Abstract
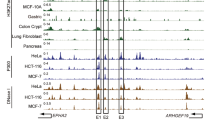
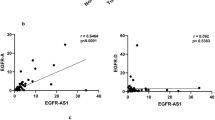
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has been shown to be overexpressed in human cancers due to mutation, amplification, and epigenetic hyperactivity, which leads to deregulated transcriptional mechanism. Among the eight different EGFR isoforms, the mechanism of regulation of full-length variant 1 is well-known, no studies have examined the function & factors regulating the expression of variant 8. This study aimed to understand the function of EGFR super-enhancer loci and its associated transcription factors regulating the expression of EGFR variant 8. Our study shows that overexpression of variant 8 and its transcription was more prevalent than variant 1 in many cancers and positively correlated with the EGFR-AS1 expression in oral cancer and HNSCC. Notably, individuals overexpressing variant 8 showed shorter overall survival and had a greater connection with other clinical traits than patients with overexpression of variant 1. In this study, TCGA enhancer RNA profiling on the constituent enhancer (CE1 and CE2) region revealed that the multiple enhancer RNAs formed from CE2 by employing CE1 as a promoter. Our bioinformatic analysis further supports the enrichment of enhancer RNA specific chromatin marks H3K27ac, H3K4me1, POL2 and H2AZ on CE2. GeneHancer and 3D chromatin capture analysis showed clustered interactions between CE1, CE2 loci and this interaction may regulates expression of both EGFR-eRNA and variant 8. Moreover, increased expression of SNAI2 and its close relationship to EGFR-AS1 and variant 8 suggest that SNAI2 could regulates variant 8 overexpression by building a MegaTrans complex with both EGFR-eRNA and EGFR-AS1. Our findings show that EGFR variant 8 and its transcriptional regulation & chromatin modification by eRNAs may provide a rationale for targeting RNA splicing in combination with targeted EGFR therapies in cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Fayçal C, Hatat AS, Gazzeri S, Eymin B (2017) Splice variants of the RTK family: their role in tumour progression and response to targeted therapy. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020383
Albitar L, Pickett G, Morgan M et al (2010) EGFR isoforms and gene regulation in human endometrial cancer cells. Mol Cancer 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-9-166
Alvarez-Dominguez JR, Knoll M, Gromatzky AA, Lodish HF (2017) The super-enhancer-derived alncRNA-EC7/bloodlinc potentiates red blood cell development in trans. Cell Rep 19:2503–2514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.082
Andersson R, Gebhard C, Miguel-Escalada I et al (2014) An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature 507:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12787
Arnold PR, Wells AD, Li XC (2020) Diversity and emerging roles of enhancer RNA in regulation of gene expression and cell fate. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00377
Arunkumar G, Anand S, Raksha P et al (2018) LncRNA OIP5-AS1 is overexpressed in undifferentiated oral tumors and integrated analysis identifies as a downstream effector of stemness-associated transcription factors. Sci Rep 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25451-3
Babic I, Anderson ES, Tanaka K et al (2013) EGFR mutation-induced alternative splicing of max contributes to growth of glycolytic tumors in brain cancer. Cell Metab 17:1000–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.013
Beagan JA, Duong MT, Titus KR et al (2017) YY1 and CTCF orchestrate a 3D chromatin looping switch during early neural lineage commitment. Genome Res 27:1139–1152. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.215160.116
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Bulger M, Groudine M (2011) Functional and mechanistic diversity of distal transcription enhancers. Cell 144:327–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.024
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U et al (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2:401–404. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
Chen H, Liang H (2020) A high-resolution map of human enhancer RNA loci characterizes super-enhancer activities in cancer. Cancer Cell 38:701-715.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2020.08.020
Chen H, Li C, Peng X et al (2018) A pan-cancer analysis of enhancer expression in nearly 9000 patient samples. Cell 173:386-399.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.027
Cheng JH, Pan DZC, Tsai ZTY, Tsai HK (2015) Genome-wide analysis of enhancer RNA in gene regulation across 12 mouse tissues. Sci Rep 5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12648
Choi S, Sathe A, Mathé E et al (2021) Identification of a putative enhancer RNA for EGFR in hyper-accessible regions in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by analysis of chromatin accessibility landscapes. Front Oncol 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.724687
Dhamodharan S, Rose MM, Chakkarappan SR et al (2021) Genetic variant rs10251977 (G>A) in EGFR-AS1 modulates the expression of EGFR isoforms A and D. Sci Rep 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88161-3
Dong ZQ, Guo ZY, Xie J (2019) The lncRNA EGFR-AS1 is linked to migration, invasion and apoptosis in glioma cells by targeting miR-133b/RACK1. Biomed Pharmacother 118:109292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109292
Dorighi KM, Swigut T, Henriques T et al (2017) Mll3 and Mll4 facilitate enhancer RNA synthesis and transcription from promoters independently of H3K4 monomethylation. Mol Cell 66:568-576.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.018
Elferink LA, Resto VA (2011) Receptor-tyrosine-kinase-targeted therapies for head and neck cancer. J Signal Transduct 2011:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/982879
Fishilevich S, Nudel R, Rappaport N et al (2017) GeneHancer: genome-wide integration of enhancers and target genes in GeneCards. Database 2017:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bax028
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U et al (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cbioportal complementary data sources and analysis options. Sci Signal 6:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2004088.Integrative
Godfrey L, Crump NT, O’Byrne S et al (2021) H3K79me2/3 controls enhancer–promoter interactions and activation of the pan-cancer stem cell marker PROM1/CD133 in MLL-AF4 leukemia cells. Leukemia 35:90–106. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0808-y
Huang Z, Du G, Huang X et al (2018) The enhancer RNA lnc-SLC4A1-1 epigenetically regulates unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss (URPL) by activating CXCL8 and NF-kB pathway. EBioMedicine 38:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.015
Jameson NM, Ma J, Benitez J et al (2019) Intron 1-mediated regulation of EGFR expression in EGFR-dependent malignancies is mediated by AP-1 and BET proteins. Mol Cancer Res 17:2208–2220. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0747
Jiao W, Chen Y, Song H et al (2018) HPSE enhancer RNA promotes cancer progression through driving chromatin looping and regulating hnRNPU/p300/EGR1/HPSE axis. Oncogene 37:2728–2745. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0128-0
Kaikkonen MU, Spann NJ, Heinz S et al (2013) Remodeling of the enhancer landscape during macrophage activation is coupled to enhancer transcription. Mol Cell 51:310–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.07.010
Kim YW, Lee S, Yun J, Kim AR (2015) Chromatin looping and eRNA transcription precede the transcriptional activation of gene in the β-globin locus. Biosci Rep 35:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20140126
Kusewitt DF, Choi C, Newkirk KM et al (2009) Slug/Snai2 is a downstream mediator of epidermal growth factor receptor-stimulated reepithelialization. J Invest Dermatol 129:491–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2008.222
Li M, Mukasa A, del Inda MM et al (2011) Guanylate binding protein 1 is a novel effector of EGFR-driven invasion in glioblastoma. J Exp Med 208:2657–2673. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20111102
Li J, Han L, Roebuck P et al (2015a) TANRIC: an interactive open platform to explore the function of IncRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res 75:3728–3737. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0273
Li Y, Wu Y, Abbatiello TC et al (2015b) Slug contributes to cancer progression by direct regulation of ERα signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 46:1461–1472. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.2878
Lurje G, Lenz HJ (2010) EGFR signaling and drug discovery. Oncology 77:400–410. https://doi.org/10.1159/000279388
Maiti GP, Mondal P, Mukherjee N et al (2013) Overexpression of EGFR in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is associated with inactivation of SH3GL2 and CDC25A genes. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063440
Manjari M, Popli R, Paul S et al (1996) Prevalence of oral cavity, pharynx, larynx and nasal cavity malignancies in Amritsar, Punjab. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03048602
Melo CA, Drost J, Wijchers PJ et al (2013) ERNAs are required for p53-dependent enhancer activity and gene transcription. Mol Cell 49:524–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.021
Nair SJ, Yang L, Meluzzi D et al (2019) Phase separation of ligand-activated enhancers licenses cooperative chromosomal enhancer assembly. Nat Struct Mol Biol 26:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0190-5
Ren C, Liu F, Ouyang Z et al (2017) Functional annotation of structural ncRNAs within enhancer RNAs in the human genome: Implications for human disease. Sci Rep 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15822-7
Sabari BR, Dall’ Agnese A, Boija A et al (2018) Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar3958
Shi J, Whyte WA, Zepeda-Mendoza CJ et al (2013) Role of SWI/SNF in acute leukemia maintenance and enhancer-mediated Myc regulation. Genes Dev 27:2648–2662. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.232710.113
Shii L, Song L, Maurer K et al (2017) SERPINB2 is regulated by dynamic interactions with pause-release proteins and enhancer RNAs. Mol Immunol 88:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.05.005
Sigova AA (2015) Transcription factor trapping by Rna in gene regulatory elements. Science 350:978–982
Spurlock CF, Shaginurova G, Tossberg JT et al (2017) Profiles of long noncoding RNAs in human naive and memory T cells. J Immunol 199:547–558. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700232
Sun W, Duan T, Ye P et al (2018) TSVdb: a web-tool for TCGA splicing variants analysis. BMC Genom 19:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4775-x
Tan DSW, Chong FT, Leong HS et al (2017) Long noncoding RNA EGFR-AS1 mediates epidermal growth factor receptor addiction and modulates treatment response in squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Med 23:1167–1175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4401
Tseng HY, Chen YA, Jen J et al (2017) Oncogenic MCT-1 activation promotes YY1-EGFR-MnSOD signaling and tumor progression. Oncogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2017.13
Vincent CA, Nissen I, Hörnblad A, Remeseiro S (2023) Epigenomic perturbation of novel EGFR enhancers reduces the proliferative and invasive capacity of glioblastoma and increases sensitivity to temozolomide. BMC Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-023-11418-9
Wang KC, Yang YW, Liu B et al (2011) A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature 472:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09819
Weinholdt C, Wichmann H, Kotrba J et al (2019) Prediction of regulatory targets of alternative isoforms of the epidermal growth factor receptor in a glioblastoma cell line. BMC Bioinform 20:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-019-2944-9
Weintraub AS, Li CH, Zamudio AV et al (2017) YY1 is a structural regulator of enhancer-promoter loops. Cell 171:1573-1588.e28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.008
Whalen S, Truty RM, Pollard KS (2016) Enhancer-promoter interactions are encoded by complex genomic signatures on looping chromatin. Nat Genet 48:488–496. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3539
Zhang Z, Lee JH, Ruan H et al (2019) Transcriptional landscape and clinical utility of enhancer RNAs for eRNA-targeted therapy in cancer. Nat Commun 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12543-5
Zhou Q, Yu M, Tirado-Magallanes R et al (2021) ZNF143 mediates CTCF-bound promoter–enhancer loops required for murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell function. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20282-1
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patients for agreeing to provide clinical samples for this study. SRC & AKM acknowledge the support of the DHR-MRU grant and infrastructural facility. SD and MMR acknowledge the research fellowship from the University Grant Commission (UGC), Govt. of India. We also gratefully acknowledge the UGC-SAP and DST-FIST of the Genetics department infrastructural facility.
Funding
This study was supported by grants Department of Health Research- starter grant (No. V.25011/536-HRD/2016-HR), DHR, Government of India and by National Institute of Genetics, NIG-JOINT (1A2022), Japan to A.K. Munirajan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Designed study—SRC, AKM. Performed research—SRC, KVU, SD, MMR. Analyzed data—SRC, KVU. Contributed new methods (qPCR)—AKM, SRC. supervision—AKM. Writing—original draft—SRC. Writing—review and editing—AKM, II, AKM. Funding acquisition— AKM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was obtained from the institutional ethics committee (IEC) of Madras Medical College, Chennai (No.04092010 and 0202201) and performed within the ethical framework of Dr. ALM PG Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Chennai.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chakkarappan, S.R., Umadharshini, K.V., Dhamodharan, S. et al. Super enhancer loci of EGFR regulate EGFR variant 8 through enhancer RNA and strongly associate with survival in HNSCCs. Mol Genet Genomics 299, 3 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02089-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02089-z