Abstract
Background
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a common modification and plays an important role in various biological processes, but m6A-related lncRNA functions in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have not been systematically clarified.
Methods
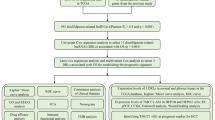
The clinical data and RNA-seq transcriptome of 375 cases of HCC and 50 cases of normal tissues were obtained from the Cancer Gene Atlas database. Co-expression analysis was used to obtain m6A-related lncRNA. The independent prognostic factors were identified by univariate and multivariate Cox regression models. Kaplan–Meier method was used in survival analysis. The core gene of the mRNA–mRNA interaction network is related to m6A-related lncRNAs obtained by the CytoHubba plugin of Cytoscape. Gene ontology and Kyoto Gene Encyclopedia were analyzed to find out the potential mechanism. CIBERSORT algorithm was used to calculate the relative proportion of immune infiltrating cells.
Results
We identified two subgroups (cluster 1 and cluster 2) according to the expression level. The survival analysis curve and receiver operating characteristic curve proved that this model could predict the prognosis of HCC patients. The univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses showed the independent prognostic value. UBE2C was screened as the pivotal gene. The expression level of m6A-related lncRNAs causes changes in the tumor immune microenvironment.
Conclusion
The expression levels of m6A-related lncRNAs were significantly different and the prognostic value of m6A-related lncRNAs was confirmed. The m6A-related lncRNAs are expected to be prognostic signatures in HCC.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available in the TCGA repository https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/.
References
Azbazdar Y, Karabicici M, Erdal E, Ozhan G (2021) Regulation of Wnt signaling pathways at the plasma membrane and their misregulation in cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:631623. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.631623
Bi KW, Wei XG, Qin XX, Li B (2020) BTK has potential to be a prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma and an indicator for tumor microenvironment remodeling: a study based on TCGA data mining. Front Oncol 10:424. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00424
Chen X, Sun YZ, Guan NN, Qu J, Huang ZA, Zhu ZX, Li JQ (2019) Computational models for lncRNA function prediction and functional similarity calculation. Brief Funct Genom 18(1):58–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/ely031
Chiang AJ, Li CJ, Tsui KH, Chang C, Chang YI, Chen LW, Chang TH, Sheu JJ (2020) UBE2C drives human cervical cancer progression and is positively modulated by mTOR. Biomolecules 11(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010037
Fernandes J, Acuña SM, Aoki JI, Floeter-Winter LM, Muxel SM (2019) Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of gene expression: physiology and disease. Non-Coding RNA 5(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010017
Frenette C, Gish RG (2011) Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular and genomic guideline for the clinician. Clin Liver Dis 15(2):307–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2011.03.010
Ghafouri-Fard S, Gholipour M, Hussen BM, Taheri M (2021) The impact of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:649107. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.649107
Huang S, Wei YK, Kaliamurthi S, Cao Y, Nangraj AS, Sui X, Chu D, Wang H, Wei DQ, Peslherbe GH et al (2020) Circulating miR-1246 Targeting UBE2C, TNNI3, TRAIP, UCHL1 genes and key pathways as a potential biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma: integrated biological network analysis. J Pers Med 10(4):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040162
Huarte M (2015) The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med 21(11):1253–1261. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3981
Imada A, Shijubo N, Kojima H, Abe S (2000) Mast cells correlate with angiogenesis and poor outcome in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Eur Respir J 15(6):1087–1093. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.01517.x
Jia AY, Popovic A, Mohan AA, Zorzi J, Griffith P, Kim AK, Anders RA, Burkhart RA, Lafaro K, Georgiades C, Azad NS, Liddell RP, Baretti M, Kamel IR, Narang A, Yarchoan M, Meyer J (2021) Development, practice patterns, and early clinical outcomes of a multidisciplinary liver cancer clinic. Cancer Control 28:10732748211009944. https://doi.org/10.1177/10732748211009945
Jiang K, Dong M, Li C, Sheng J (2021) Unraveling heterogeneity of tumor cells and microenvironment and its clinical implications for triple negative breast cancer. Front Oncol 11:557477. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.557477
Li J, Zhu Y (2020) Recent advances in liver cancer stem cells: non-coding RNAs, oncogenes and oncoproteins. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:548335. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.548335
Lu T, Xu R, Li Q, Zhao JY, Peng B, Zhang H, Guo JD, Zhang SQ, Li HW, Wang J et al (2021) Systematic profiling of ferroptosis gene signatures predicts prognostic factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Ther Oncolyt 21:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2021.02.011
Molinie B, Giallourakis CC (2017) Genome-wide location analyses of N6-methyladenosine modifications (mA-Seq). Methods Mol Biol (clifton, NJ) 1562:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6807-7_4
Muenst S, Läubli H, Soysal SD, Zippelius A, Tzankov A, Hoeller S (2016) The immune system and cancer evasion strategies: therapeutic concepts. J Intern Med 279(6):541–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12470
Nociti V, Santoro M (2021) What do we know about the role of lncRNAs in multiple sclerosis? Neural Regen Res 16(9):1715–1722. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.306061
Shen S, Yan J, Zhang Y, Dong Z, Xing J, He Y (2021) N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-mediated messenger RNA signatures and the tumor immune microenvironment can predict the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Transl Med 9(1):59. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-7396
Shi C, Sun L, Song Y (2019) FEZF1-AS1: a novel vital oncogenic lncRNA in multiple human malignancies. Biosci Rep 39(6):BSR20191202. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20191202
Siegel Rebecca L, Miller Kimberly D, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Wang L, Huang J, Jiang M, Chen Q, Jiang Z, Feng H (2014) CAMK1 phosphoinositide signal-mediated protein sorting and transport network in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by biocomputation. Cell Biochem Biophys 70(2):1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0011-8
Wang Q, Hu B, Hu X, Kim H, Squatrito M, Scarpace L, DeCarvalho AC, Lyu S, Li P, Li Y et al (2018) Tumor evolution of glioma-intrinsic gene expression subtypes associates with immunological changes in the microenvironment. Cancer Cell 33(1):152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.06.003
Xie C, Powell C, Yao M, Wu J, Dong Q (2014) Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C: a potential cancer biomarker. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 47:113–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.023
Yim HJ, Suh SJ, Um SH (2015) Current management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an Eastern perspective. World J Gastroenterol 21(13):3826–3842. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3826
Zhang L, Qiao Y, Huang J, Wan D, Zhou L, Lin S, Zheng S (2020) Expression pattern and prognostic value of key regulators for m6A RNA modification in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Med 7:556. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00556
Zhu J, Xiao J, Wang M, Hu D (2020) Pan-cancer molecular characterization of mA regulators and immunogenomic perspective on the tumor microenvironment. Front Oncol 10:618374. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.618374
Zhu M, Wu M, Bian S, Song Q, Xiao M, Huang H, You L, Zhang J, Zhang J, Cheng C et al (2021) DNA primase subunit 1 deteriorated progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating AKT/mTOR signaling and UBE2C-mediated P53 ubiquitination. Cell Biosci 11(1):42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00555-y
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Muqi Li and Liangzhen Xie for assisting in the modification of the data analysis program.
Funding
This work was supported by Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant number 2022A1515012392).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KH, Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing Reviewing and Editing. JL: Investigation, Writing Reviewing and Editing. YZ, Writing Reviewing and Editing. JF, Formal analysis. XL: Conceptualization, Methodology. WZ, Data curation. YT: Data curation. XC, Investigation, Resources. JX, Investigation, Resources. XH, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The data are all from the public database TCGA, which does not involve ethical issues.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, K., Li, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Expression and prognostic signatures of m6A-related lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 4429–4441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04338-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04338-x