Abstract
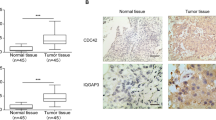
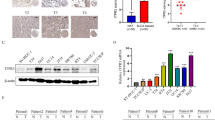
The study was designed to detect the expression and clinical significance of the HEATR3 gene in bladder cancer (BCa) and to preliminarily explore whether this gene can affect the occurrence and development of BCa through the AKT/ERK signaling pathway. The expression and prognostic value of HEATR3 were explored based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Genotypic Tissue Expression (GTEx) databases. Microarray immunohistochemical analysis was performed in 30 BCa cases to investigate the level of HEATR3 protein and to explore the relationship between HEATR3 and the clinicopathological features of BCa. Western Blot and qRT-PCR were used to detect HEATR3 protein and mRNA in BCa cell lines (5637, TCCSUP, SW780) and fallopian tube epithelial cell (SV-HUC-1). CCK8 method was employed to study the proliferation of BCa cells after heat treatment. Transwell assay was conducted to analyze the effect of HEATR3 on cell migration and invasion. And cell cycle and apoptosis were detected by flow cytometry. Furthermore, Western Blot assay was used to probe the effects of down-regulation of HEATR3 expression on the expression and phosphorylation levels of AKT and ERK proteins in BCa cells. Bioinformatics analysis showed that HEATR3 was significantly up-regulated in BCa, and high HEATR3 expression was associated with poor prognosis of BCa patients. In vitro experiments demonstrated that HEATR3 expression was up-regulated in BCa tissues compared with that in adjacent tissues. HEATR3 protein was also up-regulated in malignant cell lines. HEATR3 knockdown in BCa cells could inhibit cell proliferation, invasion and migration, block cell cycle and promote cell apoptosis. At the same time, HEATR3 knockdowns reduced the expression levels of p-AKT and p-ERK proteins. HEATR3 knockdown inhibits the development of BCa cells through the AKT/ERK signaling pathway. and it may become one of the most promising molecular targets for BCa treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Cai J, Huang S, Yi Y, Bao S (2019) Downregulation of PTPN18 can inhibit proliferation and metastasis and promote apoptosis of endometrial cancer. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 46(8):734–742. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.13098
Calvino FR, Kharde S, Ori A, Hendricks A, Wild K, Kressler D, Bange G, Hurt E, Beck M, Sinning I (2015) Symportin 1 chaperones 5S RNP assembly during ribosome biogenesis by occupying an essential rRNA-binding site. Nat Commun. 6:6510. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7510
Chen E, Yang F, He H, Li Q, Zhang W, Xing J, Zhu Z, Jiang J, Wang H, Zhao X, Liu R, Lei L, Dong J, Pei Y, Yang Y, Pan J, Zhang P, Liu S, Du L, Zeng Y, Yang J (2018) Alteration of tumor suppressor BMP5 in sporadic colorectal cancer: a genomic and transcriptomic profiling based study. Mol Cancer 17(1):176. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0925-7
Chung CC, Kanetsky PA, Wang Z, Hildebrandt MA, Koster R, Skotheim RI, Kratz CP, Turnbull C, Cortessis VK, Bakken AC, Bishop DT, Cook MB, Erickson RL, Fosså SD, Jacobs KB, Korde LA, Kraggerud SM, Lothe RA, Loud JT, Rahman N, Skinner EC, Thomas DC, Wu X, Yeager M, Schumacher FR, Greene MH, Schwartz SM, McGlynn KA, Chanock SJ, Nathanson KL (2013) Meta-analysis identifies four new loci associated with testicular germ cell tumor. Nat Genet 45(6):680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2634
Jia X, Liu P, Zhang M, Feng T, Tang H, Tang Z, Zhao H, Jin T (2015) Genetic variants at 6p21, 10q23, 16q21 and 22q12 are associated with esophageal cancer risk in a Chinese Han population. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(10):19381–19387
Lei T, Lv ZY, Fu JF, Wang Z, Fan Z, Wang Y (2018) LncRNA NBAT-1 is down-regulated in lung cancer and influences cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(7):1958–1962. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201804_14721
Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK, Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M, Pukkala E, Skytthe A, Hemminki K (2000) Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer–analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N Engl J Med 343(2):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200007133430201
Mao W, Wang K, Sun S, Wu J, Chen M, Geng J, Luo M (2021) ID2 Inhibits bladder cancer progression and metastasis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Front Cell Develop Boil. 9:738364. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.738364
Niknejad H, Yazdanpanah G, Ahmadiani A (2016) Induction of apoptosis, stimulation of cell-cycle arrest and inhibition of angiogenesis make human amnion-derived cells promising sources for cell therapy of cancer. Cell Tissue Res 363(3):599–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2364-3
O'Donohue MF, Da Costa L, Lezzerini M, Unal S, Joret C, Bartels M, Brilstra E, Scheijde-Vermeulen M, Wacheul L, De Keersmaecker K, Vereecke S, Labarque V, Saby M, Lefevre SD, Platon J, Montel-Lehry N, Laugero N, Lacazette E, Van Gassen K, Houtkooper RH, MacInnes AW (2022) HEATR3 variants impair nuclear import of uL18 (RPL5) and drive Diamond-Blackfan anemia. J Am Soc Hematol. 139(21):3111–3126. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2021011846
Pan H, Xue W, Zhao W, Schachner M (2020) Expression and function of chondroitin 4-sulfate and chondroitin 6-sulfate in human glioma. FASEB J 34(2):2853–2868. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901621RRR
Prakash R, John AA, Singh D (2019) miR-409–5p negatively regulates Wnt/Beta catenin signaling pathway by targeting Lrp-8. J Cell Physiol. 234(12):23507–23517. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28919
Ruark E, Seal S, McDonald H, Zhang F, Elliot A, Lau K, Perdeaux E, Rapley E, Eeles R, Peto J, Kote-Jarai Z, Muir K, Nsengimana J, Shipley J, Bishop DT, Stratton MR, Easton DF, Huddart RA, Rahman N, Turnbull C (2013) Identification of nine new susceptibility loci for testicular cancer, including variants near DAZL and PRDM14. Nat Genet 45(6):686–689. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2635
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Wu C, Kraft P, Zhai K, Chang J, Wang Z, Li Y, Hu Z, He Z, Jia W, Abnet CC, Liang L, Hu N, Miao X, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Zhan Q, Liu Y, Qiao Y, Zhou Y, Jin G, Guo C, Lu C, Yang H, Fu J, Yu D, Freedman ND, Ding T, Tan W, Goldstein AM, Wu T, Shen H, Ke Y, Zeng Y, Chanock SJ, Taylor PR, Lin D (2012) Genome-wide association analyses of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese identify multiple susceptibility loci and gene-environment interactions. Nat Genet 44(10):1090–1097. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2411
Yachida S, Jones S, Bozic I, Antal T, Leary R, Fu B, Kamiyama M, Hruban RH, Eshleman JR, Nowak MA, Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA (2010) Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature 467(7319):1114–1117. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09515
Zhang W, Hui KY, Gusev A, Warner N, Ng SM, Ferguson J, Choi M, Burberry A, Abraham C, Mayer L, Desnick RJ, Cardinale CJ, Hakonarson H, Waterman M, Chowers Y, Karban A, Brant SR, Silverberg MS, Gregersen PK, Katz S, Lifton RP, Zhao H, Nunez G, Pe’er I, Peter I, Cho JH (2013) Extended haplotype association study in Crohn’s disease identifies a novel, Ashkenazi Jewish-specific missense mutation in the NF-kappaB pathway gene, HEATR3. Genes Immun 14(5):310–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.19
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all participants for their support and participation.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XD: writing original draft, XM: software, conceptualization; WM: methodology, investigation; WZ: data curation, investigation; SY: software; FN: formal analysis; YX: validation, supervision; TJ: writing–review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Northwest University.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Additional information
Communicated by Shuhua Xu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, X., Ma, X., Meng, W. et al. HEATR3 involved in the cell proliferation, metastasis and cell cycle development of bladder cancer acts as a tumor suppressor. Mol Genet Genomics 298, 1353–1364 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02046-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02046-w