Abstract
Purpose
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a lethal disease with a high potency of metastasis or recurrence after radical resection. Effective predictors for metastasis and recurrence postoperatively were dominant for the development of systemic adjuvant treatment regimens. The ATP hydrolase correlated gene CD73 was described as a promoter in tumor growth and immune escape of PDAC. However, there lacked research focused on the role of CD73 in PDAC metastasis. This study aimed to investigate the expression of CD73 in PDAC patients with different outcomes as well as the prognostic effect of CD73 for disease-free survival (DFS).
Methods
The expression level of CD73 in cancerous samples from 301 PDAC patients was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and translated into a histochemistry score (H-score) by the HALO analysis system. Then, the CD73 H-score was involved in multivariate Cox regression along with other clinicopathological characteristics to find independent prognostic factors for DFS. Finally, a nomogram was constructed based on those independent prognostic factors for DFS prediction.
Results
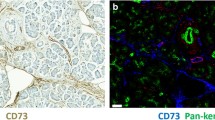
Higher CD73 expression was found in PDAC patients with tumor metastasis postoperatively. Meanwhile, higher CD73 expressions were also investigated in PDAC patients diagnosed with advanced N stage and T stage. Furthermore, CD73 H-score along with tumor margin status, CA19-9, 8th N stage, and adjuvant chemotherapy was indicated as independent prognostic factors for DFS in PDAC patients. The nomogram based on these factors predicted DFS in a good manner.
Conclusion
CD73 was associated with PDAC metastasis and served as an effective prognostic factor for DFS in PDAC patients after radical surgery.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical issues.
References
Aeffner F, Wilson K, Martin NT, Black JC, Hendriks CL, Bolon B, Rudmann DG, Gianani R, Koegler SR, Krueger J, Young GD (2017) The gold standard paradox in digital image analysis: manual versus automated scoring as ground truth. Arch Pathol Lab Med 141:1267–1275
Azambuja JH, Gelsleichter NE, Beckenkamp LR, Iser IC, Fernandes MC, Figueiró F, Battastini AM, Scholl JN, de Oliveira FH, Spanevello RM, Sévigny J (2019) CD73 downregulation decreases in vitro and in vivo glioblastoma growth. Mol Neurobiol 56:3260–3279
Bednar F, di Magliano P (2020) Chemotherapy and tumor evolution shape pancreatic cancer recurrence after resection. Cancer Discov 10:762–764
Chang DK, Johns AL, Merrett ND, Gill AJ, Colvin EK, Scarlett CJ, Nguyen NQ, Leong RW, Cosman PH, Kelly MI, Sutherland RL, Henshall SM, Kench JG, Biankin AV (2009) Margin clearance and outcome in resected pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:2855–62
Driscoll JJ, Rixe O (2009) Overall survival: still the gold standard: why overall survival remains the definitive end point in cancer clinical trials. Cancer J 15:401–5
Ellison LF, Wilkins K (2010) An update on cancer survival. Health Rep 21:55–60
Gebauer F, Tachezy M, Vashist YK, Marx AH, Yekebas E, Izbicki JR, Bockhorn M (2015) Resection margin clearance in pancreatic cancer after implementation of the Leeds Pathology Protocol (LEEPP): clinically relevant or just academic? World J Surg 39:493–9
Groot VP, Rezaee N, Wu W, Cameron JL, Fishman EK, Hruban RH, Weiss MJ, Zheng L, Wolfgang CL, He J (2018) Patterns, timing, and predictors of recurrence following pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 267:936–945
Groot VP, Gemenetzis G, Blair AB, Rivero-Soto RJ, Yu J, Javed AA, Burkhart RA, Rinkes IH, Molenaar IQ, Cameron JL, Weiss MJ, Wolfga CL, He J (2019) Defining and predicting early recurrence in 957 patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 269:1154–1162
Hainaut P, Plymoth A (2013) Targeting the hallmarks of cancer: towards a rational approach to next-generation cancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 25:50–51
Huangi S, Apasov S, Koshiba M, Sitkovsky M (1997) Role of A2a extracellular adenosine receptor-mediated signaling in adenosine-mediated inhibition of T-cell activation and expansion. Blood 90:1600–1610
Hüsemann Y, Geigl JB, Schubert F, Musiani P, Meyer M, Burghart E, Forni G, Eils R, Fehm T, Riethmüller G, Klein CA (2008) Systemic spread is an early step in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 13:58–68
Inoue Y, Yoshimura K, Kurabe N, Kahyo T, Kawase A, Tanahashi M, Ogawa H, Inui N, Funai K, Shinmura K, Niwa H (2017) Prognostic impact of CD73 and A2A adenosine receptor expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 8:8738–8751
Kawada K, Taketo MT (2011) Significance and mechanism of lymph node metastasis in cancer progression. Can Res 71:1214–1218
Lutty GA, Mathews MK, Merges C, MCleod DS (1998) Adenosine stimulates canine retinal microvascular endothelial cell migration and tube formation. Curr Eye Res 17:594–607
Ma XL, Shen MN, Hu B, Wang BL, Yang WJ, Lv LH, Wang H, Zhou Y, Jin AL, Sun YF, Zhang CY (2019) CD73 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling by inducing Rap1-mediated membrane localization of P110β and predicts poor prognosis. J Hematol Oncol 12:37
Malleo G, Maggino L, Capelli P, Gulino F, Segattini S, Scarpa A, Bassi C, Butturini G, Salvia R (2015) Reappraisal of nodal staging and study of lymph node station involvement in pancreaticoduodenectomy with the standard international study group of pancreatic surgery definition of lymphadenectomy for cancer. J Am Coll Surg 221:367–79.e4
Mathoulin-Pelissier S, Gourgou-Bourgade S, Bonnetain F, Kramar A (2008) Survival end point reporting in randomized cancer clinical trials: a review of major journals. J Clin Oncol 26:3721–6
Messaoudi N, Cousineau I, Arslanian E, Henault D, Stephen D, Vandenbroucke-Menu F, Dagenais M, Létourneau R, Plasse M, Roy A, Lapointe R (2020) Prognostic value of CD73 expression in resected colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Oncoimmunology 9:1746138
Meyerholz DK, Beck AP (2018) Principles and approaches for reproducible scoring of tissue stains in research. Lab Investig 98:844–855
Morrison LE, Lefever MR, Behman LJ, Leibold T, Roberts EA, Horchner UB, Bauer DR (2020) Brightfield multiplex immunohistochemistry with multispectral imaging. Lab Investig 100:1124–1136
Occhionorelli S, Andreotti D, Vallese P, Morganti L, Lacavalla D, Forini E, Pascale G (2018) Evaluation on prognostic efficacy of lymph nodes ratio (LNR) and log odds of positive lymph nodes (LODDS) in complicated colon cancer: the first study in emergency surgery. World J Surg Oncol 16:186
Paiella S, Sandini M, Gianotti L, Butturini G, Salvia R, Bassi C (2016) The prognostic impact of para-aortic lymph node metastasis in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 42:616–24
Prassas D, Safi SA, Stylianidi MC, Telan LA, Krieg S, Roderburg C, Esposito I, Luedde T, Knoefel WT, Krieg A (2022) N, LNR or LODDS: which is the most appropriate lymph node classification scheme for patients with radically resected pancreatic cancer? Cancers 14:1834
Rathbone MP, Middlemiss PJ, Kim JK, Gysbers JW, DeForge SP, Smith RW, Hughes DW (1992) Adenosine and its nucleotides stimulate proliferation of chick astrocytes and human astrocytoma cells. Neurosci Res 13:1–17
Rawla P, Sunkara T, Gaduputi V (2019) Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: global trends, etiology and risk factors. World J Oncol 10:10–27
Rhim AD, Mirek ET, Aiello NM, Maitra A, Bailey JM, McAllister F, Reichert M, Beatty GL, Rustgi AK, Vonderheide RH, Leach SD (2012) EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic tumor formation. Cell 148:349–61
Robinson AG, Booth CM, Eisenhauer EA (2014) Disease-free survival as an end-point in the treatment of solid tumours–perspectives from clinical trials and clinical practice. Eur J Cancer 50:2298–302
Robinson AG, Booth CM, Eisenhauer EA (2014) Progression-free survival as an end-point in solid tumours–perspectives from clinical trials and clinical practice. Eur J Cancer 50:2303–8
Schito L, Semenza GL (2016) Hypoxia-inducible factors: master regulators of cancer progression. Trends Cancer 2:758–770
Semenza GL (2016) The hypoxic tumor microenvironment: A driving force for breast cancer progression. Biochem Biophys Acta 1863:382–391
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7–30
Suenaga M, Fujii T, Kanda M, Takami H, Okumura N, Inokawa Y, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, Yamada S, Sugimoto H, Nomoto S (2014) Pattern of first recurrent lesions in pancreatic cancer: hepatic relapse is associated with dismal prognosis and portal vein invasion. Hepato-Gastroenterology 61:1756–61
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Synnestvedt K, Furuta GT, Comerford KM, Louis N, Karhausen J, Eltzschig HK, Hansen KR, Thompson LF, Colgan SP (2002) Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73) regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates permeability changes in intestinal epithelia. The J Clin Investig 110:993–1002
Tahkola K, Ahtiainen M, Kellokumpu I, Mecklin JP, Laukkarinen J, Laakkonen J, Kenessey I, Jalkanen S, Salmi M, Böhm J (2021) Prognostic impact of CD73 expression and its relationship to PD-L1 in patients with radically treated pancreatic cancer. Virchows Arch 478:209–217
Tempero MA, Malafa MP, Al-Hawary M, Behrman SW, Benson AB, Cardin DB, Chiorean EG, Chung V, Czito B, Del Chiaro M, Dillhoff M (2021) Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 19:439–457
Toki MI, Merritt CR, Wong PF, Smithy JW, Kluger HM, Syrigos KN, Ong GT, Warren SE, Beechem JM, Rimm DL (2019) High-plex predictive marker discovery for melanoma immunotherapy-treated patients using digital spatial profiling. Clin Cancer Res 25:5503–5512
Tripathi A, Lin E, Xie W et al (2020) Prognostic significance and immune correlates of CD73 expression in renal cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer 8:e001467. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-001467
Trivedi MS, Hoffner B, Winkelmann JL, Abbott ME, Hamid O, Carvajal, (2015) Programmed death 1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 13:858–68
Valsangkar NP, Bush DM, Michaelson JS, Ferrone CR, Wargo JA, Lillemoe KD, Fernández-del Castillo C, Warshaw AL, Thayer SP (2013) N0/N1, PNL, or LNR? The effect of lymph node number on accurate survival prediction in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 17:257–66
Verbeke CS, Gladhaug IP (2012) Resection margin involvement and tumour origin in pancreatic head cancer. Br J Surg 99:1036–1049
Viratham Pulsawatdi A, Craig SG, Bingham V, McCombe K, Humphries MP, Senevirathne S, Richman SD, Quirke P, Campo L, Domingo E, Maughan TS (2020) A robust multiplex immunofluorescence and digital pathology workflow for the characterisation of the tumour immune microenvironment. Mol Oncol 14:2384–2402
Xu Z, Gu C, Yao X, Guo W, Wang H, Lin T, Li F, Chen D, Wu J, Ye G, Zhao L (2020) CD73 promotes tumor metastasis by modulating RICS/RhoA signaling and EMT in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis 11:202
Yu J, Wang X, Lu Q, Wang J, Li L, Liao X, Zhu W, Lv L, Zhi X, Yu J, Jin Y (2018) Extracellular 5’-nucleotidase (CD73) promotes human breast cancer cells growth through AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin/cyclinD1 signaling pathway. Int J Cancer 142:959–967
Zhang B (2012) CD73 promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Oncoimmunology 1:67–70
Zhang H, Cao Y, Tang J, Wang R (2022) CD73 (NT5E) promotes the proliferation and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma through the EGFR/AKT/mTOR pathway. BioMed Res Int 2022:9944847
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Funds (Nos. 81972299 and 81672390) and the National Key Research and Development Plan (No. 2017YFC0910002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DQ, RW, KH, and SL were involved in the study design. DQ, RW, and KH contributed to data collection and analysis. RQW, HD, ZY, and PX performed the western blot experiments and bioinformatic analysis. All authors were involved in drafting the manuscript. SL critically reviewed the manuscript and provided final approval of the published version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare no competing interest.
Ethical approval
The study was performed according to the standards set in the Declaration of Helsinki 1964. Patients’ data were fully anonymized. The tumor tissue used was leftover material that had been collected during surgery for histopathological diagnostics. The authors were blinded for clinical information during experimental analysis. This study got approved by the Institutional Review Board of SYSUCC.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Researchers were blinded from patient data during experimental and statistical analysis.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for the publication of the images in Figs. 2, 3, and 4.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, D., Wei, R., Huang, K. et al. Prognostic effect of CD73 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma for disease-free survival after radical surgery. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 7805–7817 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04703-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04703-4