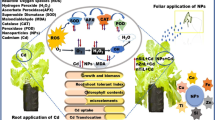
Abstract
The application of metal and metal-oxide nanoparticles (NPs) in agriculture to mitigate the abiotic environmental stress factors and pollutants has gained extensive interests in research, particularly in studying their efficiency and their mechanistic effects. In this study, we aim to assess the potential of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) in monitoring Cadmium (Cd) toxicity on pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) in vitro cultured plants, by modulating their physiological and biochemical traits. In vitro culture was carried on Murasnige and Skoog (MS) medium, containing required amounts of macro- and micronutrients, vitamins, sucrose with pH 5.8 and agar. MS and NPs were autoclaved at 120 °C during 20 min. Our results showed that Cd exposure inhibited in vitro germination of seeds (by 17% at day 7, and 7% at day 14), and the growth of shoots (around 49% decrease in length) and roots (around 55% increase in length). However, the application of ZnONPs could recover 70–85% of shoots length, 40–50% of shoots fresh weights, also 60–80% of roots length and 70% of roots fresh weights. In shoots, ZnONPs act positively by boosting the antioxidant activities of enzymes; Catalase increased 30–75% with concentrations of 2.5, 5 and 10 mg L−1. Glutathione peroxidase increased around 13% and 63%, respectively, with concentrations of 2.5, 5 and 10 mg L−1. Guaicol peroxidase increased 40% with ZnONPs 5 mg L−1 but decreased with ZnONPs 10 mg L−1. ZnONPs also increased the activities of ascorbate peroxidase and glutathione reductase, respectively, fourfolds–tenfolds and twofolds–threefolds with increasing concentrations. This improved the elimination of H2O2 by around 70% and 80% with ZnONPs 2.5, 5 and 10 mg L−1, respectively. However, the ameliorating role of ZnONPs in roots response was revealed via reversing the oxidative stress symptoms induced by Cd. Overall, these defense mechanisms depicted that ZnONPs can improve Cd tolerance of plants. In addition, our study contains novelty in using in vitro culture to provide physiological and metabolic-scale insights for understanding the action mechanism of ZnONPs-induced alleviation of Cd toxicity in pepper. Hence, application of ZnONPs can be used as a promising approach in the remediation of Cd-contaminated environment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data transparency.
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Ahanger MA, Aziz U, Alsahli A, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Combined kinetin and spermidine treatments ameliorate growth and photosynthetic inhibition in vigna angularis by up-regulating antioxidant and nitrogen metabolism under cadmium stress. Biomolecules 10, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010147
Ahmad P, Jaleel CA, Salem MA, Nabi G, Sharma S (2010) Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30:161–175
Ahmad P, Tripathi DK, Deshmukh RK, Vijay Pratap Singh VP, Corpas FJ (2019) Revisiting the role of ROS and RNS in plants under changing environment. Environ Exp Bot 161:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.02.017
Ahmad P, Alyemeni MN, Al-Huqail AA, et al (2020) Zinc oxide nanoparticles application alleviates arsenic (As) toxicity in soybean plants by restricting the uptake of as and modulating key biochemical attributes, antioxidant enzymes, ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. Plants 9:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070825
Ali S, Rizwan M, Noureen S, et al (2019) Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 26:11288–11299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04554-y
Al-Sammarraie ON, Alsharafa KY, Al-Limoun MO, Khleifat KM, Al-Sarayreh SA, Al-Shuneigat JM, Kalaji HM (2020) Effect of various abiotic stressors on some biochemical indices of Lepidium sativum plants. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78330-1
Arfaoui H, Karmous I, Mahjoubi Y, Kharbech O, Tlahig S, Loumerem M, Chaoui A (2021) Screening of the effects of Zinc oxide based nanofertilizers on the germination of Lathyrus sativa L. seeds. J Appl Bot Food Qual 94:53–60. https://doi.org/10.5073/JABFQ.2021.094.007
Baruah N, Mondal SC, Farooq M, Gogoi N (2019) Influence of heavy metals on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat, pea, and tomato. Water Air Soil Pollut 230:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4329-0
Cui J, Liu T, Li F, Yi J, Liu CH, Yu H (2017) Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: mechanisms and size effects. Environ Pollut 228:363–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.014
Das B, Imran Khan M, Jayabalan R, Behera SK, Yun S-I, Tripathy SK, Mishra A (2016) Understanding the antifungal mechanism of Ag@ZnO core–shell nanocomposites against Candida krusei. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36403
Didwania N, Jain S, Sadana D (2019) In-vitro phytotoxic effects of cadmium on morphological parameters of Allium cepa. Jordan J Biol Sci 12:37–41
Dimkpa CO, Andrews J, Sanabria J, Bindraban PS, Singh U, Elmer WH, Gardea-Torresdey JL, White JC (2020) Interactive effects of drought, organic fertilizer, and zinc oxide nanoscale and bulk particles on wheat performance and grain nutrient accumulation. Sci Total Environ 722:137808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137808
El Rasafi T, Oukarroum A, Haddioui A, Song H, Kwon EE, Bolan N, Tack FMG, Sebastian A, Prasad MNV, Rinklebe J (2020) Cadmium stress in plants: a critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1835435
Faizan M, Faraz A, Yusuf M, Khan ST, Hayat S (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticle-mediated changes in photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant system of tomato plants. Photosynthetica 56:678–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-017-0717-0
Faizan M, Faraz A, Mir AR, Hayat S (2020) Role of zinc oxide nanoparticles in countering negative effects generated by cadmium in Lycopersicon esculentum. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-10059-2
Faraji J, Sepehri A (2018) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles and sodium nitroprusside alleviate the adverse effects of cadmium stress on germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Univ Sci 23:61. https://doi.org/10.11144/Javeriana.SC23-1.tdna
Fattori V, Hohmann MSN, Rossaneis A, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Verri WA (2016) Capsaicin: current understanding of its mechanisms and therapy of pain and other pre-clinical and clinical uses. Molecules 21:844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070844
Fielding JL, Hall JL (1978) A biolchemical and cytochemical study of peroxidase activity in roots of Pisum sativum: I. A comparison of dab-peroxidase and guaiacol-peroxidase with particular emphasis on the properties of cell wall activity. J Exp Bot 29:969–981. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/29.4.969
Foyer CH, Halliwell B (1976) The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 133:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386001
Gammoudi N, Zerria K, Nagaz K, Ferchichi A (2019) Enhancement of capsaicinoids in vitro production by abiotic elicitors in placenta-derived callus of Capsicum annuum L. Tunisian var. ‘Baklouti Medenine.’ Biologia 74:725–732. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00237-8
Genchi G, Sinicropi MS, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:3782
Gull A, Lone AA, Wani NUI (2019) Biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Abiotic Biotic Stress Plants. https://doi.org/10.5772/INTECHOPEN.85832
Haider FU, Liqun C, Coulter JA, Cheema SA, Wu J, Zhang R, Wenjun M, Farooq M (2021) Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2020.111887
Hediji H, Kharbech O, Massoud MB, Boukari N, Debez A, Chaib W, Chaoui A, Djebali W (2021) Salicylic acid mitigates cadmium toxicity in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings by modulating cellular redox status. Environ Exp Bot 186:104432. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVEXPBOT.2021.104432
Ismael MA, Elyamine AM, Moussa MG, Cai M, Zhao X, Hu C (2019) Cadmium in plants: uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 11:255–277. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MT00247A
Jaspreet Kour KK, Rupinder Kaur AS (2021) Variability, behaviour and impact of nanoparticles in the environment. Plant responses to nanomaterials: recent interventions, and physiological and biochemical responses. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36740-4.pdf#page=319
Khalil RR, Nagah A, Haroun SA, Fardous B, Haroun SA (2017) Kinetin and/or calcium affect growth of Phaseolus vulgaris L. plant grown under heavy metals stress. J Environ Sci 46(2):103–120
Kohli SK, Khanna K, Bhardwaj R, Abd Allah EF, Ahmad P, Corpas FJ (2019) Assessment of subcellular ROS and NO metabolism in higher plants: multifunctional signaling molecules. Antioxidants 8:641
Konate A, He X, Zhang Z, Ma Y, Zhang P, Alugongo GM, Rui Y (2017) Magnetic (Fe3O4) nanoparticles reduce heavy metals uptake and mitigate their toxicity in wheat seedling. Sustainability (switzerland) 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9050790
Lamers J, van der Meer T, Testerink C (2020) How plants sense and respond to stressful environments. Plant Physiol 182:1624–1635. https://doi.org/10.1104/PP.19.01464
Londono N, Donovan AR, Shi H, Geisler M, Liang Y (2017) Impact of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on an aquatic microbial community: effect at environmentally relevant concentrations. Nanotoxicology 11:1140–1156. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2017.1401141
Luyckx M, Hausman JF, Lutts S, Guerriero G (2017) Silicon and plants: current knowledge and technological perspectives. Front Plant Sci 8:411. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00411
Madany MMY, Saleh AM, Habeeb TH, Hozzeincd WN, AbdElgawad H (2020) Silicon dioxide nanoparticles alleviate the threats of broomrape infection in tomato by inducing cell wall fortification and modulating ROS homeostasis. Environ Sci Nano 7:1415–1430. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en01255a
Marothia D, Kaur N, Pati PK (2020) Abiotic stress responses in plants: current knowledge and future prospects. Abiotic Stress Plants. https://doi.org/10.5772/INTECHOPEN.93824
Murasnige T, Skoog FA (1962) Revised medium for rapid growth and bio agsays with tohaoco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Muszyńska E, Hanus-Fajerska E, Koźmińska A (2018) Differential tolerance to lead and cadmium of micropropagated Gypsophila fastigiata ecotype. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3702-8
Nagalakshmi N, Prasad MNV (2001) Responses of glutathione cycle enzymes and glutathione metabolism to copper stress in Scenedesmus bijugatus. Plant Sci 160:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00392-7
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Navrot N, Collin V, Gualberto J, Gelhaye E, Hirasawa M, Rey P, Knaff DB, Issakidis E, Jacquot J-P, Rouhier N (2006) Plant glutathione peroxidases are functional peroxiredoxins distributed in several subcellular compartments and regulated during biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol 142:1364–1379. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.089458
Rajiv P, Vanathi P, Thangamani A (2018) An investigation of phytotoxicity using Eichhornia mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles on Helianthus annuus. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 16:419–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.09.017
Rajput VD, Minkina T, Mazarjia M, Shende S, Sushkova S, Mandzhieva S, Burachevskaya M, Chaplygin V, Singh A, Jatav H (2019) Toxicity assessment of metal oxide nanoparticles on terrestrial plants. Compr Anal Chem 87:189–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/BS.COAC.2019.09.003
Rajput V, Minkina T, Mazarji M, Shende S, Sushkova S, Mandzhieva S, Burachevskaya M, Chaplygin V, Singh A, Jatav H (2020) Accumulation of nanoparticles in the soil-plant systems and their effects on human health. Ann Agric Sci 65:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2020.08.001
Raliya R, Saharan V, Dimkpa C, Biswas P (2018) Nanofertilizer for precision and sustainable agriculture: current state and future perspectives. J Agric Food Chem 66:6487–6503. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02178
Ranjan A, Rajput VD, Minkina T, Bauer T, Chauhan A, Jindal T (2021) Nanoparticles induced stress and toxicity in plants. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 15:100457. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENMM.2021.100457
Rastogi A, Zivcak M, Sytar O, Kalaji HHM, Mbarki XHS, Brestic M (2017) Impact of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on plant: a critical review. Front Chem 5:78
Rastogi A, Tripathi DK, Yadav S, Chauhan DK, Živčák M, Ghorbanpour M, El-Sheery NI, Brestic M (2019) Application of silicon nanoparticles in agriculture. 3 Biotech 9:90
Rizwan M, Ali S, Zia ur Rehman M, Adrees M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF, Ali L, Hussain A, Chatha SAS, Imran M (2019a) Alleviation of cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) by foliar spray of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biochar to contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 248:358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.031
Rizwan M, Ali S, Zia Ur Rehman M, Adrees M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF, Ali L, Hussain A, Chatha SAS, Imran M (2019b) Alleviation of cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) by foliar spray of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biochar to contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 248:358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.031
Sakouhi L, Rahoui S, Gharsallah C, Munemasa S, El Ferjani E, Murata Y, Chaoui A (2018) Effects of calcium and EGTA on thiol homeostasis and defense-related enzymes in Cd-exposed chickpea roots. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2596-1
Sakouhi L, Kharbech O, Ben MM, Gharsallah C, Ben Hassine S, Munemasa S, Murata Y, Chaoui A (2021a) Calcium and ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid mitigate toxicity and alteration of gene expression associated with cadmium stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) shoots. Protoplasma 258:849–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-020-01605-x
Sakouhi L, Kharbech O, Massoud MB, Munemasa S, Murata Y, Chaoui A (2021b) Oxalic acid mitigates cadmium toxicity in Cicer arietinum L. germinating seeds by maintaining the cellular redox homeostasis. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10334-1
Samreen T, Humaira SHU, Ullah S, Javid M (2017) Zinc effect on growth rate, chlorophyll, protein and mineral contents of hydroponically grown mungbeans plant (Vigna radiata). Arab J Chem 10:S1802–S1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.005
Sergiev I, Alexieva V, Karanov E (1997) undefined Effect of spermine, atrazine and combination between them on some endogenous protective systems and stress markers in plants. Compt Rend Acas Bulg Sci 51:121–124
Sharifan H, Ma X, Moore JMC, Habib MR, Evans C (2019) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviated the bioavailability of cadmium and lead and changed the uptake of iron in hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. Longifolia). ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:16401–16409. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b03531
Singh AD, Sharma I, Khanna K, Handa N, Kumar P, Ibrahim M, Ohri P, Bhardwaj R (2021) Impact of cobalt oxide nanoparticles on the morpho-physiological and biochemical response in plants. Nanotechnol Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36740-4_11
Spanò C, Bottega S, Sorce C, Bartoli G, Castiglione MR (2019) TiO2 nanoparticles may alleviate cadmium toxicity in co-treatment experiments on the model hydrophyte Azolla filiculoides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:29872–29882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06148-0
Sun L, Song F, Zhu X, Liu S, Liu F, Wang Y, Li X (2020) Nano-ZnO alleviates drought stress via modulating the plant water use and carbohydrate metabolism in maize. Arch Agron Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2020.1723003
Thuphairo K, Sornchan P, Suttisansanee U (2019) Bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity and inhibition of key enzymes relevant to Alzheimer’s disease from sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum) extracts. Prev Nutr Food Sci 24:327–337. https://doi.org/10.3746/pnf.2019.24.3.327
Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER, Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alleviate heavy metal-induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.08.022
World Health Organization (WHO) Permissible limits of heavy metals in soil and plants. Geneva, Switzerland, 1996
Zaid A, Mohammad F, Fariduddin Q (2020) Plant growth regulators improve growth, photosynthesis, mineral nutrient and antioxidant system under cadmium stress in menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00715-y
Zhang H, Reynolds M (2019) Cadmium exposure in living organisms: a short review. Sci Total Environ 678:761–767
Zhang F, Liu M, Li Y, Che Y, Xiao Y (2019) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, biochar and cadmium on the yield and element uptake of Medicago sativa. Sci Total Environ 655:1150–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2018.11.317
Zhao L, Lu L, Wang A, Zhang H, Huang M, Wu H, Xing B, Wang Z, Ji R (2020) Nano-biotechnology in agriculture: use of nanomaterials to promote plant growth and stress tolerance. J Agric Food Chem 68:1935–1947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06615
Zhao H, Guan J, Liang Q, Zhang X, Hu H, Zhang J (2021) Effects of cadmium stress on growth and physiological characteristics of sassafras seedlings. Sci Rep 11:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89322-0
Zhou P, Adeel M, Shakoor N, Guo M, Hao Y, Azeem I, Li M, Liu M, Rui Y (2021) Application of nanoparticles alleviates heavy metals stress and promotes plant growth: an overview. Nanomaterials 11:1–18
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the Tunisian Ministery of Higher Education and Research. We also thank the Language Service in ISBAM for English editing and revision.
Funding
Tunisian Ministery of Higher Education and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [IK]; Data curation: [IK, NG]; Funding acquisition & Resources: [NG, AC]; Methodology: [IK, NG, AC]; Data analysis: [IK, NG]; Writing original draft: [IK]; Writing-Reviewing & Editing paper: [IK, NG, AC].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Author: Parvaiz Ahmad.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karmous, I., Gammoudi, N. & Chaoui, A. Assessing the Potential Role of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Mitigating Cadmium Toxicity in Capsicum annuum L. Under In Vitro Conditions. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 719–734 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10579-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10579-4