Abstract
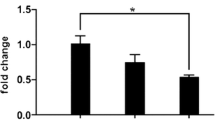
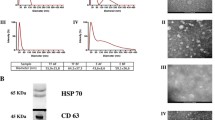
Exosome-encapsulated miRNAs could potentially be sensitive biomarkers of human diseases. Since a lipid bilayer membrane surrounds exosomes, the exosomal miRNA may stably exist in body fluids with diseases as well as biological fluids. Therefore, exosomal miRNA may be helpful for autopsy diagnosis. Assuming cadaver blood would be most useful, we initially examined serum exosome stability with regard to storage temperatures and periods. Characteristic analyses of the exosome revealed that exosomes and the content, miRNA, were stably preserved until at least three days when stored at below 20 °C. Subsequently, exosomal miRNA expression profiling was performed on the serum of acute myocardial infarction (AMI, 4 cases) autopsy bodies and on hemorrhagic shock bodies used as the control (CT, 3 cases). Results showed that significant twofold up- and downregulations of expression of 18 and 16 miRNAs were detectable in AMI as compared to the CT, respectively. miR-126-3p, which has been reported to be increased in serum of AMI patients and a mouse model, was one of the significantly upregulated miRNAs. Furthermore, dysregulation of exosomal miRNAs, such as miR-145-5p, miR-143-3p, and miR-222-3p, which are involved in cardioprotection, may be associated with AMI pathogenesis. These findings provide a novel perspective on the potential role of exosomal miRNA in determining the cause of death.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hessvik NP, Llorente A (2018) Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol Life Sci 75:193–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2595-9
Akers JC, Ramakrishnan V, Yang I, Hua W, Mao Y, Carter BS, Chen CC (2016) Optimizing preservation of extracellular vesicular miRNAs derived from clinical cerebrospinal fluid. Cancer Biomark 17:125–132. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-160609
Iaconetti C, Sorrentino S, De Rosa S, Indolfi C (2016) Exosomal miRNAs in heart disease. Physiol (Bethesda) 31:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00029.2015
Barile L, Moccetti T, Marban E, Vassalli G (2017) Roles of exosomes in cardioprotection. Eur Heart J 38:1372–1379. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehw304
Kinoshita T, Yip KW, Spence T, Liu FF (2017) MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles: potential cancer biomarkers. J Hum Genet 62:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.87
Jaiswal R, Sedger LM (2019) Intercellular vesicular transfer by exosomes, microparticles and oncosomes - implications for cancer biology and treatments. Front Oncol 9:125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00125
Russo I, Bubacco L, Greggio E (2012) Exosomes-associated neurodegeneration and progression of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Neurodegener Dis 1:217–225
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02871
Mori MA, Ludwig RG, Garcia-Martin R, Brandao BB, Kahn CR (2019) Extracellular miRNAs: from biomarkers to mediators of physiology and disease. Cell Metab 30:656–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.07.011
Liu T, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Li C, Miao YR, Lei Q, Li Q, Guo AY (2019) EVmiRNA: a database of miRNA profiling in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D89–D93. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky985
Nabel EG, Braunwald E (2012) A tale of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 366:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1112570
Markwerth P, Bajanowski T, Tzimas I, Dettmeyer R (2021) Sudden cardiac death-update. Int J Legal Med 135:483–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-020-02481-z
Zheng D, Huo M, Li B, Wang W, Piao H, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Li D, Wang T, Liu K (2020) The role of exosomes and exosomal microRNA in cardiovascular disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:616161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.616161
Akbar N, Digby JE, Cahill TJ, Tavare AN, Corbin AL, Saluja S, Dawkins S, Edgar L, Rawlings N, Ziberna K, McNeill E, Oxford Acute Myocardial Infarction S, Johnson E, Aljabali AA, Dragovic RA, Rohling M, Belgard TG, Udalova IA, Greaves DR, Channon KM, Riley PR, Anthony DC, Choudhury RP (2017) Endothelium-derived extracellular vesicles promote splenic monocyte mobilization in myocardial infarction. JCI Insight 2 https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.93344
Kanno S, Hirano S, Sakamoto T, Furuyama A, Takase H, Kato H, Fukuta M, Aoki Y (2020) Scavenger receptor MARCO contributes to cellular internalization of exosomes by dynamin-dependent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. Sci Rep 10:21795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78464-2
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita F, Matsuki Y, Ochiya T (2010) Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem 285:17442–17452. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.107821
Park SJ, Jeon H, Yoo SM, Lee MS (2018) The effect of storage temperature on the biological activity of extracellular vesicles for the complement system. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 54:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-0261-7
Ge Q, Zhou Y, Lu J, Bai Y, Xie X, Lu Z (2014) miRNA in plasma exosome is stable under different storage conditions. Molecules 19:1568–1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19021568
Schulz E, Karagianni A, Koch M, Fuhrmann G (2020) Hot EVs - How temperature affects extracellular vesicles. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 146:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.11.010
Duan S, Wang C, Xu X, Zhang X, Su G, Li Y, Fu S, Sun P, Tian J (2022) Peripheral serum exosomes isolated from patients with acute myocardial infarction promote endothelial cell angiogenesis via the miR-126-3p/TSC1/mTORC1/HIF-1α pathway. Int J Nanomed 17:1577–1592. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S338937
Ling H, Guo Z, Shi Y, Zhang L, Song C (2020) Serum exosomal microRNA-21, microRNA-126, and PTEN are novel biomarkers for diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome. Front Physiol 11:654. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00654
Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Treguer K, Boettger T, Horrevoets AJ, Zeiher AM, Scheffer MP, Frangakis AS, Yin X, Mayr M, Braun T, Urbich C, Boon RA, Dimmeler S (2012) Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 14:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2441
Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2015) Human miR-221/222 in physiological and atherosclerotic vascular remodeling. Biomed Res Int 2015:354517. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/354517
Lai TC, Lee TL, Chang YC, Chen YC, Lin SR, Lin SW, Pu CM, Tsai JS, Chen YL (2020) MicroRNA-221/222 mediates ADSC-exosome-induced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion by targeting PUMA and ETS-1. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:569150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.569150
Pang J, Ye L, Chen Q, Wang J, Yang X, He W, Hao L (2020) The effect of microRNA-101 on angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells during hypoxia and in mice with myocardial infarction. Biomed Res Int 2020:5426971. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5426971
Higashi K, Yamada Y, Minatoguchi S, Baba S, Iwasa M, Kanamori H, Kawasaki M, Nishigaki K, Takemura G, Kumazaki M, Akao Y, Minatoguchi S (2015) MicroRNA-145 repairs infarcted myocardium by accelerating cardiomyocyte autophagy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 309:H1813–H1826. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00709.2014
Ragusa M, Barbagallo C, Statello L, Caltabiano R, Russo A, Puzzo L, Avitabile T, Longo A, Toro MD, Barbagallo D, Valadi H, Di Pietro C, Purrello M, Reibaldi M (2015) miRNA profiling in vitreous humor, vitreal exosomes and serum from uveal melanoma patients: Pathological and diagnostic implications. Cancer Biol Ther 16:1387–1396. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2015.1046021
Zhao Z, Liu G, Zhang H, Ruan P, Ge J, Liu Q (2021) BIRC5, GAJ5, and lncRNA NPHP3-AS1 are correlated with the development of atrial fibrillation-valvular heart disease. Int Heart J 62:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1536/ihj.20-238
Hou J, Wang J, Lin C, Fu J, Ren J, Li L, Guo H, Han X, Liu J (2014) Circulating microRNA profiles differ between Qi-stagnation and Qi-deficiency in coronary heart disease patients with blood stasis syndrome. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014:926962. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/926962
Gryshkova V, Lushbough I, Palmer J, Burrier R, Delaunois A, Donley E, Valentin JP (2022) MicroRNAs signatures as potential biomarkers of structural cardiotoxicity in human-induced pluripotent stem-cell derived cardiomyocytes. Arch Toxicol https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03280-8
Jordan NP, Tingle SJ, Shuttleworth VG, Cooke K, Redgrave RE, Singh E, Glover EK, Ahmad Tajuddin HB, Kirby JA, Arthur HM, Ward C, Sheerin NS, Ali S (2021) MiR-126-3p Is dynamically regulated in endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition during fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci 22 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168629
Xue S, Liu D, Zhu W, Su Z, Zhang L, Zhou C, Li P (2019) Circulating MiR-17-5p, MiR-126-5p and MiR-145-3p are novel biomarkers for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Front Physiol 10:123. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00123
Li M, Ren C, Wu C, Li X, Li X, Mao W (2020) Bioinformatics analysis reveals diagnostic markers and vital pathways involved in acute coronary syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract 2020:3162581. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3162581
Xu C, Jia Z, Cao X, Wang S, Wang J, An L (2022) Hsa_circ_0007059 promotes apoptosis and inflammation in cardiomyocytes during ischemia by targeting microRNA-378 and microRNA-383. Cell Cycle 21:1003–1019. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2022.2040122
Eyyupkoca F, Ercan K, Kiziltunc E, Ugurlu IB, Kocak A, Eyerci N (2022) Determination of microRNAs associated with adverse left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Mol Cell Biochem 477:781–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04330-y
Su Y, Sun Y, Tang Y, Li H, Wang X, Pan X, Liu W, Zhang X, Zhang F, Xu Y, Yan C, Ong SB, Xu D (2021) Circulating miR-19b-3p as a novel prognostic biomarker for acute heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc 10:e022304. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.121.022304
Corsten MF, Heggermont W, Papageorgiou AP, Deckx S, Tijsma A, Verhesen W, van Leeuwen R, Carai P, Thibaut HJ, Custers K, Summer G, Hazebroek M, Verheyen F, Neyts J, Schroen B, Heymans S (2015) The microRNA-221/-222 cluster balances the antiviral and inflammatory response in viral myocarditis. Eur Heart J 36:2909–2919. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv321
Zhang Q, Kandic I, Kutryk MJ (2011) Dysregulation of angiogenesis-related microRNAs in endothelial progenitor cells from patients with coronary artery disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 405:42–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.119
Verjans R, Peters T, Beaumont FJ, van Leeuwen R, van Herwaarden T, Verhesen W, Munts C, Bijnen M, Henkens M, Diez J, de Windt LJ, van Nieuwenhoven FA, van Bilsen M, Goumans MJ, Heymans S, González A, Schroen B (2018) MicroRNA-221/222 family counteracts myocardial fibrosis in pressure overload-induced heart failure. Hypertension 71:280–288. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.10094
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the assistance of the Research Equipment Sharing Center at Nagoya City University. We would like to thank Mr. Hiroshi Takase of the Research Equipment Sharing Center of Nagoya City University for his assistance with the transmission electron microscopic observations, and Dr. Seishiro Hirano of the National Institute for Environmental Studies for his help with the dynamic light scattering analysis and suggestions.
Funding
JSPS KAKENHI grant (number 21K10526).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. K. and T. S.: conceived and designed the experiments; S. K. and T. S.: performed the experiments and data analyses; M. F., H. K., and Y. A.: performed the autopsies and examinations; S. K. wrote the manuscript with contributions from co-authors; Y. A.: project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study in use of human serum and autopsy samples was approved by the Institutional Review Board for the Protection of Human Subjects in Research at Nagoya City University (approval number: 60–18-0151 and 60–21-0144), respectively.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Data availability
All data have been reported in the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kanno, S., Sakamoto, T., Fukuta, M. et al. Stability of exosomes in the postmortem serum and preliminary study on exosomal miRNA expression profiling in serum from myocardial infarction cadavers. Int J Legal Med 137, 825–834 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-022-02913-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-022-02913-y