Abstract
Background
Kidney cancer (KC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in adults which particularly affects the survival of elderly patients. We aimed to construct a nomogram to predict overall survival (OS) in elderly KC patients after surgery.
Methods
Information on all primary KC patients aged more than 65 years and treated with surgery between 2010 and 2015 was downloaded from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis was used to identify the independent prognostic factors. Consistency index (C-index), receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), the area under curve (AUC), and calibration curve were used to assess the accuracy and validity of the nomogram. Comparison of the clinical benefits of nomogram and the TNM staging system is done by decision curve analysis (DCA) and time-dependent ROC.
Results
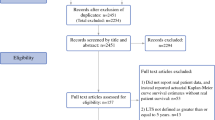
A total of 15,989 elderly KC patients undergoing surgery were included. All patients were randomly divided into training set (N = 11,193, 70%) and validation set (N = 4796, 30%). The nomogram produced C-indexes of 0.771 (95% CI 0.751–0.791) and 0.792 (95% CI 0.763–0.821) in the training and validation sets, respectively, indicating that the nomogram has excellent predictive accuracy. The ROC, AUC, and calibration curves also showed the same excellent results. In addition, DCA and time-dependent ROC showed that the nomogram outperformed the TNM staging system with better net clinical benefits and predictive efficacy.
Conclusions
Independent influencing factors for postoperative OS in elderly KC patients were sex, age, histological type, tumor size, grade, surgery, marriage, radiotherapy, and T-, N-, and M-stage. The web-based nomogram and risk stratification system could assist surgeons and patients in clinical decision-making.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data for this study were obtained from publicly available databases (https://seer.cancer.gov/). The datasets analyzed or generated by this study are available from the corresponding author with appropriate reasons.
References
Aizer AA, Chen M-H, McCarthy EP, Mendu ML, Koo S, Wilhite TJ et al (2013) Marital status and survival in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 31(31):3869–3876. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2013.49.6489
Altekruse SF, Dickie L, Wu X-C, Hsieh M-C, Wu M, Lee R, Delacroix S Jr (2014) Clinical and prognostic factors for renal parenchymal, pelvis, and ureter cancers in SEER registries: collaborative stage data collection system, version 2. Cancer 120(23):3826–3835. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29051
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP (2015) Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol 16(4):E173–E180. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71116-7
Beckendorf V, Bladou F, Farsi F, Kaemmerlen P, Negrier S, Philip T, Terrier-Lacombe MJ (2000) Standards, options, and recommendations for radiotherapy of kidney cancer. [Standards, Options et Recommandations pour la radiotherapie du cancer du rein]. Cancer Radiotherapie 4(3):223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1278-3218(00)89098-8
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL (2004) X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res 10(21):7252–7259. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-04-0713
Chen DYT, Uzzo RG (2009) Optimal management of localized renal cell carcinoma: surgery, ablation, or active surveillance. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 7(6):635–643. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2009.0044
Choi YD, Kim KS, Ryu S, Park Y, Cho NH, Rha SH et al (2007) Claudin-7 is highly expressed in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and renal oncocytoma. J Korean Med Sci 22(2):305–310. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.305
Chow W-H, Dong LM, Devesa SS (2010) Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nat Rev Urol 7(5):245–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2010.46
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ (2005) Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 353(23):2477–2490. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra043172
Hakky TS, Baumgarten AS, Allen B, Lin H-Y, Ercole CE, Sexton WJ, Spiess PE (2014) Zonal NePhRO scoring system: a superior renal tumor complexity classification model. Clin Genitourin Cancer 12(1):E13–E18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2013.07.009
Hollingsworth JM, Miller DC, Daignault S, Hollenbeck BK (2007) Five-year survival after surgical treatment for kidney cancer—a population-based competing risk analysis. Cancer 109(9):1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22600
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M et al (2017) Renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.9
Hu Y, Qi Q, Zheng Y, Wang H, Zhou J, Hao Z et al (2022) Nomogram for predicting the overall survival of patients with early-onset prostate cancer: a population-based retrospective study. Cancer Med 11(17):3260–3271. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.4694
Huang WC, Elkin EB, Levey AS, Jang TL, Russo P (2009) Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy in patients with small renal tumors-is there a difference in mortality and cardiovascular outcomes? J Urol 181(1):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.09.017
Huang X, Shu C, Chen L, Yao B (2018) Impact of sex, body mass index and initial pathologic diagnosis age on the incidence and prognosis of different types of cancer. Oncol Rep 40(3):1359–1369. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6529
Kanesvaran R, Le Saux O, Motzer R, Choueiri TK, Scotte F, Bellmunt J, Launay-Vacher V (2018) Elderly patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: position paper from the International Society of Geriatric Oncology. Lancet Oncol 19(6):E317–E326. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(18)30125-6
Kates M, Badalato G, Pitman M, McKiernan J (2011) Persistent overuse of radical nephrectomy in the elderly. Urology 78(3):555–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2011.02.066
Kim HL, Han KR, Zisman A, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS (2004) Cachexia-like symptoms predict a worse prognosis in localized T1 renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 171(5):1810–1813. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000121440.82581.d3
Klatte T, Ficarra V, Gratzke C, Kaouk J, Kutikov A, Macchi V et al (2015) A literature review of renal surgical anatomy and surgical strategies for partial nephrectomy. Eur Urol 68(6):980–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.04.010
Lee K-H, Kim B-C, Jeong S-H, Jeong CW, Ku JH, Kwak C, Kim HH (2020) Histone demethylase LSD1 regulates kidney cancer progression by modulating androgen receptor activity. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176089
Levi F, Ferlay J, Galeone C, Lucchini F, Negri E, Boyle P, La Vecchia C (2008) The changing pattern of kidney cancer incidence and mortality in Europe. BJU Int 101(8):949–958. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07451.x
Li Y, Gong Y, Ning X, Peng D, Liu L, He S et al (2018) Downregulation of CLDN7 due to promoter hypermethylation is associated with human clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression and poor prognosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0924-y
Li J, Yang S, Li Y, Li C, Xia Y, Zhu S, Xia J (2022) The C-reactive protein to albumin ratio is an independent prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization: a large cohort study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 45(9):1295–1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-022-03208-w
Liu X, Yue S, Huang H, Duan M, Zhao B, Liu J, Xiang T (2021) Risk stratification model for predicting the overall survival of elderly triple-negative breast cancer patients: a population-based study. Front Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.705515
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bensalan K, Dabestani S, Montes SF-P et al (2019) European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2019 update. Eur Urol 75(5):799–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.011
Makhov P, Joshi S, Ghatalia P, Kutikov A, Uzzo RG, Kolenko VM (2018) Resistance to systemic therapies in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: mechanisms and management strategies. Mol Cancer Ther 17(7):1355–1364. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-17-1299
Mazzone E, Nazzani S, Preisser F, Tian Z, Marchioni M, Bandini M et al (2018) Partial nephrectomy seems to confer a survival benefit relative to radical nephrectomy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol 56:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2018.08.006
Merrill RM, Johnson E (2017) Benefits of marriage on relative and conditional relative cancer survival differ between males and females in the USA. J Cancer Surviv 11(5):578–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-017-0627-y
Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N, Alva A, Baine M, Beckermann K et al (2022) Kidney cancer, version 3.2022. J Natl Comprehensive Cancer Network 20(1):71–89. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2022.0001
Nakagawa S, Cuthill IC (2007) Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists. Biol Rev 82(4):591–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2007.00027.x
Nazzani S, Mazzone E, Preisser F, Tian Z, Mistretta FA, Shariat SF et al (2019) Rates of lymph node invasion and their impact on cancer specific mortality in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Ejso 45(7):1238–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2018.12.004
Payedimarri AB, Concina D, Portinale L, Canonico M, Seys D, Vanhaecht K, Panella M (2021) Prediction models for public health containment measures on COVID-19 using artificial intelligence and machine learning: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094499
Peyton CC, Rothberg MB, Jiang V, Heavner MG, Hemal AK (2017) Comparative analysis of renal functional outcomes and overall survival of elderly vs nonelderly patients undergoing radical nephrectomy. J Endourol 31(2):198–203. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2016.0525
Quivy A, Daste A, Harbaoui A, Duc S, Bernhard J-C, Gross-Goupil M, Ravaud A (2013) Optimal management of renal cell carcinoma in the elderly: a review. Clin Interv Aging 8:433–442. https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.S30765
Ristau BT, Handorf EA, Cahn DB, Kutikov A, Uzzo RG, Smaldone MC (2018) Partial Nephrectomy is not associated with an overall survival advantage over radical nephrectomy in elderly patients with stage Ib-II renal masses: an analysis of the national cancer data base. Cancer 124(19):3839–3848. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31582
Rudnicka E, Napierala P, Podfigurna A, Meczekalski B, Smolarczyk R, Grymowicz M (2020) The World Health Organization (WHO) approach to healthy ageing. Maturitas 139:6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.05.018
Schmitges J, Trinh Q-D, Sun M, Hansen J, Bianchi M, Jeldres C et al (2012) Higher perioperative morbidity and in-hospital mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing nephrectomy for non-metastatic kidney cancer: a population-based analysis. BJU Int 110(6B):E183–E190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.10936.x
Schober P, Vetter TR (2019) Chi-square tests in medical research. Anesth Analg 129(5):1193–1193. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000004410
Shum CF, Bahler CD, Sundaram CP (2017) Matched comparison between partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy for T2 N0 M0 tumors, a study based on the national cancer database. J Endourol 31(8):800–805. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2017.0190
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA-A Cancer J Clin 71(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Tahbaz R, Schmid M, Merseburger AS (2018) Prevention of kidney cancer incidence and recurrence: lifestyle, medication and nutrition. Curr Opin Urol 28(1):62–79. https://doi.org/10.1097/mou.0000000000000454
Tan H-J, Chamie K, Daskivich TJ, Litwin MS, Hu JC (2016) Patient function, long-term survival, and use of surgery in patients with kidney cancer. Cancer 122(24):3776–3784. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30275
Thoenes W, Storkel S, Rumpelt HJ (1986) Histopathology and classification of renal cell tumors (adenomas, oncocytomas and carcinomas). The basic cytological and histopathological elements and their use for diagnostics. Pathol Res Pract 181(2):125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0344-0338(86)80001-2
Thompson RH, Boorjian SA, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Kwon ED, Cheville JC, Blute ML (2008) Radical nephrectomy for pT1a renal masses may be associated with decreased overall survival compared with partial nephrectomy. J Urol 179(2):468–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.09.077
Tian S, Sun S, Mao W, Zhang L, Zhang G, Xu B, Chen M (2021) Development and validation of prognostic nomogram for young patients with kidney cancer. Int J General Med 14:5091–5103. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.S331627
Tripepi G, Jager KJ, Dekker FW, Zoccali C (2010) Selection bias and information bias in clinical research. Nephron Clin Pract 115(2):C94–C99. https://doi.org/10.1159/000312871
Volpe A, Kachura JR, Geddie WR, Evans AJ, Gharajeh A, Saravanan A, Jewett MAS (2007) Techniques, safety and accuracy of sampling of renal tumors by fine needle aspiration and core biopsy. J Urol 178(2):379–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.131
Wang W, Liu J, Liu L (2021) Development and validation of a prognostic model for predicting overall survival in patients with bladder cancer: a SEER-based study. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.692728
Yan F, Wang Q, Xia M, Ru Y, Hu W, Yan G et al (2021) MIIP inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma proliferation and angiogenesis via negative modulation of the HIF-2 alpha-CYR61 axis. Cancer Biol Med. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0296
Yang J, Li Y, Liu Q, Li L, Feng A, Wang T et al (2020) Brief introduction of medical database and data mining technology in big data era. J Evid Based Med 13(1):57–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/jebm.12373
Yang Z, Zi Q, Xu K, Wang C, Chi Q (2021) Development of a macrophages-related 4-gene signature and nomogram for the overall survival prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma based on WGCNA and LASSO algorithm. Int Immunopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107238
Zhanghuang C, Wang J, Yao Z, Li L, Xie Y, Tang H et al (2022) Development and validation of a nomogram to predict cancer-specific survival in elderly patients with papillary renal cell carcinoma. Front Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.874427
Zhou Z-R, Wang W-W, Li Y, Jin K-R, Wang X-Y, Wang Z-W et al (2019) In-depth mining of clinical data: the construction of clinical prediction model with R. Ann Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.08.63
Zhou Y, Zhang R, Ding Y, Wang Z, Yang C, Tao S, Liang C (2020) Prognostic nomograms and Aggtrmmns scoring system for predicting overall survival and cancer-specific survival of patients with kidney cancer. Cancer Med 9(8):2710–2722. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2916
Acknowledgements
We thank each of the staff members who contributed to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DZ and LJ contributed to the conception and design of the study; LJ, CW, YT and JJ performed the experiments, collected and analyzed data; LJ wrote the manuscript; all authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential commercial or financial conflicts of interest regarding this study.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Each author agreed to publish the paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Wang, C., Tong, Y. et al. Web-based nomogram and risk stratification system constructed for predicting the overall survival of older adults with primary kidney cancer after surgical resection. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 11873–11889 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05072-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05072-8