Abstract
Purpose
The effects of electromagnetic fields of mobile phones on headaches have attracted researchers during the last decades. However, contradictory results have been reported so far.
Methods
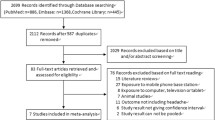
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, major databases including PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science were searched using suitable search terms and PRISMA guidelines to retrieve eligible studies for the effect of mobile phone use on headache. After the abstract and full-text screening, 33 studies were retrieved and the effect size in terms of odds ratio (OR) was extracted. Between-study heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistic and Q test, while publication bias was evaluated by funnel plot and Egger’s and Begg’s tests.
Results
Among 33 eligible studies, 30 eligible studies were included in the meta-analysis. When considering all studies, the pooled effect size of OR = 1.30(95% CI 1.21–1.39) was obtained, while the heterogeneity between studies was significant. Subgroup analyses by considering the age of participants and EMF exposure duration were performed to find the source of heterogeneity. The odds ratios when the age of participants was the variable were 1.33 (95% CI 1.14–1.53) and 1.29 (95% CI 1.20–1.37), for ages > 18 and age ≤ 18 years, respectively. When EMF exposure duration was considered, subgroup analysis obtained the pooled effect size of OR = 1.41(95% CI 1.22–1.61) and 1.23(95% CI 1.12–1.34), for EMF exposure duration > 100 and ≤ 100 minutes per week, respectively. The pooled effect sizes emphasized the effect of mobile phone use on headaches for all ages and exposure durations.
Conclusion
Results revealed that age and exposure duration (mainly call duration), both were the source of heterogeneity between studies. Furthermore, results showed that increasing call duration and mobile phone use in older individuals increased the risk of headache.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- EMF:
-
Electromagnetic field
- CS:
-
Cross-sectional
- CC:
-
Case-control
- C:
-
Cohort
- CCT:
-
Clinical controlled trial
References
Aalto S, Haarala C, Brück A, Sipilä H, Hämäläinen H, Rinne JO (2006) Mobile phone affects cerebral blood flow in humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(7):885–890. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600279
Abdel-Rassoul G et al (2007) Neurobehavioral effects among inhabitants around mobile phone base stations. Neurotoxicology 28(2):434–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2006.07.012
Augner C, Gnambs T, Winker R, Barth A (2012) Acute effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by GSM mobile phones on subjective well-being and physiological reactions: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 424:11–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.034
Auvinen A et al (2019) Headache, tinnitus and hearing loss in the international cohort study of mobile phone use and health (COSMOS) in Sweden and Finland. Int J Epidemiol 48(5):1567–1579. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyz127
Baliatsas C, Van Kamp I, Bolte J, Schipper M, Yzermans J, Lebret E (2012) Non-specific physical symptoms and electromagnetic field exposure in the general population: can we get more specific? A systematic review. Environ Int 41:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.12.002
Balikci K, Cem Ozcan I, Turgut-Balik D, Balik HH (2005) A survey study on some neurological symptoms and sensations experienced by long term users of mobile phones. Parodontol 53(1):30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patbio.2003.12.002
Berg-Beckhoff G et al (2009) Mobile phone base stations and adverse health effects: phase 2 of a cross-sectional study with measured radio frequency electromagnetic fields. Occup Environ Med 66(2):124–130. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2008.039834
Bjørk MH, Stovner LJ, Engstrøm M, Stjern M, Hagen K, Sand T (2009) Interictal quantitative EEG in migraine: a blinded controlled study. J Headache Pain 10(5):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10194-009-0140-4
Cavestro C et al (2007) Insulin metabolism is altered in migraineurs: a new pathogenic mechanism for migraine? Headache 47(10):1436–1442. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00719.x
Cerutti R, Presaghi F, Spensieri V, Valastro C, Guidetti V (2016) The potential impact of internet and mobile use on headache and other somatic symptoms in adolescence. A population-based cross-sectional study. Headache 56(7):1161–1170. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133528
Chetty-Mhlanga S et al (2020) Different aspects of electronic media use, symptoms and neurocognitive outcomes of children and adolescents in the rural Western Cape region of South Africa. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109315
Chia SE, Chia HP, Tan JS (2000a) Health hazards of mobile phones: prevalence of headache is increased among users in Singapore. Br Med J 321(7269):1155–1156
Chia SE, Chia HP, Tan JS (2000b) Prevalence of headache among handheld cellular telephone users in Singapore: a community study. Environ Health Perspect 108(11):1059–1062. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.001081059
Chiu CT, Chang YH, Chen CC, Ko MC, Li CY (2015) Mobile phone use and health symptoms in children. J Formos Med Assoc 114(7):598–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2014.07.002
Cho YM et al (2016) A follow-up study of the association between mobile phone use and symptoms of ill health. Environ Health Toxicol 32:e2017001. https://doi.org/10.5620/eht.e2017001
Chogchitpaisan W, Wiwatanadate P, Tanprawate S, Narkpongphun A, Siripon N (2020) Effect of smartphone output power on the undetermined headache among high school students: time-series study. J Med Assoc Thai 103(5):415–422. https://doi.org/10.35755/jmedassocthai.2020.05.9189
Chu MK, Song HG, Kim C, Lee BC (2011) Clinical features of headache associated with mobile phone use: a cross-sectional study in university students. BMC Neurol 11:115. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-11-115
Croft RJ, Chandler JS, Burgess AP, Barry RJ, Williams JD, Clarke AR (2002) Acute mobile phone operation affects neural function in humans. Clin Neurophysiol 113(10):1623–1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-2457(02)00215-8
Demir YP, Sümer MM (2019) Effects of smartphone overuse on headache, sleep and quality of life in migraine patients. Neurosciences 24(2):115–121. https://doi.org/10.17712/nsj.2019.2.20180037
Durusoy R, Hassoy H, Ozkurt A, Karababa AO (2017) Mobile phone use, school electromagnetic field levels and related symptoms: a cross-sectional survey among 2150 high school students in Izmir. Environ Health. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-017-0257-x
Farashi S (2017) Interaction between pancreatic β cell and electromagnetic fields: a systematic study toward finding the natural frequency spectrum of β cell system. Electromagn Biol Med 36(4):341–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/15368378.2017.1389751
Gandhi OP, Morgan LL, de Salles AA, Han YY, Herberman RB, Davis DL (2012) Exposure limits: the underestimation of absorbed cell phone radiation, especially in children. Electromagn Biol Med 31(1):34–51. https://doi.org/10.3109/15368378.2011.622827
Heinrich S, Thomas S, Heumann C, von Kries R, Radon K (2010) Association between exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields assessed by dosimetry and acute symptoms in children and adolescents: a population based cross-sectional study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x-anp-2020-0283
Heinrich S, Thomas S, Heumann C, von Kries R, Radon K (2011) The impact of exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic fields on chronic well-being in young people—a cross-sectional study based on personal dosimetry. Environ Int 37(1):26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.06.008
Henz D, Schöllhorn WI, Poeggeler B (2018) Mobile phone chips reduce increases in EEG brain activity induced by mobile phone-emitted electromagnetic fields. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00190
Hillert L et al (2008) The effects of 884 MHz GSM wireless communication signals on headache and other symptoms: an experimental provocation study. Bioelectromagnetics 29(3):185–196. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20379
Hocking B, Westerman R (2002) Neurological changes induced by a mobile phone. Occup Med 52(7):413–415
Huber R et al (2002) Electromagnetic fields, such as those from mobile phones, alter regional cerebral blood flow and sleep and waking EEG. J Sleep Res 11(4):289–295
Hutter HP, Moshammer H, Wallner P, Kundi M (2006) Subjective symptoms, sleeping problems, and cognitive performance in subjects living near mobile phone base stations. Occup Environ Med 63(5):307–313. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2005.020784
Hutter HP et al (2010) Tinnitus and mobile phone use. Occup Environ Med 67(12):804–808. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2009.048116
Johansson A, Nordin S, Heiden M, Sandström M (2010) Symptoms, personality traits, and stress in people with mobile phone-related symptoms and electromagnetic hypersensitivity. J Psychosom Res 68(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2009.06.009
Kim YS et al (2019) Altered vascular permeability in migraine-associated brain regions: evaluation with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Radiology 292(3):713–720. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2019182566
Koivisto M, Haarala C, Krause CM, Revonsuo A, Laine M, Hämäläinen H (2001) GSM phone signal does not produce subjective symptoms. Bioelectromagnetics 22(3):212–215. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.41
Kosasih SJ, Tan CK, Tan ESS (2020) Impact of mobile phone use on headache and sleep among working adults in Surabaya Indonesia. ASM Sci J 13(Specialissue5):217–222
Krause CM et al (2006) Mobile phone effects on children’s event-related oscillatory EEG during an auditory memory task. Int J Radiat Biol 82(6):443–450. https://doi.org/10.1080/09553000600840922
Kwon MS et al (2011) GSM mobile phone radiation suppresses brain glucose metabolism. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31(12):2293–2301. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2011.128
Ma L-L, Wang Y-Y, Yang Z-H, Huang D, Weng H, Zeng X-T (2020) Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools for primary and secondary medical studies: what are they and which is better? Mil Med Res 7(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-020-00238-8
Milde-Busch A, von Kries R, Thomas S, Heinrich S, Straube A, Radon K (2010) The association between use of electronic media and prevalence of headache in adolescents: results from a population-based cross-sectional study. BMC Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-10-12
Mohammadianinejad SE, Babaei M, Nazari P (2016) The effects of exposure to low frequency electromagnetic fields in the treatment of migraine headache: a cohort study. Electron Physician 8(12):3445–3449. https://doi.org/10.19082/3445
Montagni I, Guichard E, Carpenet C, Tzourio C, Kurth T (2016) Screen time exposure and reporting of headaches in young adults: a cross-sectional study. Cephalalgia 36(11):1020–1027. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102415620286
Mortazavi SM, Ahmadi J, Shariati M (2007) Prevalence of subjective poor health symptoms associated with exposure to electromagnetic fields among university students. Bioelectromagnetics 28(4):326–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20305
Mortazavi SM, Atefi M, Kholghi F (2011) The pattern of mobile phone use and prevalence of self-reported symptoms in elementary and junior high school students in Shiraz, Iran. Iran J Med Sci 36(2):96–103
Nittby H, Brun A, Eberhardt J, Malmgren L, Persson BR, Salford LG (2009) Increased blood-brain barrier permeability in mammalian brain 7 days after exposure to the radiation from a GSM-900 mobile phone. Pathophysiology 16(2–3):103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathophys.2009.01.001
Noack H, Lövdén M, Schmiedek F, Lindenberger U (2009) Cognitive plasticity in adulthood and old age: gauging the generality of cognitive intervention effects. Restor Neurol Neurosci 27(5):435–453
Oberman L, Pascual-Leone A (2013) Changes in plasticity across the lifespan: cause of disease and target for intervention. Prog Brain Res 207:91–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63327-9.00016-3
Oftedal G, Wilén J, Sandström M, Mild KH (2000) Symptoms experienced in connection with mobile phone use. Occup Med (lond) 50(4):237–245. https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/50.4.237
Oftedal G, Straume A, Johnsson A, Stovner LJ (2007) Mobile phone headache: a double blind, sham-controlled provocation study. Cephalalgia 27(5):447–455. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01336.x
Olesen J (2018) International classification of headache disorders. Lancet Neurol 17(5):396–397
Pall ML (2013) Electromagnetic fields act via activation of voltage-gated calcium channels to produce beneficial or adverse effects. J Cell Mol Med 17(8):958–965
Preece AW et al (2005) Effect of 902 MHz mobile phone transmission on cognitive function in children. Bioelectromagnetics 26(S7):S138–S143. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20128
Redmayne M, Smith E, Abramson MJ (2013) The relationship between adolescents’ well-being and their wireless phone use: a cross-sectional study. Environ Health 12:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069x-12-90
Riddervold IS et al (2008) Cognitive function and symptoms in adults and adolescents in relation to RF radiation from UMTS base stations. Bioelectromagnetics 29(4):257–267. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20388
Rubin GJ, Hahn G, Everitt BS, Cleare AJ, Wessely S (2006) Are some people sensitive to mobile phone signals? Within participants double blind randomised provocation study. BMJ (clin Res Ed) 332(7546):886–891. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38765.519850.55
Sandström M, Wilen J, Oftedal G, Hansson Mild K (2001) Mobile phone use and subjective symptoms. Comparison of symptoms experienced by users of analogue and digital mobile phones. Environ Health Toxicol 51(1):25–35. https://doi.org/10.5620/eht.e201700110.1093/occmed/51.1.25
Santini R, Santini P, Le Ruz P, Danze JM, Seigne M (2003) Survey study of people living in the vicinity of cellular phone base stations. Electromagn Biol Med 22(1):41–49. https://doi.org/10.1081/JBC-120020353
Schoeni A, Roser K, Bürgi A, Röösli M (2016) Symptoms in Swiss adolescents in relation to exposure from fixed site transmitters: a prospective cohort study. Environ Health 15(1):77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-016-0158-4
Schreier N, Huss A, Röösli M (2006) The prevalence of symptoms attributed to electromagnetic field exposure: a cross-sectional representative survey in Switzerland. Soz Praventivmed 51(4):202–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-006-5061-2
Söderqvist F, Carlberg M, Hardell L (2008) Use of wireless telephones and self-reported health symptoms: a population-based study among Swedish adolescents aged 15–19 years. Environ Health 7:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069x-7-18
Stalin P, Abraham SB, Kanimozhy K, Prasad RV, Singh Z, Purty AJ (2016) Mobile phone usage and its health effects among adults in a semi-urban area of southern India. J Clin Diagn Res. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO_2535_20
Starling AJ (2018) Diagnosis and management of headache in older adults. Mayo Clin Proc 93:252–262
Sudan M, Kheifets L, Arah O, Olsen J, Zeltzer L (2012) Prenatal and postnatal cell phone exposures and headaches in children. Open Pediatr Med J 6(2012):46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109315
Toth E et al (2008) Age-dependent effects of chronic stress on brain plasticity and depressive behavior. J Neurochem 107(2):522–532. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05642.x
Van den Bulck J (2007) Adolescent use of mobile phones for calling and for sending text messages after lights out: results from a prospective cohort study with a one-year follow-up. Sleep 30(9):1220–1223. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/30.9.1220
Wallace D et al (2010) Do TETRA (Airwave) base station signals have a short-term impact on health and well-being? A randomized double-blind provocation study. Environ Health Perspect 118(6):735–741. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901416
Wang J, Su H, Xie W, Yu S (2017) Mobile phone use and the risk of headache: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Sci Rep 7(1):1–7
Wells G, Shea B (2014) Newcastle–Ottawa quality assessment scale cohort studies. University of Ottawa, Ottawa
Zalata A, El-Samanoudy AZ, Shaalan D, El-Baiomy Y, Mostafa T (2015) In vitro effect of cell phone radiation on motility, DNA fragmentation and clusterin gene expression in human sperm. Int J Fertil Steril 9(1):129
Zarghami M, Khalilian A, Setareh J, Salehpour G (2015) the impact of using cell phones after light-out on sleep quality, headache, tiredness, and distractibility among students of a university in north of Iran. Iran J Psychiatry Behav Sci 9(4):e2010. https://doi.org/10.17795/ijpbs-2010
Zheng F et al (2015) Association between mobile phone use and self-reported well-being in children: a questionnaire-based cross-sectional study in Chongqing. China BMJ Open 5(5):e007302. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007302
Zwart JA, Dyb G, Holmen TL, Stovner LJ, Sand T (2004) The prevalence of migraine and tension-type headaches among adolescents in Norway. The Nord-Trøndelag Health Study (Head-HUNT-Youth), a large population-based epidemiological study. Cephalalgia 24(5):373–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00680.x
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Deputy of Research and Technology, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, for its support for the study (No. 140002071016). We confirm that our work was not funded by or on behalf of any governmental agency.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to study design. SF and SK performed systematic search, title, abstract and full-text screening steps. SF performed statistical and meta-analyses and wrote the initial draft. All authors contributed equally for discussing the results and revising the draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is nothing to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farashi, S., Bashirian, S., Khazaei, S. et al. Mobile phone electromagnetic radiation and the risk of headache: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 95, 1587–1601 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-022-01835-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-022-01835-x