Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the potential benefits of a hypofractionated radiotherapy boost (HRB) after chemotherapy (CT) and concomitant chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC) patients. Primary endpoints were early and late toxicity, local control (LC) and pain-free progression (PFP) assessment. Two-years overall survival (OS), metastasis-free survival (MFS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were secondary endpoints.
Materials and methods
Patients (pts) affected by unresectable non-metastatic LAPC, previously treated with CT and CRT in upfront or sandwich setting, were selected for sequential HRB. Total prescribed dose was 30 Gy in 5 fractions (fr) to pancreatic primary lesion. Dose de-escalation was allowed in case of failure in respecting organs at risk constraints. Early and late toxicity were assessed according to CTCAE v.4.0 classification. The Kersh-Hazra scale was used for pain assessment. Local Control, PFP, MFS and DFS were calculated from the date of HRB to the date of relapse or the date of the last follow-up.
Results
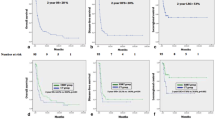
Thirty-one pts affected by unresectable, non-metastatic LAPC were consecutively enrolled from November 2004 to October 2019. All pts completed the planned HRB. Total delivered dose varied according to duodenal dose constraint: 20 Gy in 5 fr (N: 6; 19.4%), 20 Gy in 4 fr (N: 5; 16.2%), 25 Gy in 5 fr (N: 18; 58.0%) and 30 Gy in 6 fr (N: 2; 6.4%). Early and late toxicity were assessed in all pts: no Grade 3 or 4 acute gastrointestinal toxicity and no late gastrointestinal complications occurred. Median LC was 19 months (range 1–156) and 1- and 2-year PFP were 85% and 62.7%, respectively (median 28 months; range 2–139). According to the Kersh-Hazra scale, four pts had a Grade 3 and four pts had a Grade 1 abdominal pain before HRB. At the last follow-up only 3/31 pts had residual Grade 1 abdominal pain.Median MFS was 18 months (range 1–139). The 2-year OS after HRB was 57.4%, while 2-year OS from diagnosis was 77.3%.
Conclusion
Treatment intensification with hypofractionated radiotherapy boost is well tolerated in pts affected by unresectable LAPC previously treated with CT/CRT. Its rates of local and pain control are encouraging, supporting its introduction in clinical practice. Timing, schedule and dose of HRB need to be further investigated to personalize therapy and optimize clinical advantages.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03439-9
References
André T, Balosso J, Louvet C et al (2000) Combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy (cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil) as palliative treatment for localized unresectable or adjuvant treatment for resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma: results of a feasibility study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:903–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00478-2
Bockbrader M, Kim E (2009) Role of intensity-modulated radiation therapy in gastrointestinal cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 9:637–647
Bohoudi O, Bruynzeel AME, Senan S et al (2017) Fast and robust online adaptive planning in stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for pancreatic cancer. Radiother Oncol 125:439–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2017.07.028
Boldrini L, Cusumano D, Cellini F et al (2019) Online adaptive magnetic resonance guided radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer: state of the art, pearls and pitfalls. Radiat Oncol 14:71
Brunner TB, Nestle U, Grosu AL, Partridge M (2015) SBRT in pancreatic cancer: What is the therapeutic window? Radiother Oncol 114:109–116
Buwenge M, Cilla S, Guido A et al (2016) Individually optimized stereotactic radiotherapy for pancreatic head tumors: a planning feasibility study. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 21:548–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2016.09.003
Chang DT, Schellenberg D, Shen J et al (2009) Stereotactic radiotherapy for unresectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Cancer 115:665–672. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24059
De Bari B, Porta L, Mazzola R et al (2016) Hypofractionated radiotherapy in pancreatic cancer: lessons from the past in the era of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 103:49–61
Didolkar MS, Coleman CW, Brenner MJ et al (2010) Image-guided stereotactic radiosurgery for locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma results of first 85 patients. J Gastrointest Surg 14:1547–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-010-1323-7
Elhammali A, Patel M, Weinberg B et al (2015) Late gastrointestinal tissue effects after hypofractionated radiation therapy of the pancreas. Radiat Oncol 10:186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-015-0489-2
Ferlay J, Partensky C, Bray F (2016) More deaths from pancreatic cancer than breast cancer in the EU by 2017. Acta Oncol (Madr) 55:1158–1160. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2016.1197419
Hammel P, Huguet F, Van Laethem JL et al (2016) Effect of chemoradiotherapy vs chemotherapy on survival in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer controlled after 4 months of gemcitabine with or without erlotinib the LAP07 randomized clinical trial. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 315:1844–1853. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.4324
Henke L, Kashani R, Robinson C et al (2018) Phase I trial of stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for the treatment of oligometastatic or unresectable primary malignancies of the abdomen. Radiother Oncol 126:519–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2017.11.032
Hoyer M, Roed H, Sengelov L et al (2005) Phase-II study on stereotactic radiotherapy of locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 76:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2004.12.022
Huguet F, André T, Hammel P et al (2007) Impact of chemoradiotherapy after disease control with chemotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma in GERCOR phase II and III studies. J Clin Oncol 25:326–331. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.07.5663
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457
Kersh C, Hazra T (1985) Radiation therapy in the management of oncologic pain. Clin Cancer Briefs 7:3–7
Koong AC, Christofferson E, Le QT et al (2005) Phase II study to assess the efficacy of conventionally fractionated radiotherapy followed by a stereotactic radiosurgery boost in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:320–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.07.002
Koong AC, Le QT, Ho A et al (2004) Phase I study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1017–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.11.004
Krishnan S, Rana V, Janjan NA et al (2007) Induction chemotherapy selects patients with locally advanced, unresectable pancreatic cancer for optimal benefit from consolidative chemoradiation therapy. Cancer 110:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22735
Loehrer PJ, Feng Y, Cardenes H et al (2011) Gemcitabine alone versus gemcitabine plus radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: an eastern cooperative oncology group trial. J Clin Oncol 29:4105–4112. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.34.8904
Lominska CE, Unger K, Nasr NM et al (2012) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for reirradiation of localized adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Radiat Oncol 7:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-7-74
MacChia G, Morganti AG, Cilla S et al (2012) Quality of life and toxicity of stereotactic radiotherapy in pancreatic tumors: a case series. Cancer Invest 30:149–155. https://doi.org/10.3109/07357907.2011.640649
Mahadevan A, Jain S, Goldstein M et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiotherapy and gemcitabine for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:735–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.08.046
Mahadevan A, Miksad R, Goldstein M et al (2011) Induction gemcitabine and stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced nonmetastatic pancreas cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e615–e622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.04.045
Malvezzi M, Bertuccio P, Levi F et al (2014) European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2014. Ann Oncol 25:1650–1656. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu138
Manuel H (2010) Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 362:1605
Mattiucci GC, Morganti AG, Valentini V et al (2010) External beam radiotherapy plus 24-hour continuous infusion of gemcitabine in unresectable pancreatic carcinoma: long-term results of a phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:831–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.013
Murphy JD, Christman-Skieller C, Kim J et al (2010) A dosimetric model of duodenal toxicity after stereotactic body radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:1420–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.09.075
Polistina F, Costantin G, Casamassima F et al (2010) Unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer: a multimodal treatment using neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (gemcitabine plus stereotactic radiosurgery) and subsequent Surgical exploration. Ann Surg Oncol 17:2092–2101. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1019-y
Potters L, Kavanagh B, Galvin JM et al (2010) American society for therapeutic radiology and oncology (ASTRO) and american college of radiology (ACR) practice guideline for the performance of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.09.042
Reese AS, Lu W, Regine WF (2014) Utilization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy and image-guided radiation therapy in pancreatic cancer: is it beneficial? Semin Radiat Oncol 24:132–139
Rwigema J-CM, Parikh SD, Heron DE et al (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy in the treatment of advanced adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Am J Clin Oncol 34:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e3181d270b4
Rwigema JCM, Heron DE, Parikh SD et al (2012) Adjuvant stereotactic body radiotherapy for resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma with close or positive margins. J Gastrointest Cancer 43:70–76
Schwartz LH, Litière S, De Vries E et al (2016) RECIST 1.1—update and clarification: from the RECIST committee. Eur J Cancer 62:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2016.03.081
Shen ZT, Wu XH, Li B et al (2010) Preliminary efficacy of cyberknife radiosurgery for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Chin J Cancer 29:802–809. https://doi.org/10.5732/cjc.010.10112
Suker M, Beumer BR, Sadot E et al (2016) FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and patient-level meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 17:801–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00172-8
Suker M, Nuyttens JJ, Eskens FALM et al (2019) Efficacy and feasibility of stereotactic radiotherapy after folfirinox in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC-1 trial). EClinicalMedicine 17:100200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2019.10.013
Wild AT, Hiniker SM, Chang DT et al (2013) Re-irradiation with stereotactic body radiation therapy as a novel treatment option for isolated local recurrence of pancreatic cancer after multimodality therapy: experience from two institutions. J Gastrointest Oncol 4:343–351. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2013.044
Willett CG, Czito BG, Bendell JC, Ryan DP (2005) Locally advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:4538–4544. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.23.911
Funding
All authors received no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised due to the correction in the introduction section of the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattiucci, G.C., Boldrini, L., Nardangeli, A. et al. Hypofractionated sequential radiotherapy boost: a promising strategy in inoperable locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 661–667 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03411-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03411-7