Abstract
Purpose
The complications of surgical treatments of stress urinary incontinence have led to the search for less invasive and safer treatment procedures. We aimed to investigate the efficacy of locally administered injectable platelet-rich fibrin (i-PRF), an autologous material that plays an important role in tissue regeneration, in women with stress urinary incontinence.
Methods
Thirty-four women were included in this prospective, single-center, and interventional study, suffering from stress urinary incontinence refractory to conservative treatment. Three consecutive i-PRF injections were applied to the mid-urethra localization at anterior vaginal wall with an interval of 1 month. ICIQ-SF, UDI-6, IIQ-7 and POPDI-6 questionnaires were used to measure pre‑treatment, 1 month and 6 months post‑treatment symptom severity and the clinical outcomes were recorded.
Results
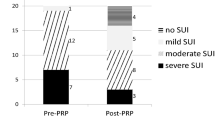
The mean age of the patients was 51.5 ± 9.8 years. ICIQ-SF, UDI-6, IIQ-7 and POPDI-6 questionnaires results revealed significant clinical improvement of stress urinary incontinence severity afer the administration of i-PRF (p < 0.001). The results at 1 and 6 months after treatment did not change statistically significantly.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that locally administiration of i-PRF is efective in relieving SUI symptoms with high success rates without any adverse effects reported. i-PRF injection may have the potential to be a novel, minimally invasive, and low-risk procedure, that could be an alternative and simple treatment modality to surgery for female patients with stress urinary incontinence. Additionally, it may create new avenues for research on therapeutic implementation of i-PRF.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
A data availability statement was not prepared.
References
Hunskaar S, Burgio K, Diokno A, Herzog AR, Hjälmås K, Lapitan MC (2003) Epidemiology and natural history of urinary incontinence in women. Urology 62(4 Suppl 1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(03)00755-6
Kwon CS, Lee JH (2014) Prevalence, risk factors, quality of life, and health-care seeking behaviors of female urinary incontinence: results from the 4th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2007–2009). Int Neurourol J 18(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.5213/inj.2014.18.1.31
Tantanasis T, Daniilidis A, Pantelis A, Chatzis P, Vrachnis N (2013) Minimally invasive techniques for female stress urinary incontinence, how, why, when. Arch Gynecol Obstet 288(5):995–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-013-3024-4
Kmietowicz Z (2018) Use mesh implants for stress urinary incontinence only as last resort, says NICE. BMJ 363:k4242. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k4242
Chiang CH, Kuo HC (2022) The efficacy and mid-term durability of urethral sphincter ınjections of platelet-rich plasma in treatment of female stress urinary ıncontinence. Front Pharmacol 13:847520. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.847520
Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A, Girard MO, Schoeffler C, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Dohan DM (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101(3):e56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.011
Malavolta EA, Assuncao JH, Gracitelli ME, Ferreira Neto AA (2016) Comments on: Evaluation of platelet-rich plasma and fibrin matrix to assist in healing and repair of rotator cuff injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil 30(7):726–727. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269215516645433
Miron R, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Bishara M, Zhang Y, Hernandez M, Choukroun J (2016) Platelet rich fibrin and soft tissue wound healing: a systematic review. Tissue Eng Pt B Rev 23(1):83–99. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2016.0233
Narayanaswamy R, Patro BP, Jeyaraman N, Gangadaran P, Rajendran RL, Nallakumarasamy A, Jeyaraman M, Ramani P, Ahn BC (2023) Evolution and clinical advances of platelet-rich fibrin in musculoskeletal regeneration. Bioengineering (Basel) 10(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010058
Choukroun J, Ghanaati S (2018) Reduction of relative centrifugation force within injectable platelet-rich-fibrin (PRF) concentrates advances patients’ own inflammatory cells, platelets and growth factors: the first introduction to the low speed centrifugation concept. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 44(1):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-017-0767-9
Abd El Raouf M, Wang X, Miusi S, Chai J, Mohamed AbdEl-Aal AB, Nefissa Helmy MM, Ghanaati S, Choukroun J, Choukroun E, Zhang Y, Miron RJ (2019) Injectable-platelet rich fibrin using the low speed centrifugation concept improves cartilage regeneration when compared to platelet-rich plasma. Platelets 30(2):213–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537104.2017.1401058
Liu J, Liu Z, Tang Y, Munoz A, Zhang Y, Li X (2022) Treatment with platelet-rich plasma attenuates proprioceptor abnormalities in a rat model of postpartum stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J 33(8):2159–2167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-022-05112-w
Long CY, Lin KL, Shen CR, Ker CR, Liu YY, Loo ZX, Hsiao HH, Lee YC (2021) A pilot study: effectiveness of local injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma in treating women with stress urinary incontinence. Sci Rep 11(1):1584. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80598-2
Athanasiou S, Kalantzis C, Zacharakis D, Kathopoulis N, Pontikaki A, Grigoriadis T (2021) The use of platelet-rich plasma as a novel nonsurgical treatment of the female stress urinary ıncontinence: a prospective pilot study. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg 27(11):e668–e672. https://doi.org/10.1097/SPV.0000000000001100
Behnia-Willison F, Nguyen TTT, Norbury AJ, Mohamadi B, Salvatore S, Lam A (2019) Promising impact of platelet rich plasma and carbon dioxide laser for stress urinary incontinence. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X 5:100099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurox.2019.100099
Grigoriadis T, Kalantzis C, Zacharakis D, Kathopoulis N, Prodromidou A, Xadzilia S, Athanasiou S (2023) Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of stress urinary ıncontinence—a randomized trial. Urogynecology (Phila) 30(1):42–49. https://doi.org/10.1097/SPV.0000000000001378
Lee PJ, Jiang YH, Kuo HC (2021) A novel management for postprostatectomy urinary incontinence: platelet-rich plasma urethral sphincter injection. Sci Rep 11(1):5371. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84923-1
Maene A, Deniz G, Bouland C, Lagneaux L, Philippart P, Buxant F (2022) Suburethral implantation of autologous regenerative cells for female stress urinary incontinence management: results of a pilot study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 278:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2022.08.028
Matz EL, Pearlman AM, Terlecki RP (2018) Safety and feasibility of platelet rich fibrin matrix injections for treatment of common urologic conditions. Investig Clin Urol 59(1):61–65. https://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2018.59.1.61
Miron RJ, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Hernandez M, Kandalam U, Zhang Y, Ghanaati S, Choukroun J (2017) Injectable platelet rich fibrin (i-PRF): opportunities in regenerative dentistry? Clin Oral Investig 21(8):2619–2627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2063-9
Litvinov RI, Weisel JW (2016) What is the biological and clinical relevance of fibrin? Semin Thromb Hemost 42(4):333–343. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1571342
Alves R, Grimalt R (2018) A review of platelet-rich plasma: history, biology, mechanism of action, and classification. Skin Appendage Disord 4(1):18–24. https://doi.org/10.1159/000477353
Miron RJ, Zucchelli G, Pikos MA, Salama M, Lee S, Guillemette V, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Bishara M, Zhang Y, Wang HL, Chandad F, Nacopoulos C, Simonpieri A, Aalam AA, Felice P, Sammartino G, Ghanaati S, Hernandez MA, Choukroun J (2017) Use of platelet-rich fibrin in regenerative dentistry: a systematic review. Clin Oral Investig 21(6):1913–1927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2133-z
Fan Y, Perez K, Dym H (2020) Clinical uses of platelet-rich fibrin in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Dent Clin North Am 64(2):291–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden2019.12.012
Karimi K, Rockwell H (2019) The benefits of platelet-rich fibrin. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 27(3):331–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2019.03.005
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Gogly B (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101(3):e37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.008
Wang X, Zhang Y, Choukroun J, Ghanaati S, Miron RJ (2018) Effects of an injectable platelet-rich fibrin on osteoblast behavior and bone tissue formation in comparison to platelet-rich plasma. Platelets 29(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537104.2017.1293807
Ozsagir ZB, Saglam E, Sen Yilmaz B, Choukroun J, Tunali M (2020) Injectable platelet-rich fibrin and microneedling for gingival augmentation in thin periodontal phenotype: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 47(4):489–499. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13247
Shah R, Gowda TM, Thomas R, Kumar T (2022) Second-generation liquid platelet concentrates: a literature review. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 23(11):1315–1326. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201022666210823102618
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ülkü Mete Ural; Project development, study design, data collection, draft manuscript, literature review, manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ural, Ü.M. The effect of injectable platelet rich fibrin as a nonsurgical treatment of the female stress urinary incontinence. Arch Gynecol Obstet 309, 2229–2236 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-024-07431-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-024-07431-3