Abstract
Background
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays a vital role in the progression of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) participate in the EMT process as an important regulatory factor and have the potential to serve as prognostic biomarkers. We aimed to construct a novel lncRNA prognostic signature for LUAD based on EMT-related lncRNAs, identify EMT-related hub lncRNA, and investigate its biological functions.
Methods
RNA-seq data, clinical and survival information were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. The EMT-related lncRNA prognostic signature (EMTscore) was constructed using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator Cox regression analysis. The efficiency of EMTscore in predicting the prognosis of LUAD was evaluated through the area under the time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The hub lncRNA of the prognostic signature was selected using a co-expression network map, and its effects on cell proliferation and metastasis were explored by in vitro experiments.
Results
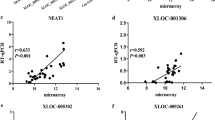
We constructed a prognostic signature (EMTscore) containing 8 tumor-high expressed lncRNAs. The EMTscore performed well in predicting overall survival rates with AUC values of 0.708 at 5 years in the training set. EMTscore could independently predict the survival of LUAD, with HR = 4.011 (95% CI 2.430–6.622) in the multivariate Cox regression. Importantly, we identified LINC01615 as the hub lncRNA in the EMTscore and revealed that LINC01615 enhanced the proliferation, migration, and EMT of lung cancer cells.
Conclusions
A new EMT-related lncRNA prognostic signature named EMTscore was developed, and LINC01615 was identified as the hub lncRNA of EMTscore. The hub lncRNA LINC01615 had an oncogenic biological function in LUAD.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The TCGA data are available in a public, open-access repository. The data of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Niksic M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ, Esteve J, Ogunbiyi OJ, Azevedo ESG, Chen WQ, Eser S, Engholm G, Stiller CA, Monnereau A, Woods RR, Visser O, Lim GH, Aitken J, Weir HK, Coleman MP, Group, CW (2018) Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37,513,025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 391:1023–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3
Cao ZQ, Wang Z, Leng P (2019) Aberrant N-cadherin expression in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 118:109320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109320
Chen Y, Li C, Pan Y, Han S, Feng B, Gao Y, Chen J, Zhang K, Wang R, Chen L (2016) The emerging role and promise of long noncoding RNAs in lung cancer treatment. Cell Physiol Biochem 38:2194–2206. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445575
Chen Z, Hu Z, Sui Q, Huang Y, Zhao M, Li M, Liang J, Lu T, Zhan C, Lin Z, Sun F, Wang Q, Tan L (2022) LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 facilitates tumor proliferation and the migration via the HIF-1alpha/glycolysis axis in lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Biol Sci 18:522–535. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.67556
Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Borghaei H, Chang AC, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D’amico TA, Demmy TL, Govindan R, Grannis FW Jr, Grant SC, Horn L, Jahan TM, Komaki R, Kong FM, Kris MG, Krug LM, Lackner RP, Lennes IT, Loo BW Jr, Martins R, Otterson GA, Patel JD, Pinder-Schenck MC, Pisters KM, Reckamp K, Riely GJ, Rohren E, Shapiro TA, Swanson SJ, Tauer K, Wood DE, Yang SC, Gregory K, Hughes M, National Comprehensive Cancer, N (2013) Non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2013. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 11:645–653. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2013.0084
Fang Y, Fullwood MJ (2016) Roles, functions, and mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Genom Proteom Bioinform 14:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.09.006
Grelet S, Link LA, Howley B, Obellianne C, Palanisamy V, Gangaraju VK, Diehl JA, Howe PH (2017) A regulated PNUTS mRNA to lncRNA splice switch mediates EMT and tumour progression. Nat Cell Biol 19:1105–1115. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3595
Gu ZR, Liu W (2020) The LncRNA AL161431.1 targets miR-1252-5p and facilitates cellular proliferation and migration via MAPK signaling in endometrial carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:2294–2302. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202003_20495
Hashemi M, Moosavi MS, Abed HM, Dehghani M, Aalipour M, Heydari EA, Behroozaghdam M, Entezari M, Salimimoghadam S, Gunduz ES, Taheriazam A, Mirzaei S, Samarghandian S (2022) Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 in human cancer: from proliferation and metastasis to therapy. Pharmacol Res 184:106418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106418
He J, Yu J (2019) Long noncoding RNA FAM83A-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by binding with NOP58 to enhance the mRNA stability of FAM83A. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20192550
Hu L, Chen SH, Lv QL, Sun B, Qu Q, Qin CZ, Fan L, Guo Y, Cheng L, Zhou HH (2016) Clinical significance of long non-coding RNA CASC8 rs10505477 polymorphism in lung cancer susceptibility, platinum-based chemotherapy response, and toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13060545
Hu Z, Yang C, Guo S, Li Y, Li Y (2022) LINC01615 activates ZEB2 through competitively binding with miR-3653-3p to promote the carcinogenesis of colon cancer cells. Cell Cycle 21:228–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2021.2015670
Huang GM, Zang HL, Geng YX, Li YH (2020) LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 aggravates the malignant development of esophageal cancer by binding to miR-495-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:9408–9415. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202009_23024
Huang H, Yang C, Zhang Q, Zhuo T, Li X, Li N, Zhu L, Luo C, Gan J, Wu Y (2022) Long non-coding RNA FAM83A antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA FAM83A-AS1) targets microRNA-141-3p to regulate lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression. Bioengineered 13:4964–4977. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2037871
Iser IC, Pereira MB, Lenz G, Wink MR (2017) The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-like process in glioblastoma: an updated systematic review and in silico investigation. Med Res Rev 37:271–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21408
Ji D, Chen GF, Liu X, Zhu J, Sun JY, Zhang XY, Lu XJ (2019) Identification of LINC01615 as potential metastasis-related long noncoding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Physiol 234:12964–12970. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27963
Jia J, Li H, Chu J, Sheng J, Wang C, Jia Z, Meng W, Yin H, Wan J, He F (2021) LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 promotes ESCC progression by regulating miR-214/CDC25B axis. J Cancer 12:1200–1211. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.54007
Jiang X, Guan J, Xu Y, Ren H, Jiang J, Wudu M, Wang Q, Su H, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Zou Z, Hu Y, Sun X, Qiu X (2021) Silencing of CASC8 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cells function and promotes sensitivity to osimertinib via FOXM1. J Cancer 12:387–396. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.47863
Jiang X, Chen M, Du J, Bi H, Guo X, Yang C, He X, Jin Z (2022) LncRNA-AC068228.1 is a novel prognostic biomarker that promotes malignant phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol 12:856655. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.856655
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:178–196. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3758
Li Z, Wu Y, Zhang C, Dai S, Wei S, Zhao R, Gao F, Zhao L, Shan B (2023) LncRNA SNHG5 suppresses cell migration and invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma via regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Oncol 2023:3335959. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/3335959
Liu W, Wan Q, Zhou E, He P, Tang L (2023) LncRNA LINC01833 is a prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltrates in patients with lung adenocarcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis. J Oncol 2023:3965198. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/3965198
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Ma G, Li G, Fan W, Xu Y, Song S, Guo K, Liu Z (2021) The role of long noncoding RNA AL161431.1 in the development and progression of pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol 11:666313. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.666313
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL, Siegel RL (2019) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69:363–385. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21565
Sang Y, Gu H, Chen Y, Shi Y, Liu C, Lv L, Sun Y, Zhang Y (2020) Long non-coding RNA CASC8 polymorphisms are associated with the risk of esophageal cancer in a Chinese population. Thorac Cancer 11:2852–2857. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13612
Shih JY, Yang PC (2011) The EMT regulator slug and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 32:1299–1304. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgr110
Wang Y, Yang Y, Wang Y, Li X, Xiao Y, Wang W (2020) High cancer susceptibility candidate 8 expression is associated with poor prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: validated analysis based on four cancer databases. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:392. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00392
Wu Q, Zhang H, Yang D, Min Q, Wang Y, Zhang W, Zhan Q (2022) The m6A-induced lncRNA CASC8 promotes proliferation and chemoresistance via upregulation of hnRNPL in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci 18:4824–4836. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.71234
Xiang Y, Feng L, Liu H, Liu Y, Li J, Su L, Liao X (2022) SIPA1 regulates LINC01615 to promote metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194815
Xiao G, Wang P, Zheng X, Liu D, Sun X (2019) FAM83A-AS1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and invasion by targeting miR-150-5p and modifying MMP14. Cell Cycle 18:2972–2985. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1664225
Xiao Y, Hu F, Li M, Mo L, Xu C, Wang X, Nie J, Yang L, Xie B (2020) Interaction between linc01615 and miR-491–5p regulates the survival and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Transl Cancer Res 9:2638–2647. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2020.03.03
Yang B, Gu B, Zhang J, Xu L, Sun Y (2020) CASC8 lncRNA promotes the proliferation of retinoblastoma cells through downregulating miR34a methylation. Cancer Manag Res 12:13461–13467. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S268380
Yang D, Niu Y, Ni H, Leng J, Xu X, Yuan X, Chen K, Wu Y, Wu H, Lu H, Xu J, Wang L, Jiang Y, Cui D, Hu J, Xia D, Wu Y (2022) Identification of metastasis-related long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer through a novel tumor mesenchymal score. Pathol Res Pract 237:154018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2022.154018
Zhang Y, Li W, Lin Z, Hu J, Wang J, Ren Y, Wei B, Fan Y, Yang Y (2020) The long noncoding RNA Linc01833 enhances lung adenocarcinoma progression via MiR-519e-3p/S100A4 axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:11157–11167. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S279623
Zhang Q, Wu X, Sun Y, Yang L, Wang Z, Yang Y, Zhao X, Zhang X (2022) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related lncRNAs associated with prognosis and immune cell infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Transl Res 14:7308–7323
Zhao H, Wang Y, Wu X, Zeng X, Lin B, Hu S, Zhang S, Li Y, Zhou Z, Zhou Y, Du C, Beer DG, Bai S, Chen G (2022) FAM83A antisense RNA 1 (FAM83A-AS1) silencing impairs cell proliferation and induces autophagy via MET-AMPKa signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. Bioengineered 13:13312–13327. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2081457
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81871896 and No. 81672316 to L. Yafei).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL, YX and LB contributed to the conception and design of the study. YS and TX participated in study design, result interpretation and manuscript writing. TX, LW and ZY extracted the TCGA data. YS and WW analyzed the data. QH, CL and YS performed the experiments and coordinated the result interpretation. ZC, WW and YS performed the bioinformatics analysis. TC, WX and NW contributed to the interpretation of the results and discussions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, Y., Xia, T., Xie, W. et al. Construction of an EMT-related lncRNA prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma and functional verification of its hub gene LINC01615. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 17781–17793 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05476-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05476-6