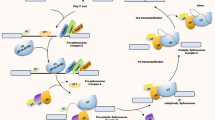
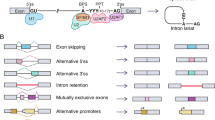
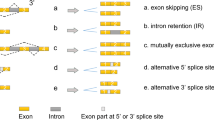
Abstract
During eukaryotic gene expression, alternative splicing of messenger RNA precursors is critical in increasing protein diversity and regulatory complexity. Multiple transcript isoforms could be produced by alternative splicing from a single gene; they could eventually be translated into protein isoforms with deleted, added, or altered domains or produce transcripts containing premature termination codons that could be targeted by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Alternative splicing can generate proteins with similar, different, or even opposite functions. Increasingly strong evidence indicates that abnormal RNA splicing is a prevalent and crucial occurrence in cellular differentiation, tissue advancement, and the development and progression of cancer. Aberrant alternative splicing could affect cancer cell activities such as growth, apoptosis, invasiveness, drug resistance, angiogenesis, and metabolism. This systematic review provides a comprehensive overview of the impact of abnormal RNA alternative splicing on the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert T, Herzel L, Neugebauer KM (2017) Perfect timing: splicing and transcription rates in living cells. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1401
Aravalli RN, Cressman EN, Steer CJ (2013) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Arch Toxicol 87:227–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0931-2
Ardui S, Ameur A, Vermeesch JR, Hestand MS (2018) Single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing comes of age: applications and utilities for medical diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res 46:2159–2168. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky066
Arif W, Mathur B, Saikali MF, Chembazhi UV, Toohill K, Song YJ, Hao Q, Karimi S, Blue SM, Yee BA et al (2023) Splicing factor SRSF1 deficiency in the liver triggers NASH-like pathology and cell death. Nat Commun 14:551. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-35932-3
Bangru S, Arif W, Seimetz J, Bhate A, Chen J, Rashan EH, Carstens RP, Anakk S, Kalsotra A (2018) Alternative splicing rewires Hippo signaling pathway in hepatocytes to promote liver regeneration. Nat Struct Mol Biol 25:928–939. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-018-0129-2
Baralle FE, Giudice J (2017) Alternative splicing as a regulator of development and tissue identity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18:437–451. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.27
Barash Y, Calarco JA, Gao W, Pan Q, Wang X, Shai O, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ (2010) Deciphering the splicing code. Nature 465:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09000
Berasain C, Elizalde M, Urtasun R, Castillo J, Garcia-Irigoyen O, Uriarte I, Latasa MU, Prieto J, Avila MA (2014) Alterations in the expression and activity of pre-mRNA splicing factors in hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepat Oncol 1:241–252. https://doi.org/10.2217/hep.13.17
Bhate A, Parker DJ, Bebee TW, Ahn J, Arif W, Rashan EH, Chorghade S, Chau A, Lee JH, Anakk S et al (2015) ESRP2 controls an adult splicing programme in hepatocytes to support postnatal liver maturation. Nat Commun 6:8768. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9768
Bonnal S, Vigevani L, Valcarcel J (2012) The spliceosome as a target of novel antitumour drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:847–859. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3823
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Bruun GH, Doktor TK, Borch-Jensen J, Masuda A, Krainer AR, Ohno K, Andresen BS (2016) Global identification of hnRNP A1 binding sites for SSO-based splicing modulation. BMC Biol 14:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-016-0279-9
Chang C, Rajasekaran M, Qiao Y, Dong H, Wang Y, Xia H, Deivasigamani A, Wu M, Sekar K, Gao H et al (2022) The aberrant upregulation of exon 10-inclusive SREK1 through SRSF10 acts as an oncogenic driver in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun 13:1363. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29016-x
Chen LL, Wang WJ (2021) p53 regulates lipid metabolism in cancer. Int J Biol Macromol 192:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.188
Chen H, Gao F, He M, Ding XF, Wong AM, Sze SC, Yu AC, Sun T, Chan AW, Wang X et al (2019a) Long-read RNA sequencing identifies alternative splice variants in hepatocellular carcinoma and tumor-specific isoforms. Hepatology 70:1011–1025. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30500
Chen QF, Li W, Wu P, Shen L, Huang ZL (2019b) Alternative splicing events are prognostic in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 11:4720–4735. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102085
Chen D, Zhao Z, Chen L, Li Q, Zou J, Liu S (2021) PPM1G promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via phosphorylation regulation of alternative splicing protein SRSF3. Cell Death Dis 12:722. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-04013-y
Cheng Y, Luo C, Wu W, Xie Z, Fu X, Feng Y (2016) Liver-specific deletion of SRSF2 caused acute liver failure and early death in mice. Mol Cell Biol 36:1628–1638. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01071-15
Chettouh H, Fartoux L, Aoudjehane L, Wendum D, Claperon A, Chretien Y, Rey C, Scatton O, Soubrane O, Conti F et al (2013) Mitogenic insulin receptor-A is overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma due to EGFR-mediated dysregulation of RNA splicing factors. Can Res 73:3974–3986. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3824
Choi UY, Kang JS, Hwang YS, Kim YJ (2015) Oligoadenylate synthase-like (OASL) proteins: dual functions and associations with diseases. Exp Mol Med 47:e144. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2014.110
Choi S, Lee HS, Cho N, Kim I, Cheon S, Park C, Kim E-M, Kim W, Kim KK (2022) RBFOX2-regulated TEAD1 alternative splicing plays a pivotal role in Hippo-YAP signaling. Nucleic Acids Res 50:8658–8673. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac509
Choi S, Cho N, Kim KK (2023) The implications of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in cell signal transduction. Exp Mol Med 55:755–766. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-023-00981-7
Climente-Gonzalez H, Porta-Pardo E, Godzik A, Eyras E (2017) The functional impact of alternative splicing in cancer. Cell Rep 20:2215–2226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.012
Cui H, Wu F, Sun Y, Fan G, Wang Q (2010) Up-regulation and subcellular localization of hnRNP A2/B1 in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 10:356. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-356
Dauki AM, Blachly JS, Kautto EA, Ezzat S, Abdel-Rahman MH, Coss CC (2020) Transcriptionally active androgen receptor splice variants promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Res 80:561–575. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-1117
de Oliveira Freitas machado C, Schafranek M, Brüggemann M, Hernández Cañás MC, Keller M, Di Liddo A, Brezski A, Blümel N, Arnold B, Bremm A et al (2023) Poison cassette exon splicing of SRSF6 regulates nuclear speckle dispersal and the response to hypoxia. Nucleic Acids Res 51:870–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1225
D’Souza S, Lau KC, Coffin CS, Patel TR (2020) Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 26:5759–5783. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5759
El Awady MK, Anany MA, Esmat G, Zayed N, Tabll AA, Helmy A, El Zayady AR, Abdalla MS, Sharada HM, El Raziky M et al (2011) Single nucleotide polymorphism at exon 7 splice acceptor site of OAS1 gene determines response of hepatitis C virus patients to interferon therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:843–850. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06605.x
Elizalde M, Urtasun R, Azkona M, Latasa MU, Goñi S, García-Irigoyen O, Uriarte I, Segura V, Collantes M, Di Scala M et al (2014) Splicing regulator SLU7 is essential for maintaining liver homeostasis. J Clin Invest 124:2909–2920. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci74382
Endo K, Terada T (2000) Protein expression of CD44 (standard and variant isoforms) in hepatocellular carcinoma: relationships with tumor grade, clinicopathologic parameters, p53 expression, and patient survival. J Hepatol 32:78–84
Fujimoto A, Totoki Y, Abe T, Boroevich KA, Hosoda F, Nguyen HH, Aoki M, Hosono N, Kubo M, Miya F et al (2012) Whole-genome sequencing of liver cancers identifies etiological influences on mutation patterns and recurrent mutations in chromatin regulators. Nat Genet 44:760–764. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2291
Geuens T, Bouhy D, Timmerman V (2016) The hnRNP family: insights into their role in health and disease. Hum Genet 135:851–867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1683-5
Ghosh A, Stewart D, Matlashewski G (2004) Regulation of human p53 activity and cell localization by alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol 24:7987–7997. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.24.18.7987-7997.2004
He R, Peng J, Yuan P, Xu F, Wei W (2015) Divergent roles of BECN1 in LC3 lipidation and autophagosomal function. Autophagy 11:740–747. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1034404
He A-D, Xie W, Song W, Ma Y-Y, Liu G, Liang M-L, Da X-W, Yao G-Q, Zhang B-X, Gao C-J et al (2017) Platelet releasates promote the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by suppressing the expression of KLF6. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02801-1
Hernández Borrero LJ, El-Deiry WS (2021) Tumor suppressor p53: Biology, signaling pathways, and therapeutic targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1876:188556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188556
Huang S, Luo K, Jiang L, Zhang XD, Lv YH, Li RF (2021) PCBP1 regulates the transcription and alternative splicing of metastasis-related genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 11:23356. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-02642-z
Huang DQ, Terrault NA, Tacke F, Gluud LL, Arrese M, Bugianesi E, Loomba R (2023) Global epidemiology of cirrhosis—aetiology, trends and predictions. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 20:388–398. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-023-00759-2
Hwang HM, Heo CK, Lee HJ, Kwak SS, Lim WH, Yoo JS, Yu DY, Lim KJ, Kim JY, Cho EW (2018a) Identification of anti-SF3B1 autoantibody as a diagnostic marker in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med 16:177. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1546-z
Hwang B, Lee JH, Bang D (2018b) Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and bioinformatics pipelines. Exp Mol Med 50:96. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0071-8
Hyun J, Al Abo M, Dutta RK, Oh SH, Xiang K, Zhou X, Maeso-Díaz R, Caffrey R, Sanyal AJ, Freedman JA et al (2021) Dysregulation of the ESRP2-NF2-YAP/TAZ axis promotes hepatobiliary carcinogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 75:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.033
Iguchi T, Komatsu H, Masuda T, Nambara S, Kidogami S, Ogawa Y, Hu Q, Saito T, Hirata H, Sakimura S et al (2016) Increased copy number of the gene encoding SF3B4 indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res 36:2139–2144
Jeong S (2017) SR proteins: binders, regulators, and connectors of RNA. Mol Cells 40:1–9. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.2319
Jiang W, Chen L (2021) Alternative splicing: Human disease and quantitative analysis from high-throughput sequencing. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2020.12.009
Jiang H, Lin Q, Ma L, Luo S, Jiang X, Fang J, Lu Z (2021) Fructose and fructose kinase in cancer and other pathologies. J Genet Genom 48:531–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2021.06.006
Jimenez M, Arechederra M, Avila MA, Berasain C (2018) Splicing alterations contributing to cancer hallmarks in the liver: central role of dedifferentiation and genome instability. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:84. https://doi.org/10.21037/tgh.2018.10.11
Jimenez M, Urtasun R, Elizalde M, Azkona M, Latasa MU, Uriarte I, Arechederra M, Alignani D, Barcena-Varela M, Alvarez-Sola G et al (2019) Splicing events in the control of genome integrity: role of SLU7 and truncated SRSF3 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 47:3450–3466. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz014
Ke RS, Zhang K, Lv LZ, Dong YP, Pan F, Yang F, Cai QC, Jiang Y (2019) Prognostic value and oncogene function of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 overexpression in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Macromol 129:140–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.012
Keren H, Lev-Maor G, Ast G (2010) Alternative splicing and evolution: diversification, exon definition and function. Nat Rev Genet 11:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2776
Kim E, Viatour P (2020) Hepatocellular carcinoma: old friends and new tricks. Exp Mol Med 52:1898–1907. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-00527-1
Kim MS, Pinto SM, Getnet D, Nirujogi RS, Manda SS, Chaerkady R, Madugundu AK, Kelkar DS, Isserlin R, Jain S et al (2014) A draft map of the human proteome. Nature 509:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13302
Kudo M (2020) Scientific rationale for combined immunotherapy with PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies and VEGF inhibitors in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051089
Kumar D, Das M, Sauceda C, Ellies LG, Kuo K, Parwal P, Kaur M, Jih L, Bandyopadhyay GK, Burton D et al (2019) Degradation of splicing factor SRSF3 contributes to progressive liver disease. J Clin Invest 129:4477–4491. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci127374
Kumar D, Das M, Oberg A, Sahoo D, Wu P, Sauceda C, Jih L, Ellies LG, Langiewicz MT, Sen S et al (2022) Hepatocyte Deletion of IGF2 prevents DNA damage and tumor formation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Sci (weinh) 9:e2105120. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202105120
Kurahashi H, Takami K, Oue T, Kusafuka T, Okada A, Tawa A, Okada S, Nishisho I (1995) Biallelic inactivation of the APC gene in hepatoblastoma. Can Res 55:5007–5011
Lai MY, Chang HC, Li HP, Ku CK, Chen PJ, Sheu JC, Huang GT, Lee PH, Chen DS (1993) Splicing mutations of the p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Can Res 53:1653–1656
Lee SC, Abdel-Wahab O (2016) Therapeutic targeting of splicing in cancer. Nat Med 22:976–986. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4165
Lei S, Zhang B, Huang L, Zheng Z, Xie S, Shen L, Breitzig M, Czachor A, Liu H, Luo H et al (2021) SRSF1 promotes the inclusion of exon 3 of SRA1 and the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by interacting with exon 3 of SRA1pre-mRNA. Cell Death Discov 7:117. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00498-w
Li K, Wang Z (2021) Splicing factor SRSF2-centric gene regulation. Int J Biol Sci 17:1708–1715. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.58888
Li X, Qian X, Peng LX, Jiang Y, Hawke DH, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Lee JH, Cote G, Wang H et al (2016) A splicing switch from ketohexokinase-C to ketohexokinase-A drives hepatocellular carcinoma formation. Nat Cell Biol 18:561–571. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3338
Li Y, Sahni N, Pancsa R, McGrail DJ, Xu J, Hua X, Coulombe-Huntington J, Ryan M, Tychhon B, Sudhakar D et al (2017) Revealing the determinants of widespread alternative splicing perturbation in cancer. Cell Rep 21:798–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.09.071
Li S, Hu Z, Zhao Y, Huang S, He X (2019) Transcriptome-wide analysis reveals the landscape of aberrant alternative splicing events in liver cancer. Hepatology 69:359–375. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30158
Li G, Chen H, Shen F, Smithson SB, Shealy GL, Ping Q, Liang Z, Han J, Adams AC, Li Y et al (2023) Targeting hepatic serine-arginine protein kinase 2 ameliorates alcohol-associated liver disease by alternative splicing control of lipogenesis. Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1097/hep.0000000000000433
Lin KT, Ma WK, Scharner J, Liu YR, Krainer AR (2018) A human-specific switch of alternatively spliced AFMID isoforms contributes to TP53 mutations and tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Genome Res. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.227181.117
Lin YH, Wu MH, Liu YC, Lyu PC, Yeh CT, Lin KH (2021) LINC01348 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through inhibition of SF3B3-mediated EZH2 pre-mRNA splicing. Oncogene 40:4675–4685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01905-3
Liu L, Xie S, Zhang C, Zhu F (2014) Aberrant regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in hepatocellular carcinoma. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 24:133–149
Liu ZY, Li W, Pang YN, Zhou ZX, Liu SP, Cheng K, Qin Q, Jia Y, Liu SR (2018) SF3B4 is regulated by microRNA-133b and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 38:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.10.067
Liu X, Zheng Y, Xiao M, Chen X, Zhu Y, Xu C, Wang F, Liu Z, Cao K (2022) SRSF10 stabilizes CDC25A by triggering exon 6 skipping to promote hepatocarcinogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 41:353. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-022-02558-0
Llères D, Denegri M, Biggiogera M, Ajuh P, Lamond AI (2010) Direct interaction between hnRNP-M and CDC5L/PLRG1 proteins affects alternative splice site choice. EMBO Rep 11:445–451. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2010.64
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Lencioni R, Koike K, Zucman-Rossi J, Finn RS (2021) Hepatocell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7:6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3
Long JC, Caceres JF (2009) The SR protein family of splicing factors: master regulators of gene expression. Biochem J 417:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20081501
Long Y, Sou WH, Yung KWY, Liu H, Wan SWC, Li Q, Zeng C, Law COK, Chan GHC, Lau TCK et al (2019) Distinct mechanisms govern the phosphorylation of different SR protein splicing factors. J Biol Chem 294:1312–1327. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.003392
López-Cánovas JL, Del Rio-Moreno M, García-Fernandez H, Jiménez-Vacas JM, Moreno-Montilla MT, Sánchez-Frias ME, Amado V, Fernando LL, Fondevila MF, Ciria R et al (2021) Splicing factor SF3B1 is overexpressed and implicated in the aggressiveness and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 496:72–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.010
López-Cánovas JL, Hermán-Sánchez N, Del Rio-Moreno M, Fuentes-Fayos AC, Lara-López A, Sánchez-Frias ME, Amado V, Ciria R, Briceño J, de la Mata M et al (2023) PRPF8 increases the aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating FAK/AKT pathway via fibronectin 1 splicing. Exp Mol Med 55:132–142. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-022-00917-7
Lu ZX, Jiang P, Xing Y (2012) Genetic variation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing in human populations. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 3:581–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.120
Lu Y, Xu W, Ji J, Feng D, Sourbier C, Yang Y, Qu J, Zeng Z, Wang C, Chang X et al (2015) Alternative splicing of the cell fate determinant Numb in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 62:1122–1131. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27923
Luk K-C, Gersch J, Harris BJ, Holzmayer V, Mbanya D, Sauleda S, Rodgers MA, Cloherty G (2021) More DNA and RNA of HBV SP1 splice variants are detected in genotypes B and C at low viral replication. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-03304-w
Luo C, Cheng Y, Liu Y, Chen L, Liu L, Wei N, Xie Z, Wu W, Feng Y (2017) SRSF2 regulates alternative splicing to drive hepatocellular carcinoma development. Cancer Res 77:1168–1178. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-1919
Ma WK, Voss DM, Scharner J, Costa ASH, Lin KT, Jeon HY, Wilkinson JE, Jackson M, Rigo F, Bennett CF et al (2022) ASO-Based PKM splice-switching therapy inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Cancer Res 82:900–915. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-20-0948
MacParland SA, Liu JC, Ma XZ, Innes BT, Bartczak AM, Gage BK, Manuel J, Khuu N, Echeverri J, Linares I et al (2018) Single cell RNA sequencing of human liver reveals distinct intrahepatic macrophage populations. Nat Commun 9:4383. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06318-7
Makokha GN, Abe-Chayama H, Chowdhury S, Hayes CN, Tsuge M, Yoshima T, Ishida Y, Zhang Y, Uchida T, Tateno C et al (2019) Regulation of the hepatitis B virus replication and gene expression by the multi-functional protein TARDBP. Sci Rep 9:8462. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44934-5
Marasco LE, Kornblihtt AR (2022) The physiology of alternative splicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 24:242–254. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-022-00545-z
Marengo A, Rosso C, Bugianesi E (2016) Liver cancer: connections with obesity, fatty liver, and cirrhosis. Annu Rev Med 67:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-090514-013832
Martinez-Contreras R, Cloutier P, Shkreta L, Fisette JF, Revil T, Chabot B (2007) hnRNP proteins and splicing control. Adv Exp Med Biol 623:123–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-77374-2_8
Méndez-Blanco C, Fondevila F, García-Palomo A, González-Gallego J, Mauriz JL (2018) Sorafenib resistance in hepatocarcinoma: role of hypoxia-inducible factors. Exp Mol Med 50:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0159-1
Mo M, Ma X, Luo Y, Tan C, Liu B, Tang P, Liao Q, Liu S, Yu H, Huang D et al (2022) Liver-specific lncRNA FAM99A may be a tumor suppressor and promising prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 22:1098. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-10186-2
Narla G, Difeo A, Reeves HL, Schaid DJ, Hirshfeld J, Hod E, Katz A, Isaacs WB, Hebbring S, Komiya A et al (2005) A germline DNA polymorphism enhances alternative splicing of the KLF6 tumor suppressor gene and is associated with increased prostate cancer risk. Can Res 65:1213–1222. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4249
Nault JC, Martin Y, Caruso S, Hirsch TZ, Bayard Q, Calderaro J, Charpy C, Copie-Bergman C, Ziol M, Bioulac-Sage P et al (2019) Clinical impact of genomic diversity from early to advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30811
Ng CKY, Dazert E, Boldanova T, Coto-Llerena M, Nuciforo S, Ercan C, Suslov A, Meier MA, Bock T, Schmidt A et al (2022) Integrative proteogenomic characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma across etiologies and stages. Nat Commun 13:2436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29960-8
Nurk S, Koren S, Rhie A, Rautiainen M, Bzikadze AV, Mikheenko A, Vollger MR, Altemose N, Uralsky L, Gershman A et al (2022) The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 376:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abj6987
Omenn GS, Yocum AK, Menon R (2010) Alternative splice variants, a new class of protein cancer biomarker candidates: findings in pancreatic cancer and breast cancer with systems biology implications. Dis Markers 28:241–251. https://doi.org/10.3233/DMA-2010-0702
Paz S, Ritchie A, Mauer C, Caputi M (2021) The RNA binding protein SRSF1 is a master switch of gene expression and regulation in the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 57:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.10.008
Pihlajamaki J, Lerin C, Itkonen P, Boes T, Floss T, Schroeder J, Dearie F, Crunkhorn S, Burak F, Jimenez-Chillaron JC et al (2011) Expression of the splicing factor gene SFRS10 is reduced in human obesity and contributes to enhanced lipogenesis. Cell Metab 14:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.007
Qiao Y, Shi Q, Yuan X, Ding J, Li X, Shen M, Huang S, Chen Z, Wang L, Zhao Y et al (2022) RNA binding protein RALY activates the cholesterol synthesis pathway through an MTA1 splicing switch in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 538:215711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215711
Sas Z, Cendrowicz E, Weinhäuser I, Rygiel TP (2022) Tumor microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and opportunities for new treatment options. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073778
Savarese M, Jonson PH, Huovinen S, Paulin L, Auvinen P, Udd B, Hackman P (2018) The complexity of titin splicing pattern in human adult skeletal muscles. Skeletal Muscle 8:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13395-018-0156-z
Sen S, Jumaa H, Webster NJ (2013) Splicing factor SRSF3 is crucial for hepatocyte differentiation and metabolic function. Nat Commun 4:1336. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2342
Sen S, Langiewicz M, Jumaa H, Webster NJ (2015) Deletion of serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3 in hepatocytes predisposes to hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology 61:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27380
Shalek AK, Satija R, Adiconis X, Gertner RS, Gaublomme JT, Raychowdhury R, Schwartz S, Yosef N, Malboeuf C, Lu D et al (2013) Single-cell transcriptomics reveals bimodality in expression and splicing in immune cells. Nature 498:236–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12172
Shen Q, Nam SW (2018) SF3B4 as an early-stage diagnostic marker and driver of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMB Rep 51:57–58. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2018.51.2.021
Shen M, Zhang R, Jia W, Zhu Z, Zhao X, Zhao L, Huang G, Liu J (2021) Nuclear scaffold protein p54(nrb)/NONO facilitates the hypoxia-enhanced progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 40:4167–4183. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01848-9
Shen C, Jiang X, Li M, Luo Y (2023) Hepatitis virus and hepatocellular carcinoma: recent advances. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020533
Shilo A, Ben Hur V, Denichenko P, Stein I, Pikarsky E, Rauch J, Kolch W, Zender L, Karni R (2014) Splicing factor hnRNP A2 activates the Ras-MAPK-ERK pathway by controlling A-Raf splicing in hepatocellular carcinoma development. RNA 20:505–515. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.042259.113
Shin C, Manley JL (2002) The SR protein SRp38 represses splicing in M phase cells. Cell 111:407–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01038-3
Shin C, Feng Y, Manley JL (2004) Dephosphorylated SRp38 acts as a splicing repressor in response to heat shock. Nature 427:553–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02288
Shuai SM, Suzuki H, Diaz-Navarro A, Nadeu F, Kumar SA, Gutierrez-Fernandez A, Delgado J, Pinyol M, Lopez-Otin C, Puente XS et al (2019) The U1 spliceosomal RNA is recurrently mutated in multiple cancers. Nature 574:712–716. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1651-z
Singh B, Eyras E (2017) The role of alternative splicing in cancer. Transcription 8:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/21541264.2016.1268245
Snider NT, Altshuler PJ, Wan S, Welling TH, Cavalcoli J, Omary MB (2014) Alternative splicing of human NT5E in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma produces a negative regulator of ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73). Mol Biol Cell 25:4024–4033. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E14-06-1167
Spitali P, Aartsma-Rus A (2012) Splice modulating therapies for human disease. Cell 148:1085–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.014
Sun C (2020) The SF3b complex: splicing and beyond. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:3583–3595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03493-z
Sveen A, Kilpinen S, Ruusulehto A, Lothe RA, Skotheim RI (2016) Aberrant RNA splicing in cancer; expression changes and driver mutations of splicing factor genes. Oncogene 35:2413–2427. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.318
Tang Q, Rodriguez-Santiago S, Wang J, Pu J, Yuste A, Gupta V, Moldon A, Xu YZ, Query CC (2016) SF3B1/Hsh155 HEAT motif mutations affect interaction with the spliceosomal ATPase Prp5, resulting in altered branch site selectivity in pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev 30:2710–2723. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.291872.116
Thibault PA, Ganesan A, Kalyaanamoorthy S, Clarke JWE, Salapa HE, Levin MC (2021) hnRNP A/B proteins: an encyclopedic assessment of their roles in homeostasis and disease. Biology (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080712
Tian J, Wang Z, Mei S, Yang N, Yang Y, Ke J, Zhu Y, Gong Y, Zou D, Peng X et al (2019) CancerSplicingQTL: a database for genome-wide identification of splicing QTLs in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D909–D916. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky954
Tremblay MP, Armero VES, Allaire A, Boudreault S, Martenon-Brodeur C, Durand M, Lapointe E, Thibault P, Tremblay-Letourneau M, Perreault JP et al (2016) Global profiling of alternative RNA splicing events provides insights into molecular differences between various types of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Genom 17:683. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12864-016-3029-Z
Urtasun R, Elizalde M, Azkona M, Latasa MU, García-Irigoyen O, Uriarte I, Fernández-Barrena MG, Vicent S, Alonso MM, Muntané J et al (2016) Splicing regulator SLU7 preserves survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and other solid tumors via oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster expression. Oncogene 35:4719–4729. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.517
Wang Z, Burge CB (2008) Splicing regulation: from a parts list of regulatory elements to an integrated splicing code. RNA 14:802–813. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.876308
Wang BD, Lee NH (2018) Aberrant RNA splicing in cancer and drug resistance. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10110458
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP, Burge CB (2008) Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 456:470–476. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07509
Wang M, Zhang P, Shu Y, Yuan F, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Jiang M, Zhu Y, Hu L, Kong X et al (2014) Alternative splicing at GYNNGY 5’ splice sites: more noise, less regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 42:13969–13980. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1253
Wang TH, Hsueh C, Chen CC, Li WS, Yeh CT, Lian JH, Chang JL, Chen CY (2018) Melatonin inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through MicroRNA Let7i-3p mediated RAF1 reduction. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092687
Wang H, Lekbaby B, Fares N, Augustin J, Attout T, Schnuriger A, Cassard AM, Panasyuk G, Perlemuter G, Bieche I et al (2019a) Alteration of splicing factors’ expression during liver disease progression: impact on hepatocellular carcinoma outcome. Hep Intl 13:454–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-019-09950-7
Wang H, Zhang CZ, Lu SX, Zhang MF, Liu LL, Luo RZ, Yang X, Wang CH, Chen SL, He YF et al (2019b) A coiled-coil domain containing 50 splice variant is modulated by serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3 and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice by the ras signaling pathway. Hepatology 69:179–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30147
Wang X, Guo J, Che X, Jia R (2019c) PCBP1 inhibits the expression of oncogenic STAT3 isoform by targeting alternative splicing of STAT3 exon 23. Int J Biol Sci 15:1177–1186. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.33103
Waxman S, Wurmbach E (2007) De-regulation of common housekeeping genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Genom 8:243. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-8-243
Webster NJG (2017) Alternative RNA splicing in the pathogenesis of liver disease. Front Endocrinol 8:133. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00133
Witten JT, Ule J (2011) Understanding splicing regulation through RNA splicing maps. Trends Genet TIG 27:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2010.12.001
Wu P, Zhou D, Wang Y, Lin W, Sun A, Wei H, Fang Y, Cong X, Jiang Y (2019a) Identification and validation of alternative splicing isoforms as novel biomarker candidates in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 41:1929–1937. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6947
Wu HY, Peng ZG, He RQ, Luo B, Ma J, Hu XH, Dang YW, Chen G, Pan SL (2019b) Prognostic index of aberrant mRNA splicing profiling acts as a predictive indicator for hepatocellular carcinoma based on TCGA SpliceSeq data. Int J Oncol 55:425–438. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4834
Wu P, Zhang M, Webster NJG (2021) Alternative RNA splicing in fatty liver disease. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 12:613213. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.613213
Xing S, Li Z, Ma W, He X, Shen S, Wei H, Li ST, Shu Y, Sun L, Zhong X et al (2019) DIS3L2 promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via hnRNP U-mediated alternative splicing. Can Res 79:4923–4936. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0376
Yamazaki D, Hashizume O, Taniguchi S, Funato Y, Miki H (2021) Role of adenomatous polyposis coli in proliferation and differentiation of colon epithelial cells in organoid culture. Sci Rep 11:3980. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83590-6
Yang F, Wang XY, Zhang ZM, Pu J, Fan YJ, Zhou JH, Query CC, Xu YZ (2013) Splicing proofreading at 5’ splice sites by ATPase Prp28p. Nucleic Acids Res 41:4660–4670. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt149
Yang H, Zhu R, Zhao X, Liu L, Zhou Z, Zhao L, Liang B, Ma W, Zhao J, Liu J et al (2019) Sirtuin-mediated deacetylation of hnRNP A1 suppresses glycolysis and growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 38:4915–4931. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0764-z
Yea S, Narla G, Zhao X, Garg R, Tal-Kremer S, Hod E, Villanueva A, Loke J, Tarocchi M, Akita K et al (2008) Ras promotes growth by alternative splicing-mediated inactivation of the KLF6 tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 134:1521–1531. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.015
Yeo G, Holste D, Kreiman G, Burge CB (2004) Variation in alternative splicing across human tissues. Genome Biol 5:R74. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r74
Yu L, Kim J, Jiang L, Feng B, Ying Y, Ji KY, Tang Q, Chen W, Mai T, Dou W et al (2020) MTR4 drives liver tumorigenesis by promoting cancer metabolic switch through alternative splicing. Nat Commun 11:708. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14437-3
Yuan P, Li J, Zhou F, Huang Q, Zhang J, Guo X, Lyu Z, Zhang H, Xing J (2017) NPAS2 promotes cell survival of hepatocellular carcinoma by transactivating CDC25A. Cell Death Dis 8:e2704. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.131
Zhan YT, Li L, Zeng TT, Zhou NN, Guan XY, Li Y (2020) SNRPB-mediated RNA splicing drives tumor cell proliferation and stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 13:537–554. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202164
Zhang L, Liu X, Zhang X, Chen R (2016) Identification of important long non-coding RNAs and highly recurrent aberrant alternative splicing events in hepatocellular carcinoma through integrative analysis of multiple RNA-Seq datasets. Mol Genet Genom : MGG 291:1035–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1163-y
Zhang J, Zhang Q, Lou Y, Fu Q, Chen Q, Wei T, Yang J, Tang J, Wang J, Chen Y et al (2018) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/interleukin-1β signaling enhances hepatoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition through macrophages in a hypoxic-inflammatory microenvironment. Hepatology 67:1872–1889. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29681
Zhang D, Duan Y, Wang Z, Lin J (2019) Systematic profiling of a novel prognostic alternative splicing signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 42:2450–2472. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7342
Zhang C, Shen L, Yuan W, Liu Y, Guo R, Luo Y, Zhan Z, Xie Z, Wu G, Wu W et al (2020) Loss of SRSF2 triggers hepatic progenitor cell activation and tumor development in mice. Commun Biol 3:210. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-0893-5
Zhang B, Wang HY, Zhao DX, Wang DX, Zeng Q, Xi JF, Nan X, He LJ, Zhou JN, Pei XT et al (2021) The splicing regulatory factor hnRNPU is a novel transcriptional target of c-Myc in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett 595:68–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13943
Zhang YZ, Zeb A, Cheng LF (2022) Exploring the molecular mechanism of hepatitis virus inducing hepatocellular carcinoma by microarray data and immune infiltrates analysis. Front Immunol 13:1032819. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1032819
Zhao YJ, Wu LY, Pang JS, Liao W, Chen YJ, He Y, Yang H (2021) Integrated multi-omics analysis of the clinical relevance and potential regulatory mechanisms of splicing factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioengineered 12:3978–3992. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1948949
Zhou G, Wang J, Zhao M, Xie TX, Tanaka N, Sano D, Patel AA, Ward AM, Sandulache VC, Jasser SA et al (2014) Gain-of-function mutant p53 promotes cell growth and cancer cell metabolism via inhibition of AMPK activation. Mol Cell 54:960–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.04.024
Zhu GQ, Zhou YJ, Qiu LX, Wang B, Yang Y, Liao WT, Luo YH, Shi YH, Zhou J, Fan J et al (2019) Prognostic alternative mRNA splicing signature in hepatocellular carcinoma: a study based on large-scale sequencing data. Carcinogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgz073
Zhu GQ, Wang Y, Wang B, Liu WR, Dong SS, Chen EB, Cai JL, Wan JL, Du JX, Song LN et al (2022) Targeting HNRNPM inhibits cancer stemness and enhances antitumor immunity in wnt-activated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:1413–1447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.02.006
Zhuo H, Miao S, Jin Z, Zhu D, Xu Z, Sun D, Ji J, Tan Z (2022) Metformin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating alternative splicing of LGR4. J Oncol 2022:1774095. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1774095
Acknowledgements
We thank Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) for expert assistance in the pattern drawing. The authors thanks Faustina Halm-Lai (University of Cape Coast) for proofreading the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82071770); Research Level Improvement Project of Anhui Medical University (2021xkjT001); Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2008085QH371); Scientific Research of BSKY in Anhui Medical University (XJ201601); and Research and Practical Innovation Projects of AHMU (YJS20230039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WS: designed the theme and direction of the manuscript. MS, YW, YZ, WL, XW, TK, PL, SW, and WS: drafted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Decoding the role of aberrant RNA alternative splicing in hepatocellular carcinoma: a comprehensive review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 17691–17708 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05474-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05474-8