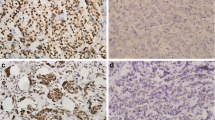
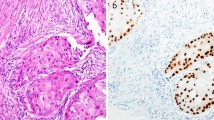
Abstract
Purpose
Little is known about the prognostic value of androgen receptor (AR) status in mammary Paget’s disease (MPD). The purpose of this study was to explore AR status and the distribution of molecular subtypes in MPD as well as the relationship between AR expression and clinicopathological factors and to evaluate its prognostic value.
Methods
We analyzed 170 MPD patients of varying subtypes. AR expression was verified by immunohistochemical staining, and the correlations between AR expression and clinicopathological characteristics and survival status were analyzed. We further investigated 91 MPD patients with invasive ductal carcinoma (MPD-IDC).
Results
AR was expressed in 55.3% of overall MPD patients, and 78.2% had the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression subtype. AR positivity was significantly correlated with BMI (P = 0.037) and pathological N stage (P = 0.023). Multivariate analysis indicated that pathological T stage and pathological N stage were independent prognostic factors for overall survival (OS). The positive AR group was significantly associated with better OS (P = 0.014). Among 91 MPD-IDC patients, AR was expressed in 56.0%, and 80.0% had the HER2 overexpression subtype. AR positivity was significantly correlated with pathological N stage (P = 0.033). Multivariate analysis indicated that AR and pathological T stage were independent prognostic factors for OS. Furthermore, AR positivity was significantly related to better OS (P = 0.005) in MPD-IDC patients as well as in patients with the HER2 overexpression subtype (P = 0.029).
Conclusion
Our results confirmed that AR is a potential biomarker for evaluating the prognosis of patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akashi M, Yamaguchi R, Kusano H, Ogasawara S, Abe E, Obara H, Yamaguchi M, Akiba J, Kakuma T, Tanaka M, Akagi Y, Yano H (2020) Androgen receptor expression is useful to predict the therapeutic effect in HER2-positive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 184(2):277–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05855-4
Anestis A, Zoi I, Papavassiliou AG, Karamouzis MV (2020) Androgen receptor in breast cancer-clinical and preclinical research insights. Molecules 25(2):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020358
Apalla Z, Errichetti E, Kyrgidis A, Stolz W, Puig S, Malvehy J, Zalaudek I, Moscarella E, Longo C, Blum A, Lanssens S, Savoia F, Tschandl P, Kittler H, Sinz C, Stinco G, Argenziano G, Lazaridou E, Lallas A (2019) Dermoscopic features of mammary Paget’s disease: a retrospective case-control study by the International Dermoscopy Society. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereo 33(10):1892–1898. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.15732
Astvatsaturyan K, Yue Y, Walts AE, Bose S (2018) Androgen receptor positive triple negative breast cancer: clinicopathologic, prognostic, and predictive features. PLoS One 13(6):e0197827. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197827
Basile D, Cinausero M, Iacono D, Pelizzari G, Bonotto M, Vitale MG, Gerratana L, Puglisi F (2017) Androgen receptor in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer: beyond expression. Cancer Treat Rev 61:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.09.006
Chen S, Chen H, Yi Y, Jiang X, Lei H, Luo X, Chen Y, Liu S, Yuan D, Jia X, Li J (2019) Comparative study of breast cancer with or without concomitant Paget disease: an analysis of the SEER database. Cancer Med 8(8):4043–4054. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2242
Chen M, Yang Y, Xu K, Li L, Huang J, Qiu F (2020) Androgen receptor in breast cancer: from bench to bedside. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:573. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00573
Drews-Elger K, Sandoval-Leon AC, Ergonul AB, Jegg AM, Gomez-Fernandez C, Miller PC, El-Ashry D, Lippman ME (2020) Paget’s disease of the nipple in a Her2-positive breast cancer xenograft model. Breast Cancer Res Treat 179(3):577–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05490-8
Elebro K, Borgquist S, Simonsson M, Markkula A, Jirström K, Ingvar C, Rose C, Jernström H (2015) Combined androgen and estrogen receptor status in breast cancer: treatment prediction and prognosis in a population-based prospective cohort. Clin Cancer Res 21(16):3640–3650. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2564
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber R (2013) Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol 24(9):2206–2223. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt303
Huang R, Han J, Liang X, Huang R, Han J, Liang X, Sun S, Jiang Y, Xia B, Niu M, Li D, Zhang J, Wang S, Wei W, Liu Q, Zheng W, Zhang G, Song Y, Panga D (2017) Androgen receptor expression and bicalutamide antagonize androgen receptor inhibit β-catenin transcription complex in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 43(6):2212–2225. https://doi.org/10.1159/000484300
Kono M, Fujii T, Lim B, Karuturi MS, Tripathy D, Ueno NT (2017) Androgen receptor function and androgen receptor-targeted therapies in breast cancer: a review. JAMA Oncol 3(9):1266–1273. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.4975
Liegl B, Horn LC, Moinfar F (2005) Androgen receptors are frequently expressed in mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. Mod Pathol 18(10):1283–1288. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800437
Lohsiriwat V, Martella S, Rietjens M, Botteri E, Rotmensz N, Mastropasqua MG, Garusi C, De Lorenzi F, Manconi A, Sommario M, Barbieri B, Cassilha M, Minotti I, Petit JY (2012) Paget’s disease as a local recurrence after nipple-sparing mastectomy: clinical presentation, treatment, outcome, and risk factor analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 19(6):1850–1855. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2226-5
Mai R, Zhou S, Zhou S, Zhong W, Hong L, Wang Y, Lu S, Pan J, Huang Y, Su M, Crawford R, Zhou Y, Zhang G (2018) Transcriptome analyses reveal FOXA1 dysregulation in mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. Hum Pathol 77:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2017.12.030
Ozgur E, Ozgur E, Gezer U (2020) Investigation of lncRNA H19 in prostate cancer cells and secreted exosomes upon androgen stimulation or androgen receptor blockage. Bratisl Lek Listy 121(5):362–365. https://doi.org/10.4149/BLL_2020_058
Pan B, Zhao D, Liu Y, Li N, Song C, Li N, Li X, Li M, Zhao Z (2020) Establishment and characterization of breast cancer organoids from a patient with mammary Paget’s disease. Cancer Cell Int 20:365. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01459-6
Patel M, Ayyaswami V, Prabhu AV (2018) Sir James Paget-contributions of a surgeon and pathologist. JAMA Dermatol 154(3):335. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6127
Prekovic S, Van den Broeck T, Moris L, Smeets E, Claessens F, Joniau S, Helsen C, Attard G (2018) Treatment-induced changes in the androgen receptor axis: liquid biopsies as diagnostic/prognostic tools for prostate cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 462(Pt A):56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2017.08.020
Rahim B, O’Regan R (2017) AR signaling in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 9(3):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9030021
Salvi S, Bonafè M, Bravaccini S (2020) Androgen receptor in breast cancer: a wolf in sheep’s clothing? A lesson from prostate cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 60:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.04.002
Sek P, Zawrocki A, Biernat W, Piekarski JH (2010) HER2 molecular subtype is a dominant subtype of mammary Paget’s cells. An immunohistochemical study. Histopathology 57(4):564–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03665.x
Song Y, Guerrero-Juarez CF, Chen Z, Tang Y, Ma X, Lv C, Bi X, Deng M, Bu L, Tian Y, Liu R, Zhao R, Xu J, Sheng X, Du S, Liu Y, Zhu Y, Shan SJ, Chen HD, Zhao Y, Zhou G, Shuai J, Ren F, Xue L, Ying Z, Dai X, Lengner CJ, Andersen B, Plikus MV, Nie Q, Yu Z (2020) The Msi1-mTOR pathway drives the pathogenesis of mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. Cell Res 30(10):854–872. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0334-5
Vellaisamy G, Tirumalae R, Inchara YK (2019) Expression of androgen receptor in primary breast carcinoma and its relation with clinicopathologic features, estrogen, progesterone, and her-2 receptor status. J Cancer Res Ther 15(5):989–993. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_572_17
Wachter DL, Wachter PW, Fasching PA, Beckmann MW, Hack CC, Riener MO, Hartmann A, Strehl JD (2019) Characterization of molecular subtypes of Paget disease of the breast using immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Arch Pathol Lab Med 143(2):206–211. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2017-0578-OA
Wong SM, Freedman RA, Sagara Y, Stamell EF, Desantis SD, Barry WT, Golshan M (2015) The effect of Paget disease on axillary lymph node metastases and survival in invasive ductal carcinoma. Cancer 121(24):4333–4340. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29687
Zhang G, Zhou S, Zhong W, Hong L, Wang Y, Lu S, Pan J, Huang Y, Su M, Crawford R, Zhou Y, Mai R (2019) Whole-exome sequencing reveals frequent mutations in chromatin remodeling genes in mammary and extramammary Paget’s diseases. J Invest Dermatol 139(4):789–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2018.08.030
Zhang M, Meng X, Guo C, Liu J, Xing Z, Wang X, Wang X (2020) Clinicopathological relevance and prognostic value of androgen receptor in mammary Paget’s disease with underlying invasive ductal carcinoma. Oncol Res Treat 43(7–8):346–353. https://doi.org/10.1159/000507893
Zhao Y, Sun HF, Chen MT, Gao SP, Li LD, Jiang HL, Jin W (2018) Clinicopathological characteristics and survival outcomes in Paget disease: a SEER population-based study. Cancer Med 7(6):2307–2318. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1475
Zhou S, Zhong W, Mai R, Zhang G (2017) Mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease presented different expression pattern of steroid hormone receptors. Biomed Res Int 2017:3768247. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3768247
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Education Chunhui Project Cooperative Research Project (No. HLJ2019010), Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LH2020H120), and the Haiyan Research Fund of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital (No. JJZD2020-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW, YS and SC contributed to the study design. Data collection was performed by BX, SZ, KQ, QW and JX. Data analysis and interpretation were performed by SS, YH, MX, XZ and XL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YW, and all authors have commented on the manuscript. The final draft was read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals participating in the study.
Consent to publish
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Sun, S., Huang, Y. et al. Correlation analysis between androgen receptor and the clinicopathological features and prognosis of mammary Paget’s disease. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 1175–1184 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-03988-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-03988-1