Abstract
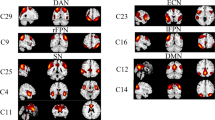
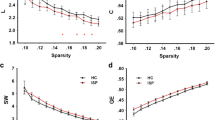
Coronary heart disease (CHD) confers a high risk of cognitive and mental impairments in patients. This study aimed to explore the association of CHD with functional connectivity and topological properties of brain networks. A total of 27 patients with CHD and 44 healthy controls (HCs) participated in this study and underwent a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) scan. Intra- and internetwork functional connectivity alterations were explored using independent component analysis in CHD patients. Furthermore, graph theoretical analysis was adopted to assess abnormalities in small-world properties and network efficiency metrics of brain networks. Compared to HCs, CHD patients exhibited increased functional connectivity between the posterior default mode network and posterior visual network, as well as decreased functional connectivity between the left frontoparietal network and auditory network. In terms of graph theoretical analysis, small-world network topology was identified in both CHD patients and HCs. Furthermore, the nodal local efficiency of the left putamen was significantly decreased in CHD patients compared to HCs. This study revealed alterations in brain functional connectivity and topological properties in CHD patients, shedding light on the potential neurological mechanism underlying cognitive and mental impairments in these patients and suggesting unexplored connections between CHD and higher order cognitive processing.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Arntzen KA, Schirmer H, Wilsgaard T, Mathiesen EB (2011) Impact of cardiovascular risk factors on cognitive function: the troms circle divide study. Eur J Neurol 18(5):737–743. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03263.x
Bassett DS, Bullmore ET (2006) Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12(6):512–523. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858406293182
Bernard C, Catheline G, Dilharreguy B, Couffinhal T, Ledure S, Lassalle-Lagadec S, Callaert D, Allard M, Sibon I (2016) Cerebral changes and cognitive impairment after an ischemic heart disease: a multimodal MRI study. Brain Imaging Behav 10(3):893–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9483-4
Buckner RL, DiNicola LM (2019) The brain’s default network: updated anatomy, physiology and evolving insights. Nat Rev Neurosci 20(10):593–608. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0212-7
Cai SP, Chong T, Peng YL, Shen WY, Li J, von Deneen KM, Huang LY, Alzheimer’s Dis N (2017) Altered functional brain networks in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a resting-state fMRI study. Brain Imaging Behav 11(3):619–631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9539-0
Cao QJ, Shu N, An L, Wang P, Sun L, Xia MR, Wang JH, Gong GL, Zang YF, Wang YF, He Y (2013) Probabilistic diffusion tractography and graph theory analysis reveal abnormal white matter structural connectivity networks in drug-naive boys with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Neurosci 33(26):10676–10687. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4793-12.2013
Corbetta M, Shulman GL (2002) Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(3):201–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn755
Deckers K, Schievink SHJ, Rodriquez MMF, van Oostenbrugge RJ, van Boxtel MPJ, Verhey FRJ, Kohler S (2017) Coronary heart disease and risk for cognitive impairment or dementia: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184244
Eggermont LHP, de Boer K, Muller M, Jaschke AC, Kamp O, Scherder EJA (2012) Cardiac disease and cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Heart 98(18):1334–1340. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2012-301682
Goncalves PD, Garcia-Garcia HM, Carvalho MS, Dores H, Sousa PJ, Marques H, Ferreira A, Cardim N, Teles RC, Raposo L, Gabriel HM, Almeida M, Aleixo A, Carmo MM, Machado FP, Mendes M (2013) Diabetes as an independent predictor of high atherosclerotic burden assessed by coronary computed tomography angiography: the coronary artery disease equivalent revisited. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29(5):1105–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-012-0168-4
Grodstein F (2007) Cardiovascular risk factors and cognitive function. Alzheimers & Dementia 3(2):S16–S22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2007.01.001
He Y, Dagher A, Chen Z, Charil A, Zijdenbos A, Worsley K, Evans A (2009) Impaired small-world efficiency in structural cortical networks in multiple sclerosis associated with white matter lesion load. Brain 132:3366–3379. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp089
Himberg J, Hyvarinen A, & ieee. (2003, Sep 17–19). ICASSO: Software for investigating the reliability of ICA estimates by clustering and visualization. [2003 ieee xiii workshop on neural networks for signal processing - nnsp'03]. 13th IEEE Workshop on Neural Networks for Signal Processing (NNSP 2003), Toulouse, FRANCE
Hou JC, Mohanty R, Nair VA, Dodd K, Beniwal-Patel P, Saha S, Prabhakaran V (2019) Alterations in resting-state functional connectivity in patients with Crohn’s disease in remission. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43878-0
Hudetz JA, Patterson KM, Pagel PS (2012) Comparison of pre-existing cognitive impairment, amnesic mild cognitive impairment, and multiple domain mild cognitive impairment in men scheduled for coronary artery surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol 29(7):320–325. https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0b013e328354223d
Jafari A, Xavier LD, Bernstein JD, Simonyan K, Bleier BS (2021) Association of sinonasal inflammation with functional brain connectivity. Jama Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 147(6):534–543. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0204
Kornelsen J, Wilson A, Labus JS, Witges K, Mayer EA, Bernstein CN (2020) Brain resting-state network alterations associated with crohn’s disease. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00048
Lei D, Li K, Li L, Chen F, Huang X, Lui S, Li J, Bi F, Gong QJR (2015) Disrupted functional brain connectome in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder. Radiology 276(3):818–827
Li HY, Sun K, Zhao RP, Hu J, Hao ZR, Wang F, Lu YJ, Liu F, Zhang Y (2017) Inflammatory biomarkers of coronary heart disease. Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark 22:504–515. https://doi.org/10.2741/4498
Li R, Zou T, Wang XY, Wang HY, Hu XF, Xie FF, Meng L, Chen HF (2022) Basal ganglia atrophy-associated causal structural network degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 43(3):1145–1156. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.25715
Liao D, Guo ZP, Tang LR, Gao Y, Zhang ZQ, Yang MH, Wang RP, Liu CH (2023) Alterations in regional homogeneity and functional connectivity associated with cognitive impairment in patients with hypertension: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Hypertens Res 46(5):1311–1325. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01168-3
Lin SM, Han Y, Duan SY, Wu PY, Wu NM, Xie T, Li Q, Lu Q, Zhao HY (2022) Aberrant spontaneous brain activity in coronary heart disease using fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations: a preliminary resting-state functional mri study. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2501886
Lin SM, Nie MM, Wang BS, Duan SY, Huang QW, Wu NM, Chen ZS, Zhao HY, Han Y (2023) Intrinsic brain abnormalities in chronic rhinosinusitis associated with mood and cognitive function. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1131114
Lopez C, Blanke O, Mast FW (2012) The human vestibular cortex revealed by coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Neuroscience 212:159–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.03.028
Lu SJ, Gao WJ, Wei ZG, Wang DD, Hu SH, Huang ML, Xu Y, Li LJ (2017) Intrinsic brain abnormalities in young healthy adults with childhood trauma: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study of regional homogeneity and functional connectivity. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 51(6):614–623. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004867416671415
Luscher TF, von Eckardstein A, Simic B (2012) Therapeutic targets to raise HDL in patients at risk or with coronary artery disease. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 10(6):720–724
Lynall ME, Bassett DS, Kerwin R, McKenna PJ, Kitzbichler M, Muller U, Bullmore ET (2010) Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 30(28):9477–9487. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0333-10.2010
Marek S, Dosenbach NUF (2019) Control networks of the frontal lobes. Handb Clin Neurol 163:333–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-804281-6.00018-5
Menon V (2011) Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model. Trends Cogn Sci 15(10):483–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Benitez-Temino B, Blesa FJ, Guridi J, Marin C, Rodriguez M (2008) Functional organization of the basal ganglia: Therapeutic implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23:S548–S559. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22062
Petroni F, Panzeri S, Hilgetag CC, Kotter R, Young MP (2001) Simultaneity of responses in a hierarchical visual network. NeuroReport 12(12):2753–2759. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200108280-00032
Roberts RO, Knopman DS, Geda YE, Cha RH, Roger VL, Petersen RC (2010) Coronary heart disease is associated with non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 31(11):1894–1902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.10.018
Rovio SP, Pahkala K, Raitakari OT (2019) Cognitive decline before and after incident coronary heart disease opportunity to intervene cognitive function trajectories. J Am Coll Cardiol 73(24):3051–3053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2019.04.020
Silbert BS, Scott DA, Evered LA, Lewis MS, Maruff PT (2007) Preexisting cognitive impairment in patients scheduled for elective coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Anesth Analg 104(5):1023–1028. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000263285.03361.3a
Smallwood J, Bernhardt BC, Leech R, Bzdok D, Jefferies E, Margulies DS (2021) The default mode network in cognition: a topographical perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci 22(8):503–513. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-021-00474-4
Stam CJ, de Haan W, Daffertshofer A, Jones BF, Manshanden I, van Walsum AMV, Montez T, Verbunt JPA, de Munck JC, van Dijk BW, Berendse HW, Scheltens P (2009) Graph theoretical analysis of magnetoencephalographic functional connectivity in Alzheimers disease. Brain 132:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn262
Wang J, Wang L, Zang Y, Yang H, Tang H, Gong Q, Chen Z, Zhu C, He YJH, b. m. (2009) Parcellation-dependent small-world brain functional networks: a resting-state fMRI study. Human Brain Mapp 30(5):1511–1523
Wang HD, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, Casey DC, Charlson FJ, Chen AZ, Coates MM, Coggeshall M, Dandona L, Dicker DJ, Erskine HE, Ferrari AJ, Fitzmaurice C, Foreman K, Forouzanfar MH, Fraser MS, Causes D (2016) Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet 388(10053):1459–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1
Wang CL, Cai HH, Sun XT, Si L, Zhang M, Xu YH, Qian YF, Zhu JJ (2020) Large-scale internetwork functional connectivity mediates the relationship between serum triglyceride and working memory in young adulthood. Neural Plast. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8894868
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature 393(6684):440–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/30918
Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Ford JM (2012) Default mode network activity and connectivity in psychopathology. Annu Rev Clinical Psychol 8:49–76. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143049
Xiao FL, Spruyt K, Lu C, Zhao DJ, Zhang J, Han F (2020) Resting-state brain network topological properties and the correlation with neuropsychological assessment in adolescent narcolepsy. Sleep. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsaa018
Yan AT, Shayne AJ, Brown KA, Gupta SN, Chan CW, Luu TM, Di Carli MF, Reynolds HG, Stevenson WG, Kwong RY (2006) Characterization of the peri-infarct zone by contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful predictor of post-myocardial infarction mortality. Circulation 114(1):32–39. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.106.613414
Zhang ZQ, Lu GM, Zhong Y, Tan QF, Yang ZG, Liao W, Chen ZL, Shi JX, Liu YJ (2009) Impaired attention network in temporal lobe epilepsy: a resting FMRI study. Neurosci Lett 458(3):97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.04.040
Zhang JR, Wang JH, Wu QZ, Kuang WH, Huang XQ, He Y, Gong QY (2011) Disrupted brain connectivity networks in drug-naive, first-episode major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiat 70(4):334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.05.018
Zhang YJ, Li M, Wang RN, Bi YZ, Li YD, Yi Z, Liu JX, Yu DH, Yuan K (2018) Abnormal brain white matter network in young smokers: a graph theory analysis study. Brain Imaging Behav 12(2):345–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9699-6
Zhang DS, Huang Y, Gao J, Lei YM, Ai K, Tang M, Yan XJ, Lei XY, Yang Z, Shao ZR, Zhang XL (2021a) Altered functional topological organization in type-2 diabetes mellitus with and without microvascular complications. Front Neurosci 15:726350. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.726350
Zhang SJ, Qian YF, Li Q, Xu XT, Li XY, Wang CL, Cai HH, Zhu JJ, Yu YQ (2021b) Metabolic and neural mechanisms underlying the associations between gut bacteroides and cognition: a large-scale functional network connectivity study. Front Neurosci 15:750704. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.750704
Zhang JC, Yan JY, Niu JH, Xu ZP, Fang X, You JY, Li T (2022) Irregular baseline brain activity in coronary artery disease patients with cognitive impairment: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Curr Neurovasc Res 19(2):131–136. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567202619666220516124552
Zheng L, Mack WJ, Chui HC, Heflin L, Mungas D, Reed B, DeCarli C, Weiner MW, Kramer JH (2012) Coronary artery disease is associated with cognitive decline independent of changes on magnetic resonance imaging in cognitively normal elderly adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 60(3):499–504. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03839.x
Zhong ZX, Zhao TD, Luo J, Guo ZH, Guo M, Li P, Sun J, He Y, Li ZJ (2014) Abnormal topological organization in white matter structural networks revealed by diffusion tensor tractography in unmedicated patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 51:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.01.005
Zhu JJ, Zhuo CJ, Liu F, Qin W, Xu LX, Yu CS (2016) Distinct disruptions of resting-state functional brain networks in familial and sporadic schizophrenia. Sci Rep 6:23577. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23577
Zhu JJ, Qian YF, Zhang B, Li XH, Bai Y, Li XS, Yu YQ (2020) Abnormal synchronization of functional and structural networks in schizophrenia. Brain Imaging Behav 14(6):2232–2241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00175-8
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all participants in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China (Grant No. J01535).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Si-Min Lin designed the study, analyzed the data and wrote the original manuscript. Yi Han, Shao-Yin Duan and Shu-Jia Guo undertook the statistical analysis. Qian-Ni Du, Nai-Ming Wu, Ting Xie and collected the clinical information and imaging data of healthy controls. Zhi-Shang Chen, Xiao-Yan Chen collected the clinical information and imaging data of patients. Heng-Yu Zhao, Yi Han and Pu-Yeh Wu revised the manuscript and supervised the research. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Wu, P., Duan, S. et al. Altered functional brain networks in coronary heart disease: independent component analysis and graph theoretical analysis. Brain Struct Funct 229, 133–142 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02724-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02724-w