Abstract
Purpose
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps can be classified as eosinophilic or neutrophilic based on the major inflammatory cell type in the tissue. There is a need for predictive parameters to enable rhinologists to identify the type of nasal polyp in a patient without surgery. The aim of the present study was to test the predictive value of the markers of inflammation to estimate eosinophilic nasal polyps.
Methods
The study analyzed 299 patients who underwent sinus surgery for nasal polyps from 2012 to 2019. Patients were divided into two groups according to pathology results (eosinophilic polyps = group 1, neutrophilic polyps = group 2). The values of preoperative complete blood count, systemic immune inflammation index, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio were compared.
Results
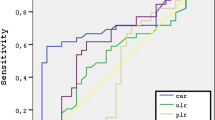
In our series, results of ROC analyses for both mean eosinophil count and systemic immune inflammation index were statistically significant. For the eosinophil count (AUC = 0.681, p < 0.001) and systemic immune inflammation index (AUC = 0.621, p = 0.001). Patients with an eosinophil cut-off value of 0.25 cells × 109/L had ORs of 49.27 (95% CI 11.68–207.81) and sensitivity: 0.69, specificity: 0.64. Patients with a systemic immune inflammation index cut-off value of 332.39 had ORs of 1.003 (95% CI 1.002–1.004) and sensitivity: 0.84, specificity: 0.39.
Conclusion
The systemic immune inflammation index and absolute blood eosinophil count could be used to predict nasal polyp subtypes before surgery. We believe that systemic immune inflammation index should also be studied to estimate postoperative recurrence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pleis JR, Coles R (2002) Summary health statistics for U.S. adults: National Health Interview Survey,1998. Vital Health Stat 10(209):1–113
Pleis JR, Lucas JW, Ward BW (2009) Summary health statistics for U.S. adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2008. Vital Health Stat 10(242):1–157
Adams PF, Hendershot GE, Marano MA (1999) Current estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 1996. Vital Health Stat 10(200):1–203
Shi JB, Fu QL, Zhang H, Cheng L, Wang YJ, Zhu D, Lv W, Liu SX, Li PZ, Ou CQ, Xu G (2015) Epidemiology of chronic rhinosinusitis: results from a cross-sectional survey in seven Chinese cities. Allergy 70(5):533–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12577
Hastan D, Fokkens WJ, Bachert C, Newson RB, Bislimovska J, Bockelbrink A, Bousquet PJ, Brozek G, Bruno A, Dahlén SE, Forsberg B, Gunnbjörnsdóttir M, Kasper L, Krämer U, Kowalski ML, Lange B, Lundbäck B, Salagean E, Todo-Bom A, Tomassen P, Toskala E, van Drunen CM, Bousquet J, Zuberbier T, Jarvis D, Burney P (2011) Chronic rhinosinusitis in European underestimated disease A GA2LEN study. Allergy 66(9):1216–1223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02646.x
Yenigun A (2015) Assessment of patients with nasal polyposis by the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 25(4):193–199. https://doi.org/10.5606/kbbihtisas.2015.10734
Hu Y, Cao PP, Liang GT, Cui Y, Liu Z (2012) Diagnostic significance of blood eosinophil count in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Chinese adults. Laryngoscope 122(3):498–503. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.22507
Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, Lanza DC, Marple BF, Nicklas RA, Adinoff AD, Bachert C, Borish L, Chinchilli VM, Danzig MR, Ferguson BJ, Fokkens WJ, Jenkins SG, Lund VJ, Mafee MF, Naclerio RM, Pawankar R, Ponikau JU, Schubert MS, Slavin RG, Stewart MG, Togias A, Wald ER, Winther B, Initiative R (2006) Rhinosinusitis: developing guidance for clinical trials. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135(5):31–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2006.09.014
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, Cohen N, Cervin S, Douglas R, Gevaert P, Georgalas C, Goossens H, Harvey R, Hellings P, Hopkins C, Jones N, Joos G, Kalogjera L, Kern B, Kowalski M, Price D, Riechelmann H, Schlosser R, Senior B, Thomas M, Toskala E, Voegels R, Wang DY, Wormald PJ (2012) EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology 50(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.4193/rhino50e2
Tecimer SH, Kasapoglu F, Demir UL, Ozmen OA, Coskun H, Basut O (2015) Correlation between clinical findings and eosinophil/neutrophil ratio in patients with nasal polyps. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(4):915–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-0143174-4
Ishitoya J, Sakuma Y, Tsukuda M (2010) Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan. Allergol Int 59(3):239–245. https://doi.org/10.2332/allergolint.10-RAI-0231
Brescia G, Zanotti C, Parrino D, Barion U, Marioni G (2018) Nasal polyposis pathophysiology: endotype and phenotype open issues. Am J Otolaryngol 39(4):441–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.03.020
Lou H, Zhang N, Bachert C, Zhang L (2018) Highlights of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in definition, prognosis, and advancement. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 8(11):1218–1225. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22214
Wang X, Zhang N, Bo M, Holtappels G, Zheng M, Lou H, Wang H, Zhang L, Bachert C (2016) Diversity of TH cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138(5):1344–1353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.05.041
Eltohami YI, Kao HK, Lao WW, Huang Y, Abdelrahman M, Liao CT, Yen TC, Chang KP (2018) The prediction value of the systemic inflammation score for oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 158(6):1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599817751678
Jiang W, Chen Y, Huang J, Xi D, Chen J, Shao Y, Xu G, Ying W, Wei J, Chen J, Ning Z, Gu W, Pei H (2017) Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts the clinical outcome in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a propensity score-matched analysis. Oncotarget 8(39):66075–66086. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19796
Boztepe OF, Gun T, Demir M, Gur OE, Ozel D, Dogru H (2016) A novel predictive marker for the recurrence of nasal polyposis following endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(6):1439–1444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3753-z
Atan D, Özcan KM, Köseoğlu S, Ikinciogullari A, Cetin MA, Ensari S, Dere H (2015) New predictive parameters of nasal polyposis: neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 25(2):97–101. https://doi.org/10.5606/kbbihtisas.2015.01947
Brescia G, Pedruzzi B, Barion U, Cinetto F, Giacomelli L, Martini A, Marioni G (2016) Are neutrophil-, eosinophil-, and basophil-to-lymphocyte ratios useful markers for pinpointing patients at higher risk of recurrent sinonasal polyps? Am J Otolaryngol 37(4):339–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.02.002
Wang H, Pan L, Liu Z (2019) Neutrophils as a protagonist and target in chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 12(4):337–347. https://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2019.00654
Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, Bai J, Fan Y, Xia W, Luo Q, Zheng J, Wang H, Li Z, Xia J, Jiang H, Liu Z, Shi J, Li H, Xu G, Nasal Health Group China (2012) Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129(6):1522–1528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.079
Liao B, Liu JX, Li ZY, Zhen Z, Cao PP, Yao Y, Long XB, Wang H, Wang Y, Schleimer R, Liu Z (2018) Multidimensional endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis and their association with treatment outcomes. Allergy 73(7):1459–1469. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.13411
Cervin A, Wallwork B (2007) Macrolide therapy of chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 45(4):259–267
Kim DK, Jin HR, Eun KM, Mo JH, Cho SH, Oh S, Cho D, Kim W (2017) The role of interleukin-33 in chronic rhinosinusitis. Thorax 72(7):635–645. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208772
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was approved by the ethical committee of Suleyman Demirel University (date: 16.04.2020, number: 116).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the parents of all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivrice, M.E., Okur, E., Yasan, H. et al. Can the systemic immune inflammation index preoperatively predict nasal polyp subtypes?. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277, 3045–3050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06174-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06174-6