Abstract
Introduction
Intracranial aneurysms are rare in the pediatric population, and their diagnosis can be challenging. They differ from their adult counterparts in several aspects, and hemorrhage is the most common presentation.
Objective
To evaluate clinical data, aneurysm characteristics, and therapeutic results in a series of patients younger than 19 years of age with intracranial aneurysms.
Method
A retrospective cross-sectional observational study design analyzed medical records and imaging studies. Variables included age, sex, clinical presentation, comorbidities, aneurysmal characteristics, treatment modality, and clinical outcomes.
Results
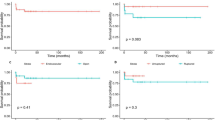
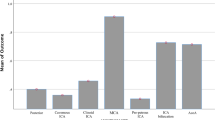
We identified 15 intracranial aneurysms in 11 patients (6 male), with ages ranging from 3 months to 15 years (mean age 5.2 years). Five patients had associated medical conditions, and hemorrhage was the most frequent clinical presentation (45%). Three patients (27%) had multiple aneurysms, and seven aneurysms were fusiform or dysplastic. The internal carotid artery was the most affected site, involved in 47% of cases. Aneurysm size ranged from 2 to 60 mm (mean 16.8 mm), with giant aneurysms in 27%. Seven patients were treated with endovascular procedures, while three aneurysms were clipped. Symptomatic vasospasm requiring angioplasty occurred in two patients and led to worse outcomes. One patient died due to severe aspiration pneumonia and sepsis that precluded treatment. Good functional outcome (modified Rankin scale – mRS ≤ 2) was achieved in all treated patients (91%).
Conclusion
The patients with aneurysms in this series were mostly male, presented mostly hemorrhagic syndromes, and mainly had internal carotid artery involvement. The outcome of treated patients was favorable, regardless of treatment modality.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. Further enquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Amelot A, Saliou G, Benichi S, Alias Q, Boulouis G, Zerah M et al (2019) Long-term outcomes of cerebral aneurysms in children. Pediatrics 143(6):e20183036. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2018-3036
Ghali MGZ, Srinivasan VM, Cherian J, Wagner KM, Chen SR, Johnson J et al (2018) Multimodal treatment of intracranial aneurysms in children: clinical case series and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 111:e294-307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.12.057
Nam SM, Jang D, Wang K-C, Kim S-K, Phi JH, Lee JY et al (2019) Characteristics and treatment outcome of intracranial aneurysms in children and adolescents. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 62(5):551–560. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2019.0140
Demartini Z Jr, Santos D, de Alencar G, Cardoso-Demartini A, Sprengel SL, Zanine SC, Borba LAB (2021) Delayed diagnosis of intracranial aneurysm in pediatrics: the risk of misdiagnosis-a case report. Childs Nerv Syst 37(10):3245–3249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-05006-6
Garrido E, Metayer T, Borha A, Langlois O, Curey S, Papagiannaki C et al (2021) Intracranial aneurysms in pediatric population: a two-center audit. Childs Nerv Syst 37(8):2567–2575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05151-6
Kim M, Lee HS, Lee S, Park JC, Ahn JS, Kwon DH et al (2019) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: favorable outcomes despite rareness and complexity. World Neurosurg 125:e1203-1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.280
Saraf R, Shrivastava M, Siddhartha W, Limaye U (2012) Intracranial pediatric aneurysms: endovascular treatment and its outcome: clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10(3):230–240. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.5.PEDS1210
Slator N, Talibi SS, Mundil N, Thomas A, Lamin S, Walsh R et al (2019) Paediatric intracranial aneurysms: a British institutional review. Childs Nerv Syst 35(7):1197–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04159-3
terBrugge KG (1999) Neurointerventional procedures in the pediatric age group. Child Nerv Syst 15(11):751–754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810050465
Kaku Y, Kouda K, Yoshimura S, Sakai N (2004) Cerebral aneurysms in scleroderma. Cerebrovasc Dis 17(4):339–341. https://doi.org/10.1159/000077952
Heyer GL, Dowling MM, Licht DJ, Tay SK-H, Morel K, Garzon MC et al (2008) The cerebral vasculopathy of PHACES syndrome. Stroke 39(2):308–316. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.485185
Metry D, Heyer G, Hess C, Garzon M, Haggstrom A, Frommelt P et al (2009) Consensus statement on diagnostic criteria for PHACE syndrome. Pediatrics 124(5):1447–1456. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0082
Chen R, Zhang S, Guo R, You C, Ma L (2018) Pediatric intracranial pseudoaneurysms: a report of 15 cases and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 116:e951-959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.140
Sanai N, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Gupta NM, Perry V, Sun PP, Wilson CB et al (2006) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: durability of treatment following microsurgical and endovascular management. J Neurosurg Pediatr 104(2):82–89. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2006.104.2.3
Clarke JE, Luther E, Oppenhuizen B, Leuchter JD, Ragheb J, Niazi TN et al (2022) Intracranial aneurysms in the infant population: an institutional case series and individual participant data meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Pediatr Apr 15:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2022.2.PEDS21234. Online ahead of print
de Aguiar GB, Ozanne A, Elawady A, Samoyeau T, Niknejad HR, Caroff J et al (2022) Intracranial aneurysm in the pediatric population: a single-center experience. Pediatr Neurosurg 55(4):270–278. https://doi.org/10.1159/000524523
Zhang YS, Wang S, Wang Y, Tian ZB, Liu J, Wang K et al (2016) Treatment for spontaneous intracranial dissecting aneurysms in childhood: a retrospective study of 26 cases. Front Neurol 6(7):224. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2016.00224
Demartini Z Jr, Gatto LAM, da Rocha TC, Maeda AK, Valerio A, Koppe GL et al (2018) Is the Mayfield head holder obligatory for intracranial aneurysm clipping? Pediatr Neurosurg 53(5):360–363. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491825
Rass V, Helbok R (2021) How to diagnose delayed cerebral ischaemia and symptomatic vasospasm and prevent cerebral infarction in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Curr Opin Crit Care 27(2):103–114. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCC.0000000000000798
Scherschinski L, Catapano JS, Karahalios K, Koester SW, Benner D, Winkler EA et al (2022) Electroencephalography for detection of vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a retrospective analysis and systematic review. Neurosurg Focus 52(3):E3. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.12.FOCUS21656
Shlobin NA, Raz E, Shapiro M, Moretti L, Cantrell DR, Lam SK et al (2021) Pipeline embolization of cerebral aneurysms in pediatric patients: combined systematic review of patient-level data and multicenter retrospective review. J Neurosurg Pediatr 27(6):668–676. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.10.PEDS20324
Xu R, Xie ME, Yang W, Gailloud P, Caplan JM, Jackson CM et al (2021) Epidemiology and outcomes of pediatric intracranial aneurysms: comparison with an adult population in a 30-year, prospective database. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.6.PEDS21268. Online ahead of print
Heffren J, McIntosh AM, Reiter PD (2015) Nimodipine for the prevention of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage in 12 children. Pediatr Neurol 52(3):356–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.11.003
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Roberta Russi for her help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z. D. J., A. A. C. D., and A. K. M.: conception of the work; J. P. P. and G. L. K. acquisition of the data. Z. D. J., J. P. P., and G. L. K.: analysis and interpretation of the data. A. A. C. D. and J. P. P.: drafting of the work. Z. D. J., J. P. P., and A. A. C. D.: critically revising the work for intellectual content. All authors: accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee. It was performed in accordance with the ICMJE Recommendations for the Protection of Research Participants. All patients’ identifications were removed to preserve anonymity. This study was conducted ethically in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of data and images was provided and signed by the patient’s surrogates.
Conflict interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Demartini, Z., Pardins, J.P., Koppe, G.L. et al. Pediatric intracranial aneurysms in a Southern Brazilian population. Childs Nerv Syst 39, 3543–3549 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-05965-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-05965-6