Abstract
Purpose
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertions (ex20ins) are associated with poor prognosis and resistance to traditional therapies in patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We aimed to elucidate the characteristics and treatment patterns to improve outcomes among this population in Taiwan.
Methods
Patients with advanced or recurrent NSCLC harboring EGFR ex20ins from 2011 to 2021 were reviewed. The treatment groups were classified as platinum-based chemotherapy (PtC), EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), and others. The response to therapy, objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and factors associated with survival were analyzed.
Results
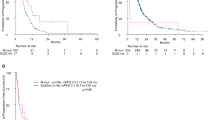
Among the 71 patients, most were never-smoking males with stage IVB adenocarcinoma. The most common first-line (1L) regimen was PtC, followed by TKI. The most common second-line (2L) regimen was TKI. The median PFS of 1L treatment was 5.03 months, and the median OS was 18.43 months. Compared with that of TKI, 1L PtC use was associated with a higher ORR (26.3% vs. 9.1%) and DCR (60.5% vs. 18.2%) and a longer PFS (5.37 vs. 3.13 months, p = 0.044). PFS was also significantly longer in the 2L PtC group than in the 2L TKI group (4.73 vs. 2.25 months, p = 0.047). No patients receiving an immune checkpoint inhibitor–based regimen exhibited a therapeutic response.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the heterogeneous clinical characteristics and treatment pattern of NSCLC patients with EGFR ex20ins, underscoring the need for more effective therapies for this distinct molecular subtype.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arcila ME, Nafa K, Chaft JE, Rekhtman N, Lau C, Reva BA, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Ladanyi M (2013) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol Cancer Ther 12(2):220–229. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-12-0620
Bazhenova L, Minchom A, Viteri S, Bauml JM, Ou SI, Gadgeel SM, Trigo JM, Backenroth D, Li T, Londhe A, Mahadevia P, Girard N (2021) Comparative clinical outcomes for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and common EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 162:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.10.020
Beau-Faller M, Prim N, Ruppert AM, Nanni-Metéllus I, Lacave R, Lacroix L, Escande F, Lizard S, Pretet JL, Rouquette I, de Crémoux P, Solassol J, de Fraipont F, Bièche I, Cayre A, Favre-Guillevin E, Tomasini P, Wislez M, Besse B, Cadranel J (2014) Rare EGFR exon 18 and exon 20 mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer on 10 117 patients: a multicentre observational study by the French ERMETIC-IFCT network. Ann Oncol 25(1):126–131. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt418
Byeon S, Kim Y, Lim SW, Cho JH, Park S, Lee J, Sun JM, Choi YL, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Park K, Ahn MJ (2019) Clinical outcomes of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Korea. Cancer Res Treat 51(2):623–631. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.151
Cai Y, Wang X, Guo Y, Sun C, Xu Y, Qiu S, Ma K (2019) Successful treatment of a lung adenocarcinoma patient with a novel EGFR exon 20-ins mutation with afatinib: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(1):e13890. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000013890
Chan RT (2018) Afatinib for an EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation: A case report of progressive stage IV metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with 54 months’ survival. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 14(Suppl 1):7–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.12853
Chen D, Song Z, Cheng G (2016) Clinical efficacy of first-generation EGFR-TKIs in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 mutations. Onco Targets Ther 9:4181–4186. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S108242
Choudhury NJ, Schoenfeld AJ, Flynn J, Falcon CJ, Rizvi H, Rudin CM, Kris MG, Arcila ME, Heller G, Yu HA, Ladanyi M, Riely GJ (2021) Response to standard therapies and comprehensive genomic analysis for patients with lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR Exon 20 insertions. Clin Cancer Res 27(10):2920–2927. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-4650
Fang W, Huang Y, Hong S, Zhang Z, Wang M, Gan J, Wang W, Guo H, Wang K, Zhang L (2019) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and response to osimertinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 19(1):595. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5820-0
He C, Wei C, Wen J, Chen S, Chen L, Wu Y, Shen Y, Bai H, Zhang Y, Chen X, Li X (2022) Comprehensive analysis of NGS and ARMS-PCR for detecting EGFR mutations based on 4467 cases of NSCLC patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148(2):321–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03818-w
Hou J, Li H, Ma S, He Z, Yang S, Hao L, Zhou H, Zhang Z, Han J, Wang L, Wang Q (2022) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: current status and perspectives. Biomark Res 10(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-022-00372-6
Kirchner M, Kluck K, Brandt R, Volckmar AL, Penzel R, Kazdal D, Endris V, Neumann O, Seker-Cin H, Goldschmid H, Glade J, Allgäuer M, Kriegsmann M, Winter H, Muley T, Perner S, Frost N, Reck M, Fröhling S, Stenzinger A (2021) The immune microenvironment in EGFR- and ERBB2-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. ESMO Open 6(5):100253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100253
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T (2004) Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications. Cancer Res 64(24):8919–8923. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-04-2818
Linardou H, Dahabreh IJ, Bafaloukos D, Kosmidis P, Murray S (2009) Somatic EGFR mutations and efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(6):352–366. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.62
Morita C, Yoshida T, Shirasawa M, Masuda K, Matsumoto Y, Shinno Y, Yagishita S, Okuma Y, Goto Y, Horinouchi H, Yamamoto N, Motoi N, Yatabe Y, Ohe Y (2021) Clinical characteristics of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR exon 20 insertions. Sci Rep 11(1):18762. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98275-3
O’Kane GM, Bradbury PA, Feld R, Leighl NB, Liu G, Pisters KM, Kamel-Reid S, Tsao MS, Shepherd FA (2017) Uncommon EGFR mutations in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 109:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.04.016
Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK (2018) Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol 52(Pt 1):103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019
Ou SHI, Lin HM, Hong JL, Yin Y, Jin S, Lin J, Mehta M, Nguyen D, Neal JW (2021) Real-world response and outcomes in NSCLC patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. J Clin Oncol 39(15):9098–9098. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.9098
Ou SHI, Hong JL, Christopoulos P, Lin HM, Vincent S, Churchill EN, Soeda J, Kazdal D, Stenzinger A, Thomas M (2023) Distribution and detectability of EGFR exon 20 insertion variants in NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2023.01.086
Oxnard GR, Lo PC, Nishino M, Dahlberg SE, Lindeman NI, Butaney M, Jackman DM, Johnson BE, Jänne PA (2013) Natural history and molecular characteristics of lung cancers harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions. J Thorac Oncol 8(2):179–184. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182779d18
Park K, Haura EB, Leighl NB, Mitchell P, Shu CA, Girard N, Viteri S, Han JY, Kim SW, Lee CK, Sabari JK, Spira AI, Yang TY, Kim DW, Lee KH, Sanborn RE, Trigo J, Goto K, Lee JS, Cho BC (2021) Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 insertion-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer progressing on platinum chemotherapy: initial results from the CHRYSALIS phase I study. J Clin Oncol 39(30):3391–3402. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.21.00662
Riely GJ, Neal JW, Camidge DR, Spira AI, Piotrowska Z, Costa DB, Tsao AS, Patel JD, Gadgeel SM, Bazhenova L, Zhu VW, West HL, Mekhail T, Gentzler RD, Nguyen D, Vincent S, Zhang S, Lin J, Bunn V, Jänne PA (2021) Activity and safety of mobocertinib (TAK-788) in previously treated non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations from a phase I/II Trial. Cancer Discov 11(7):1688–1699. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-20-1598
Sai-Hong Ignatius Ou, Hong JL, Christopoulos P, Lin HM, Vincent S, Churchill EN, Soeda J, Kazdal D, Stenzinger A, Thomas M (2023) Distribution and detectability of EGFR exon 20 insertion variants in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2023.01.086
Shen CI, Chiang CL, Shiao TH, Luo YH, Chao HS, Huang HC, Chiu CH (2022) Real-world evidence of the intrinsic limitations of PCR-based EGFR mutation assay in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 12(1):13566. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-17394-7
van Veggel B, Madeira RSJFV, Hashemi SMS, Paats MS, Monkhorst K, Heideman DAM, Groves M, Radonic T, Smit EF, Schuuring E, van der Wekken AJ, de Langen AJ (2020) Osimertinib treatment for patients with EGFR exon 20 mutation positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 141:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.12.013
Viteri S, Minchom A, Bazhenova L, Ou SI, Bauml JM, Shell SA, Schaffer M, Gu J, Rose JB, Curtin JC, Mahadevia P, Girard N (2023) Frequency, underdiagnosis, and heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertion mutations using real-world genomic datasets. Mol Oncol 17(2):230–237. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.13327
Wang F, Li C, Wu Q, Lu H (2020) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Cancer Res 9(4):2982–2991. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2020.03.10
Yang JCH, Sequist LV, Geater SL, Tsai C-M, Mok TSK, Schuler M, Yamamoto N, Yu CJ, Ou S-HI, Zhou C, Massey D, Zazulina V, Wu YL (2015) Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: a combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung 6. Lancet Oncol 16(7):830–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00026-1
Yang G, Li J, Xu H, Yang Y, Yang L, Xu F, Xia B, Zhu VW, Nagasaka M, Yang Y, Li Y, Qiu W, Ying J, Ou SI, Wang Y (2020) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients: Molecular heterogeneity and treatment outcome from nationwide real-world study. Lung Cancer 145:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.03.014
Yang G, Yang Y, Liu R, Li W, Xu H, Hao X, Li J, Zhang S, Xu F, Lei S, Wang Y (2023) First-line immunotherapy or angiogenesis inhibitor combined with chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertions: real-world evidence from China. Cancer Med 12(1):335–344. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.4852
Yasuda H, Park E, Yun CH, Sng NJ, Lucena-Araujo AR, Yeo WL, Huberman MS, Cohen DW, Nakayama S, Ishioka K, Yamaguchi N, Hanna M, Oxnard GR, Lathan CS, Moran T, Sequist LV, Chaft JE, Riely GJ, Arcila ME, Costa DB (2013) Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci Transl Med 5(216):216177. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3007205
Zöchbauer-Müller S, Kaserer B, Prosch H, Cseh A, Solca F, Bauer MJ, Müllauer L (2020) Case report: afatinib treatment in a patient With NSCLC harboring a rare EGFR exon 20 mutation. Front Oncol 10:593852. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.593852
Funding
This study was supported by Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan. (Project number: V112A-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: YTL and CLC. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YTL, RLS, CLC, HCH, CIS, YHT, THH, HSC, YHL. The PCR and NGS database were collected, reviewed, and summarized by LCW and YCY. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
CLC had received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, and Roche. CIS had received honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim and Pfizer. YHL had received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. YMC had received honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Roche/Genentech/Chugai, MSD, Pfizer, Novartis, BMS, Ono Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, and Takeda Oncology; and served as an advisor for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Roche/Chugai, MSD, AstraZeneca, and Takeda Oncology.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan. (Approval number: 2022-07-028CC).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, YT., Wang, LC., Sun, RL. et al. Characteristics, treatment patterns, and clinical outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 10365–10376 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04921-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04921-w