, Chao MV (2017) Neurotrophin signalling: novel insights into mechanisms and pathophysiology. Clin Sci (Lond) 131:13–23
Motta M, Tatti M, Furlan F, Celato A, Di Fruscio G, Polo G, Manara R, Nigro V, Tartaglia M, Burlina A, Salvioli R (2016) Clinical, biochemical and molecular characterization of prosaposin deficiency. Clin Genet 90:220–229
Nabeka H, Uematsu K, Takechi H, Shimokawa T, Yamamiya K, Li C, Doihara T, Saito S, Kobayashi N, Matsuda S (2014) Prosaposin overexpression following kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity. PLoS One 9:e110534
Nabeka H, Shimokawa T, Doihara T, Saito S, Wakisaka H, Hamada F, Kobayashi N, Matsuda S (2015) A prosaposin-derived peptide alleviates kainic acid-induced brain injury. PLoS One 10:e0126856
Nabeka H, Saito S, Li X, Shimokawa T, Khan MSI, Yamamiya K, Kawabe S, Doihara T, Hamada F, Kobayashi N, Matsuda S (2017) Interneurons secrete prosaposin, a neurotrophic factor, to attenuate kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity. IBRO Rep 3:17–32
Nohara M, Tohei A, Sato T, Amao H (2016) Evaluation of response to restraint stress by salivary corticosterone levels in adult male mice. J Vet Med Sci 78:775–780
Nunes LA, Mussavira S, Bindhu OS (2015) Clinical and diagnostic utility of saliva as a non-invasive diagnostic fluid: a systematic review. Biochem Med (Zagreb) 25:177–192
O'Brien JS, Kishimoto Y (1991) Saposin proteins: structure, function, and role in human lysosomal storage disorders. FASEB J 5:301–308
O'Brien JS, Carson GS, Seo HC, Hiraiwa M, Kishimoto Y (1994) Identification of prosaposin as a neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:9593–9596
Patton S, Carson GS, Hiraiwa M, O'Brien JS, Sano A (1997) Prosaposin, a neurotrophic factor: presence and properties in milk. J Dairy Sci 80:264–272
Pawlik P, Błochowiak K (2021) The role of salivary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Diagnostics (Basel) 11:371
Quinville BM, Deschenes NM, Ryckman AE, Walia JS (2021) A comprehensive review: sphingolipid metabolism and implications of disruption in sphingolipid homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 22:5793
Sakamoto K, Saito T, Orman R, Koizumi K, Lazar J, Salciccioli L, Stewart M (2008) Autonomic consequences of kainic acid-induced limbic cortical seizures in rats: peripheral autonomic nerve activity, acute cardiovascular changes, and death. Epilepsia 49:982–996
Saruta J, Kondo Y, Sato C, Shiiki N, Tsukinoki K, Sato S (2010) Salivary glands as the source of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor in stressed rats engaged in biting behavior. Stress 13:238–247
Saruta J, Fujino K, To M, Tsukinoki K (2012) Expression and localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA and protein in human submandibular gland. Acta Histochem Cytochem 45:211–218
Saruta J, To M, Hayashi T, Kawashima R, Shimizu T, Kamata Y, Kato M, Takeuchi M, Tsukinoki K (2014) Relationship between brain-derived neurotrophic factor and stress in saliva and salivary glands. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol 26:379–389
Saruta J, To M, Sugimoto M, Yamamoto Y, Shimizu T, Nakagawa Y, Inoue H, Saito I, Tsukinoki K (2017) Salivary gland derived BDNF overexpression in mice exerts an anxiolytic effect. Int J Mol Sci 18:1902
Saruta J, To M, Sakaguchi W, Kondo Y, Tsukinoki K (2020) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is related to stress and chewing in saliva and salivary glands. Jpn Dent Sci Rev 56:43–49
Schepici G, Silvestro S, Trubiani O, Bramanti P, Mazzon E (2020) Salivary biomarkers: future approaches for early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Sci 10:245
Shimokawa T, Nabeka H, Yamamiya K, Wakisaka H, Takeuchi T, Kobayashi N, Matsuda S (2013) Distribution of prosaposin in rat lymphatic tissues. Cell Tissue Res 352:685–693
Shimokawa T, Nabeka H, Khan SI, Yamamiya K, Doihara T, Kobayashi N, Wakisaka H, Matsuda S (2021) Prosaposin in the rat oviductal epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 383:1191–1202
Tiwari M (2011) Science behind human saliva. J Nat Sci Biol Med 2:53–58
Tsukinoki K, Saruta J (2012) Role of stress-related brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the rat submandibular gland. Acta Histochem Cytochem 45:261–267
Unuma K, Chen J, Saito S, Kobayashi N, Sato K, Saito K, Wakisaka H, Mominoki K, Sano A, Matsuda S (2005) Changes in expression of prosaposin in the rat facial nerve nucleus after facial nerve transection. Neurosci Res 52:220–227
Van Den Berghe L, Sainton K, Gogat K, Marchant D, Dufour E, Bonnel S, Gadin S, Menasche M, Abitbol M (2004) Prosaposin gene expression in normal and dystrophic RCS rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1297–1305
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank D. Shimizu for his technical support with electron microscopic imaging.
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to S.K. (No. 21K09324).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors have no competing financial or non-financial interests to declare. The research involving animals and ethical permission was obtained from Ehime University School of Medicine, Japan (05A261).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1:
Figures S1-S2 (PDF 949 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F., Khan, S., Nabeka, H. et al. Neurotoxic stimulation alters prosaposin levels in the salivary systems of rats. Cell Tissue Res 395, 159–169 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-023-03847-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-023-03847-6