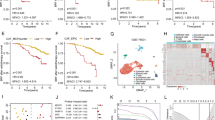
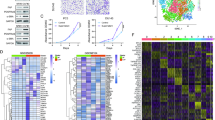
Abstract
Background
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are an essential component of the tumor immune microenvironment that are involved in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. We aim to investigate the characteristics of CAFs in prostate cancer and develop a biochemical recurrence (BCR)-related CAF signature for predicting the prognosis of PCa patients.
Methods
The bulk RNA-seq and relevant clinical information were obtained from the TCGA and GEO databases, respectively. The infiltration scores of CAFs in prostate cancer patients were calculated using the MCP counter and EPIC algorithms. The single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was downloaded from the GEO database. Subsequently, univariate Cox regression analysis was employed to identify prognostic genes associated with CAFs. We identified two subtypes (C1 and C2) of prostate cancer that were associated with CAFs via non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) clustering. In addition, the BCR-related CAF signatures were constructed using Lasso regression analysis. Finally, a nomogram model was established based on the risk score and clinical characteristics of the patients.
Results
Initially, we found that patients with high CAF infiltration scores had shorter biochemical recurrence-free survival (BCRFS) times. Subsequently, CAFs in four pairs of tumors and paracancerous tissues were identified. We discovered 253 significantly differentially expressed genes, of which 13 had prognostic significance. Using NMF clustering, we divided PCa patients into C1 and C2 subgroups, with the C1 subgroup having a worse prognosis and substantially enriched cell cycle, homologous recombination, and mismatch repair pathways. Furthermore, a BCR-related CAFs signature was established. Multivariate COX regression analysis confirmed that the BCR-related CAFs signature was an independent prognostic factor for BCR in PCa. In addition, the nomogram was based on the clinical characteristics and risk scores of the patient and demonstrated high accuracy and reliability for predicting BCR. Lastly, our findings indicate that the risk score may be a useful tool for predicting PCa patients’ sensitivity to immunotherapy and drug treatment.
Conclusion
NMF clustering based on CAF-related genes revealed distinct TME immune characteristics between groups. The BCR-related CAF signature accurately predicted prognosis and immunotherapy response in prostate cancer patients, offering a promising new approach to cancer treatment.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All the data used to support the conclusions of this study are included in the article. Please contact the corresponding author for data requests.
References
Anderson AC (2012) Tim-3, a negative regulator of anti-tumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 24(2):213–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2011.12.005
Barrett RL, Pure E (2020) Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their influence on tumor immunity and immunotherapy. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.57243
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L, Buttard B, Elarouci N, Petitprez F et al (2016) Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol 17(1):218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1070-5
Bhargava HK, Leo P, Elliott R, Janowczyk A, Whitney J, Gupta S et al (2020) Computationally derived image signature of stromal morphology is prognostic of prostate cancer recurrence following prostatectomy in African American Patients. Clin Cancer Res 26(8):1915–1923. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2659
Butler A, Hoffman P, Smibert P, Papalexi E, Satija R (2018) Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat Biotechnol 36(5):411–420. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4096
Calcinotto A, Spataro C, Zagato E, Di Mitri D, Gil V, Crespo M et al (2018) IL-23 secreted by myeloid cells drives castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 559(7714):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0266-0
Cao C, Xue C (2021) More than just cleaning: ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis in fungal pathogenesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:774613. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.774613
Chen R, Ganesan A, Okoye I, Arutyunova E, Elahi S, Lemieux MJ et al (2020) Targeting B7–1 in immunotherapy. Med Res Rev 40(2):654–682. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21632
Chen Y, McAndrews KM, Kalluri R (2021) Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 18(12):792–804. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-021-00546-5
Gaujoux R, Seoighe C (2010) A flexible R package for nonnegative matrix factorization. BMC Bioinform 11:367. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-367
Hanzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J (2013) GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform 14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-7
Hayashi N, Osaka K, Muraoka K, Hasumi H, Makiyama K, Kondo K et al (2020) Outcomes of treatment for localized prostate cancer in a single institution: comparison of radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy by propensity score matching analysis. World J Urol 38(10):2477–2484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-03056-3
Heidegger I, Fotakis G, Offermann A, Goveia J, Daum S, Salcher S et al (2022) Comprehensive characterization of the prostate tumor microenvironment identifies CXCR4/CXCL12 crosstalk as a novel antiangiogenic therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer 21(1):132. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-022-01597-7
Horn LA, Chariou PL, Gameiro SR, Qin H, Iida M, Fousek K et al (2022) Remodeling the tumor microenvironment via blockade of LAIR-1 and TGF-beta signaling enables PD-L1-mediated tumor eradication. J Clin Investig. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI155148
Hu C, Xia R, Zhang X, Li T, Ye Y, Li G et al (2022) circFARP1 enables cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via the LIF/STAT3 axis. Mol Cancer 21(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-022-01501-3
Hugo W, Zaretsky JM, Sun L, Song C, Moreno BH, Hu-Lieskovan S et al (2016) Genomic and transcriptomic features of response to anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cell 165(1):35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.065
Huo H, Shen S, He D, Liu B, Yang F (2023) Head-to-head comparison of (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT and (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI in the detection of biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer: summary of head-to-head comparison studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 26(1):16–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00581-y
Hurley PJ, Sundi D, Shinder B, Simons BW, Hughes RM, Miller RM et al (2016) Germline variants in asporin vary by race, modulate the tumor microenvironment, and are differentially associated with metastatic prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 22(2):448–458. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0256
Ishii K, Sasaki T, Iguchi K, Kajiwara S, Kato M, Kanda H et al (2018) Interleukin-6 induces VEGF secretion from prostate cancer cells in a manner independent of androgen receptor activation. Prostate 78(11):849–856. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23643
Jain S, Lyons CA, Walker SM, McQuaid S, Hynes SO, Mitchell DM et al (2018) Validation of a metastatic assay using biopsies to improve risk stratification in patients with prostate cancer treated with radical radiation therapy. Ann Oncol 29(1):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx637
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D, Fu J, Sahu A, Hu X et al (2018) Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 24(10):1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1
Jurmeister S, Ramos-Montoya A, Sandi C, Pertega-Gomes N, Wadhwa K, Lamb AD et al (2018) Identification of potential therapeutic targets in prostate cancer through a cross-species approach. EMBO Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201708274
Keerthivasan S, Senbabaoglu Y, Martinez-Martin N, Husain B, Verschueren E, Wong A et al (2021) Homeostatic functions of monocytes and interstitial lung macrophages are regulated via collagen domain-binding receptor LAIR1. Immunity 54(7):1511–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.012. (e1518)
Lavie D, Ben-Shmuel A, Erez N, Scherz-Shouval R (2022) Cancer-associated fibroblasts in the single-cell era. Nat Cancer 3(7):793–807. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-022-00411-z
Liu M, Liao L, Gao Y, Yin Y, Wei X, Xu Q et al (2022a) BCAM deficiency may contribute to preeclampsia by suppressing the PIK3R6/p-STAT3 signaling. Hypertension 79(12):2830–2842. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.20085
Liu S, He B, Li H (2022b) Bisphenol S promotes the progression of prostate cancer by regulating the expression of COL1A1 and COL1A2. Toxicology 472:153178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2022.153178
Maeser D, Gruener RF, Huang RS (2021) oncoPredict: an R package for predicting in vivo or cancer patient drug response and biomarkers from cell line screening data. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbab260
Magnusson LU, Hagberg Thulin M, Plas P, Olsson A, Damber JE, Welen K (2016) Tasquinimod inhibits prostate cancer growth in bone through alterations in the bone microenvironment. Prostate 76(4):383–393. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23133
Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, Liang C, Hua J, Liu J et al (2021) Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer 20(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01428-1
Maris P, Blomme A, Palacios AP, Costanza B, Bellahcene A, Bianchi E et al (2015) Asporin is a fibroblast-derived TGF-beta1 inhibitor and a tumor suppressor associated with good prognosis in breast cancer. PLoS Med 12(9):e1001871. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001871
Owen JS, Clayton A, Pearson HB (2022) Cancer-associated fibroblast heterogeneity, activation and function: implications for prostate cancer. Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010067
Peng DH, Rodriguez BL, Diao L, Chen L, Wang J, Byers LA et al (2020) Collagen promotes anti-PD-1/PD-L1 resistance in cancer through LAIR1-dependent CD8(+) T cell exhaustion. Nat Commun 11(1):4520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18298-8
Piao Y, Jin X (2017) Analysis of Tim-3 as a therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Tumour Biol 39(7):1010428317716628. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317716628
Qin X, Lu M, Li G, Zhou Y, Liu Z (2021) Downregulation of tumor-derived exosomal miR-34c induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to promote cholangiocarcinoma progress. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):373. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01726-6
Racle J, Gfeller D (2020) EPIC: a tool to estimate the proportions of different cell types from bulk gene expression data. Methods Mol Biol 2120:233–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0327-7_17
Rochette A, Boufaied N, Scarlata E, Hamel L, Brimo F, Whitaker HC et al (2017) Asporin is a stromally expressed marker associated with prostate cancer progression. Br J Cancer 116(6):775–784. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.15
Romanel A, Garritano S, Stringa B, Blattner M, Dalfovo D, Chakravarty D et al (2017) Inherited determinants of early recurrent somatic mutations in prostate cancer. Nat Commun 8(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00046-0
Ross-Adams H, Lamb AD, Dunning MJ, Halim S, Lindberg J, Massie CM et al (2015) Integration of copy number and transcriptomics provides risk stratification in prostate cancer: a discovery and validation cohort study. EBioMedicine 2(9):1133–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.07.017
Sawicki LM, Kirchner J, Buddensieck C, Antke C, Ullrich T, Schimmoller L et al (2019) Prospective comparison of whole-body MRI and (68)Ga-PSMA PET/CT for the detection of biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46(7):1542–1550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04308-5
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Spratt DE, Dai DLY, Den RB, Troncoso P, Yousefi K, Ross AE et al (2018) Performance of a prostate cancer genomic classifier in predicting metastasis in men with prostate-specific antigen persistence postprostatectomy. Eur Urol 74(1):107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.11.024
Tibshirani R (1997) The lasso method for variable selection in the Cox model. Stat Med 16(4):385–395. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19970228)16:4%3c385::aid-sim380%3e3.0.co;2-3
Turley SJ, Cremasco V, Astarita JL (2015) Immunological hallmarks of stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol 15(11):669–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3902
Van Allen EM, Miao D, Schilling B, Shukla SA, Blank C, Zimmer L et al (2015) Genomic correlates of response to CTLA-4 blockade in metastatic melanoma. Science 350(6257):207–211. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad0095
Van den Broeck T, van den Bergh RCN, Arfi N, Gross T, Moris L, Briers E et al (2019) Prognostic value of biochemical recurrence following treatment with curative intent for prostate cancer: a systematic review. Eur Urol 75(6):967–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.10.011
Wong HY, Sheng Q, Hesterberg AB, Croessmann S, Rios BL, Giri K et al (2022) Single cell analysis of cribriform prostate cancer reveals cell intrinsic and tumor microenvironmental pathways of aggressive disease. Nat Commun 13(1):6036. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33780-1
Yamauchi N, Kanke Y, Saito K, Okayama H, Yamada S, Nakajima S et al (2021) Stromal expression of cancer-associated fibroblast-related molecules, versican and lumican, is strongly associated with worse relapse-free and overall survival times in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett 21(6):445. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2021.12706
Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martinez E, Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W et al (2013) Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun 4:2612. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3612
Yu L, Shen N, Shi Y, Shi X, Fu X, Li S et al (2022) Characterization of cancer-related fibroblasts (CAF) in hepatocellular carcinoma and construction of CAF-based risk signature based on single-cell RNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq data. Front Immunol 13:1009789. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1009789
Zhang Y, Zhao J, Ding M, Su Y, Cui D, Jiang C et al (2020a) Loss of exosomal miR-146a-5p from cancer-associated fibroblasts after androgen deprivation therapy contributes to prostate cancer metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):282. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01761-1
Zhang Z, Bai M, Barbosa GO, Chen A, Wei Y, Luo S et al (2020b) Broadly conserved roles of TMEM131 family proteins in intracellular collagen assembly and secretory cargo trafficking. Sci Adv 6(7):eaay7667. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aay7667
Zhang J, Zhang N, Fu X, Wang W, Liu H, McKay MJ et al (2022) Bioinformatic analysis of cancer-associated fibroblast related gene signature as a predictive model in clinical outcomes and immune characteristics of gastric cancer. Ann Transl Med 10(12):698. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-22-2810
Zhao Z, Li W, Zhu L, Xu B, Jiang Y, Ma N et al (2022) Construction and verification of a fibroblast-related prognostic signature model for colon cancer. Front Genet 13:908957. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.908957
Zheng X, Wang P, Li L, Yu J, Yu C, Xu L et al (2021) Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote vascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulating decorin-integrin beta1 signaling. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:678670. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.678670
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 81870516).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL, ZZ, and ZX designed and completed original manuscript writing; XF and YZ implemented data analysis and literature collection; YZ and XS reviewed the manuscript; YR supervised and funded this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Our study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Shanghai General Hospital. Moreover, all patients signed an informed consent form.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
: Prognosis and expression distribution of 10 BCR-related CAF signature genes. (A) K-M curves for evaluating ASPN, MT1X, ALDH1A1, HOPX, ANGPT1, FXYD6, CCL2, BCAM, GADD45B, and COL1A2 in the TCGA-PRAD cohort. (B) UMAP displayed the distribution of 10 genes in scRNA-seq from prostate cancer patients. (PNG 812 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Zhou, Z., Xie, Z. et al. Identification and validation of cancer-associated fibroblast-related subtypes and the prognosis model of biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer based on single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 11379–11395 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05011-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05011-7