Abstract
Background
Placenta accreta is one of the most serious complications in obstetrics and gynecology. Villous trophoblasts (VT) and extravillous trophoblasts (EVT) play a central role in normal placentation. Placenta accreta is characterized by abnormal invasion of EVT cells through the uterine layers, due to changes in several parameters, including adhesion proteins. Although αvβ3 integrin is a central adhesion molecule, participating in multiple invasive pathological conditions including cancer, data on placenta accreta are lacking.
Objective
To study the expression pattern of αvβ3 integrin in placenta accreta in comparison with normal placentas.
Study design
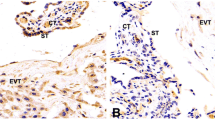
We collected tissue samples from placentas defined as percreta, the most severe presentation of placenta accreta and from normal control placentas (n = 10 each). The samples underwent protein extractions for analyses of αvβ3 expression by Western blots (WB) and a parallel tissue assessment by immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Results
WB results indicated significantly elevated αvβ3 integrin expression in the percreta samples compared to normal placentas. These elevated levels were mainly contributed by EVT cells, as demonstrated by IHC. αvβ3 integrin demonstrated a classical membranal expression in the VT cells, whereas a uniformly distributed expression was documented in the EVT cells. These patterns of the αvβ3 integrin localization were similar in both accreta and normal placental samples.
Conclusions
Enhanced αvβ3 integrin expression, mainly in extra villous trophoblasts of placenta percreta, implies for a role of this adhesion molecule in pathological placentation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Usta I, Hobeika E, Abu MA et al (2005) Placenta previa-accreta: risk factors and complications. Am J Obs Gynecol 193:1045–1049
Shellhaas CS, Gilbert S, Landon MB et al (2010) The frequency and complication rates of hysterectomy accompanying Cesarean delivery. Obstet Anesth Dig. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aoa.0000386823.05009.27
Eller AG, Porter TT, Soisson P, Silver RM (2009) Optimal management strategies for placenta accreta. BJOG An Int J Obstet Gynaecol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.02037.x
Warshak CR, Ramos GA, Eskander R et al (2010) Effect of predelivery diagnosis in 99 consecutive cases of placenta accreta. Obstet Gynecol. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181c4f12a
Eller AG, Bennett MA, Sharshiner M et al (2011) Maternal morbidity in cases of placenta accreta managed by a multidisciplinary care team compared with standard obstetric care. Obstet Gynecol. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3182051db2
Shamshirsaz AA, Fox KA, Salmanian B et al (2015) Maternal morbidity in patients with morbidly adherent placenta treated with and without a standardized multidisciplinary approach. Am J Obstet Gynecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2014.08.019
Tantbirojn P, Crum CP, Parast MM (2008) Pathophysiology of placenta creta: the role of decidua and extravillous trophoblast. Placenta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2008.04.008
Khong TY (2008) The pathology of placenta accreta, a worldwide epidemic. J Clin Pathol 61(12):1243–1246
Rosenberg T, Pariente G, Sergienko R et al (2011) Critical analysis of risk factors and outcome of placenta previa. Arch Gynecol Obstet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-010-1598-7
Eshkoli T, Weintraub AY, Sergienko R, Sheiner E (2013) Placenta accreta: Risk factors, perinatal outcomes, and consequences for subsequent births. Am J Obstet Gynecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.12.037
Tarrade A, Lai Kuen R, Malassiné A et al (2001) Characterization of human villous and extravillous trophoblasts isolated from first trimester placenta. Lab Investig. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.3780334
Fisher SJ, Damsky CH (1993) Human cytotrophoblast invasion. Semin Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.1006/scel.1993.1022
Chakraborty C, Gleeson LM, McKinnon T, Lala PK (2002) Regulation of human trophoblast migration and invasiveness. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1139/y02-016
Kim S, Harris M, Varner JA (2000) Regulation of integrin α(v)β3-mediated endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis by integrin α5β1 and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M003668200
Somanath PR, Malinin NL, Byzova T V. (2009) Cooperation between integrin ανβ3 and VEGFR2 in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 12(2):177–185
Horton MA (1997) The alpha v beta 3 integrin "vitronectin receptor". Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29(5):721–725
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA (2010) Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10(1):9–22
Carduner L, Leroy-Dudal J, Picot CR et al (2014) Ascites-induced shift along epithelial-mesenchymal spectrum in ovarian cancer cells: Enhancement of their invasive behavior partly dependant on αv integrins. Clin Exp Metastasis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-014-9658-1
Merviel P, Challier J, Carbillon L et al (2001) The role of integrins in human embryo implantation. Fetal Diagn Ther 16:364–371
Keramidas M, Lavaud J, Sergent F et al (2014) Noninvasive and quantitative assessment of in vivo fetomaternal interface angiogenesis using RGD-based fluorescence. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/309082
Cohen K, Ellis M, Khoury S et al (2011) Thyroid hormone is a MAPK-dependent growth factor for human myeloma cells acting via αvβ3 integrin. Mol Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0187
Maldonado-Estrada J, Menu E, Roques P et al (2004) Evaluation of Cytokeratin 7 as an accurate intracellular marker with which to assess the purity of human placental villous trophoblast cells by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2003.03.001
Pollheimer J, Vondra S, Baltayeva J, et al (2018) Regulation of placental extravillous trophoblasts by the maternal uterine environment. Front Immunol 9:2597
Bartels HC, Postle JD, Downey P, Brennan DJ (2018) Placenta accreta spectrum: a review of pathology, molecular biology, and biomarkers. Dis Markers 2018:1507674
Damsky CH, Librach C, Lim KH, et al (1994) Integrin switching regulates normal trophoblast invasion. Development 120(12):3657–3666
Chen Y, Zhang H, Han F et al (2018) The depletion of MARVELD1 leads to murine placenta accreta via integrin β4-dependent trophoblast cell invasion. J Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26098
Sülz L, Valenzuela JP, Salvatierra AM et al (1998) The expression of α(v) and β3 integrin subunits in the normal human Fallopian tube epithelium suggests the occurrence of a tubal implantation window. Hum Reprod. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/13.10.2916
Ruck P, Marzusch K, Kaiserling E, et al (1994) Distribution of cell adhesion molecules in decidua of early human pregnancy: an immunohistochemical study. Lab Investig 71(1):94–101
Ruck P, Kaiserling E, Horny H et al (1994) Cell adhesion molecules on large granular lymphocytes and endothelial cells in decidua of early human pregnancy. Virchows Arch 424:228
Lessey BA, Castelbaum AJ, Buck CA et al (1994) Further characterization of endometrial integrins during the menstrual cycle and in pregnancy. Fertil Steril. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-0282(16)56937-4
Gray CA, Adelson DL, Bazer FW et al (2004) Discovery and characterization of an epithelial-specific galectin in the endometrium that forms crystals in the trophectoderm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402669101
Illera MJ, Cullinan E, Gui Y et al (2000) Blockade of the αvβ3 integrin adversely affects implantation in the mouse1. Biol Reprod. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod62.5.1285
Illera MJ, Lorenzo PL, Gui YT et al (2003) A role for αvβ3 integrin during implantation in the rabbit model. Biol Reprod. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolreprod/68.3.766
Lessey BA, Castelbaum AJ, Sawin SW et al (1994) Aberrant integrin expression in the endometrium of women with endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.79.2.7519194
Xia J, Qiao F, Su F, Liu H (2009) Implication of expression of osteopontin and its receptor integrin ανβ3 in the placenta in the development of preeclampsia. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol - Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0617-z
Robinson NJ, Baker PN, Jones CJP, Aplin JD (2007) A role for tissue transglutaminase in stabilization of membrane-cytoskeletal particles shed from the human placenta. Biol Reprod. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.107.061747
Hynes RO (1992) Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69(1):11–25
Bowen JA, Hunt JS (2000) The role of integrins in reproduction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 223(4):331–343
Grasso E, Calo G, Vota D et al (2015) Trophoblast cells primed with vasoactive intestinal peptide enhance monocyte migration and apoptotic cell clearance through αvβ3 integrin portal formation in a model of maternal-placental interaction. Mol Hum Reprod. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gav059
Wang S, Zhou X, Yang J (2018) Integrin αvβ3 is essential for maintenance of decidua tissue homeostasis and of natural killer cell immune tolerance during pregnancy. Reprod Sci. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719117746766
Wang Y, Liu J, Lin B et al (2011) Study on the expression and clinical significances of Lewis y antigen and integrin αv, β3 in epithelial ovarian tumors. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12063409
Guo W, Giancotti FG (2004) Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(10):816–826
Rathinam R, Alahari SK (2010) Important role of integrins in the cancer biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29(1):223–237
Cohen K, Flint N, Shalev S et al (2014) Thyroid hormone regulates adhesion, migration and matrix metalloproteinase 9 activity via avß3 integrin in myeloma cells. Oncotarget. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2205
Funding
We declare no funding support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OW declare that he participated in collection of the data for this project, cleaned, assimilated and analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. DK declare that she participated in collecting and analysis of the data. OW, TBS and OFA declare that they cleaned, assimilated and analyzed the data. OAF conceptualized the project and led data collection and analysis. CSB, TBS, AF, YY, KTG, SF, DK and ME declares that they reviewed the analysis and the manuscript and participated in editing. All authors approved this final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by Meir medical center ethics committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weitzner, O., Seraya-Bareket, C., Biron-Shental, T. et al. Enhanced expression of αVβ3 integrin in villus and extravillous trophoblasts of placenta accreta. Arch Gynecol Obstet 303, 1175–1183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-020-05844-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-020-05844-4