Abstract
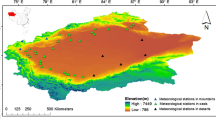
A thorough understanding of regional differences in change patterns of surface air temperature (SAT) at various spatial scales can help people cope well with global warming. In this study, a SAT change pattern recognition method was firstly established based on k-mean++ algorithm. By creating a clustering effect evaluation index (DBWk) to select the optimal cluster number k, the pattern of SAT change in 1960–2016 of China was recognized at national and regional scales. Results showed that China’s SAT change patterns were grouped into 3 clusters, namely, Clusters I, II and III, at the national scale. These clusters were further divided into 3, 7, and 4 subclusters at the regional scale, respectively. The SAT change in Cluster I was intense, with a relatively cold period (1960–1987) and a relatively warm period (1988–2016). The SAT of Cluster II decreased slightly in the first phase (1960–1983), minimally increased in the third phase (1999–2016), but rose strongly in the second phase (1984–1998). The linear trend (LT) of SAT increase of Cluster III was high and statistically significant, especially in 1983–2016. The analysis of the SAT change pattern of subclusters showed that the SAT fluctuations of the Altai Mountains and Junggar Basin were the strongest. The Northern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau had the highest warming rate, and the LT of warming was statistically the most significant in China.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available from the lead/corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arthur D, Vassilvitskii S (2007) k-means++: The advantages of careful seeding. In: Proceedings of the eighteenth annual ACM-SIAM symposium on Discrete algorithms (SODA 2007). Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, pp 1027–1035. https://doi.org/10.1145/1283383.1283494
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning. Springer, New York
Chakraborty A, Seshasai MVR, Rao SVCK et al (2016) Geo-spatial analysis of temporal trends of temperature and its extremes over India using daily gridded (1°×1°) temperature data of 1969–2005. Theor Appl Climatol 130:133–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1869-8
Chen H, Zhu Q, Peng C et al (2013) The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob Change Biol 19:2940–2955. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12277
Cheng J, Li Q, Chao L et al (2020) Development of high resolution and homogenized gridded land surface air temperature data: a case study over Pan-East Asia. Front Environ Sci SWITZ 8:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2020.588570
Choi WN, Hong HK, Lee YW et al (2019) First-time estimation of HCHO column over Asia using multiple regression with OMI and MODIS data. J Environ Inform 34:88–98. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.201900412
Diffenbaugh N, Scherer M, Ashfaq M (2013) Response of snow-dependent hydrologic extremes to continued global warming. Nat Clim Change 3:379–384. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1732
Ding YH (2013) China Climate. Science Press, Beijing ((in Chinese))
ECNARCC (Editorial Committee of National Assessment Report of Climate Change) (2015) Third National Assessment Report of Climate Change. Science Press, Beijing ((in Chinese))
Fallucchi F, Luccasen RA, Turocy TL (2019) Identifying discrete behavioural types: a re-analysis of public goods game contributions by hierarchical clustering. J Econ Sci Assoc 5:238–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40881-018-0060-7
Fang C, Gong YJS et al (2017) Seasonal responses of soil respiration to warming and nitrogen addition in a semi-arid alfalfa-pasture of the Loess Plateau, China. Sci Total Environ 590:729–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.034
Feng QY, Dijkstra H (2014) Are North Atlantic multidecadal SST anomalies westward propagating. Geophys Res Lett 41:541–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL058687
Gaget E, Galewski T, Jiguet F et al (2018) Waterbird communities adjust to climate warming according to conservation policy and species protection status. Biol Conserv 227:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2018.09.019
Gorczyński L (1920) Sur le calcul du degré du continentalisme et son application dans la climatologie. Geogr Ann 2:324–331
Guo J, Huang G, Wang X et al (2018a) Future changes in precipitation extremes over China projected by a regional climate model ensemble. Atmos Environ 188:142–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.06.026
Guo Y, Tang Y, Du Y et al (2018b) Cluster analysis of polymers using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with K-means. Plasma Sci Technol 20:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-6272/aaaade
Hamerly G, Drake J (2015) Accelerating Lloyd’s algorithm for k-means clustering. In: Celebi M (ed) Partitional clustering algorithms. Springer, Cham
Hartigan JA, Wong MA (1979) Algorithm AS 136: a k-means clustering algorithm. J R Stat Soc 28:100–108. https://doi.org/10.2307/2346830
Hutchinson MF, Xu T (2004) Anusplin version 4.2 user guide. Centre for Resource and Environmental Studies, The Australian National University, Canberra
Hyung-II E, Anil G (2019) Hybrid climate datasets from a climate data evaluation system and their impacts on hydrologic simulations for the Athabasca River basin in Canada. Hydrol Earth Syst Sc 23:5151–5173. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-23-5151-2019
IPCC (2014) Climate Change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kukal M, Irmak S (2016) Long-term patterns of air temperatures, daily temperature range, precipitation, grass-reference evapotranspiration and aridity index in the USA Great Plains: Part II. Temporal trends. J Hydrol 542:978–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.06.008
Li X, He Y, Zeng Z et al (2018) Spatiotemporal pattern of terrestrial evapotranspiration in China during the past thirty years. Agric For Meteorol 259:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.04.020
Li N, Bai K, Zhang Z et al (2019) The nonlinear relationship between temperature changes and economic development for individual provinces in China. Theor Appl Climatol 137:2477–2486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2744-6
Liu F, Zhang Y, Luo J (2018) The effects of experimental warming and CO2 concentration doubling on soil organic carbon fractions of a montane coniferous forest on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Eur J For Res 137:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-018-1100-9
Liu Q, Zhou T, Mao H et al (2019a) Decadal variations in the relationship between the western Pacific subtropical high and summer heat waves in East China. J Climate 32:1627–1640. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0093.1
Liu X, Wang JF, Christakos G et al (2019b) China population distributions at multiple geographical scales and their correlates. J Environ Inform 34:15–27. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.201900414
Lloyd SP (1982) Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 28:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1982.1056489
Mansfield LA, Nowack PJ, Kasoar M et al (2020) Predicting global patterns of long-term climate change from short-term simulations using machine learning. NPJ Clim Atmos Sci 3:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-020-00148-5
Matuszko D, Weglarczyk S (2015) Relationship between sunshine duration and air temperature and contemporary global warming. Int J Climatol 35:3640–3653. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4238
Merrifield AL, Xie SP (2016) Summer US surface air temperature variability: controlling factors and AMIP simulation biases. J Climate 29:5123–5139. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0705.1
Mohri M, Rostamizadeh A, Talwalkar A (2018) Foundations of machine learning. MIT Press, Boston
Oberhuber W, Bendler U, Gamper V et al (2020) Growth trends of coniferous species along elevational transects in the Central European Alps indicate decreasing sensitivity to climate warming. Forests 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11020132
Ogbuabor G, Ugwoke FN (2018) Clustering algorithm for a healthcare dataset using silhouette score value. Int J Comput Sci Inform Technol 10:27–37. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijcsit.2018.10203
Pan T, Wu S, He D et al (2012) Effects of longitudinal range-gorge terrain on the eco-geographical pattern in Southwest China. J Geogr Sci 22:825–842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-012-0966-6
Pasupathi S, Shanmuganthan V, Madasamy K et al (2021) Trend analysis using agglomerative hierarchical clustering approach for time series big data. J Supercomput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03580-9
Pearson K (1895) Notes on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc R Soc Lond 58:240–242
Pekel JF, Cottam A, Gorelick N et al (2016) High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 540:418–422. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20584
Qiu J (2008) China: the third pole. Nature 454:393–396. https://doi.org/10.1038/454393a
Root TL, Price JT, Hall KR et al (2003) Fingerprints of global warming on wild animals and plants. Nature 421:57–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01333
Safdar F, Khokhar MF, Arshad M et al (2019) Climate change indicators and spatiotemporal shift in monsoon patterns in Pakistan. Adv Meteorol 2019:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8281201
Schiermeier Q (2018) Clear signs of global warming will hit poorer countries first. Nature 556:415–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-04854-2
Seeley JT, Romps DM (2015) The effect of global warming on severe thunderstorms in the United States. J Climate 28:2443–2458. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-14-00382.1
Shen X, Liu B, Li G et al (2014) Spatiotemporal change of diurnal temperature range and its relationship with sunshine duration and precipitation in China. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:13163–13179. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD022326
Shi P, Sun S, Wang M (2014) Regionalization of climate change in China (1961–2010). Sci China Earth Sci 44:2294–2306 ((in Chinese))
Shivam G, Goyal MK, Sarma AK (2019) Index-based study of future precipitation changes over Subansiri river catchment under changing climate. J Environ Inform 34:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.201700376
Sibanda TZ, Welch M, Schneider D et al (2020) Characterising free-range layer flocks using unsupervised cluster analysis. Animals 10:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10050855
Soon W, Connolly R, Connolly M (2015) Re-evaluating the role of solar variability on Northern Hemisphere temperature trends since the 19th century. Earth Sci Rev 150:409–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.010
Sun S, Zhang Y, Huang D et al (2020) The effect of climate change on the richness distribution pattern of oaks (Quercus L.) in China. Sci Total Environ 744:140786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140786
Szczurek A, Maciejewska M, Wyłomańska A et al (2016) Detection of occupancy profile based on carbon dioxide concentration pattern matching. Measurement 93:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.07.036
Tait PW, Hanna EG (2015) A conceptual framework for planning systemic human adaptation to global warming. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:10700–10722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120910700
Tebaldi C, Knutti R (2018) Evaluating the accuracy of climate change pattern emulation for low warming targets. Environ Res Lett 13:055006. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aabef2
Tong S, Li X, Zhang JC (2019) Spatial and temporal variability in extreme temperature and precipitation events in Inner Mongolia (China) during 1960–2017. Sci Total Environ 649:75–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.262
Travis WR, Smith JB, Yohe GW (2018) Moving toward 1.5°C of warming: implications for climate adaptation strategies. Curr Opin Environ Sust 31:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2018.03.003
UNFCCC (2015) Adoption of the Paris Agreement. Report No. FCCC/CP/2015/L.9/Rev.1. http://unfccc.int/resource/docs/2015/cop21/eng/l09r01.pdf
van den Besselaar EJM, Sanchez-Lorenzo A, Wild M et al (2015) Relationship between sunshine duration and temperature trends across Europe since the second half of the twentieth century. J Geophys Res Atmos 120:10823–10836. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023640
Wang Y, Zhou B, Qin D et al (2017) Changes in mean and extreme temperature and precipitation over the arid region of northwestern China: Observation and projection. Adv Atmos Sci 34:289–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-016-6160-5
Wang K, Qi X, Liu H et al (2018) Deep belief network based k-means cluster approach for short-term wind power forecasting. Energy 165:840–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.09.118
Wang X, Chen M, Gong P et al (2019) Perfluorinated alkyl substances in snow as an atmospheric tracer for tracking the interactions between westerly winds and the Indian Monsoon over western China. Environ Int 124:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.057
Wu Q, Yao Y, Liu S et al (2018) Tropical Indian Ocean warming contributions to China winter climate trends since 1960. Clim Dyn 51:2965–2987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-4059-1
Wu Y, Ji H, Wen J et al (2019) The characteristics of regional heavy precipitation events over eastern monsoon China during 1960–2013. Glob Planet Change 172:414–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.11.001
Xi Y, Miao C, Wu J et al (2018) Spatiotemporal changes in extreme temperature and precipitation events in the three-rivers headwater region, China. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:5827–5844. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD028226
Xia J, Duan QY, Luo Y et al (2017) Climate change and water resources: case study of Eastern Monsoon Region of China. Adv Clim Change Res 8:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accre.2017.03.007
Yang YJ, Wu BW, Shi CE et al (2013) Impacts of urbanization and station-relocation on surface air temperature series in Anhui Province, China. Pure Appl Geophys 170:1969–1983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0619-9
Yuan Q, Wu S, Dai E et al (2017) Spatio-temporal variation of the wet-dry conditions from 1961 to 2015 in China. Sci China Earth Sci 60:2041–2050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9097-1
Zhang Q, Yang Z, Hao X (2019) Conversion features of evapotranspiration responding to climate warming in transitional climate regions in northern China. Clim Dyn 52:3891–3903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4364-3
Zhao J (2018) New version of China’s physical geography. Higher Education Press, Beijing ((in Chinese))
Zhu J, Huang G, Baetz B et al (2019) Climate warming will not decrease perceived low-temperature extremes in China. Clim Dyn 52:5641–5656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4469-8
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Meteorological Information Center of China for providing the meteorological data in our study. We thank the Editor and anonymous reviewers for their detailed evaluation and constructive suggestions on the manuscript. We thank Qian Kuang for her suggestions during the revision.
Funding
National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFC1509002), and the Projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41701100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare to have no conflict of interest connected with the presented research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Q., Wu, S., Zhao, D. et al. Regional differences in surface air temperature changing patterns from 1960 to 2016 of China. Clim Dyn 57, 1733–1749 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05774-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05774-0