Abstract
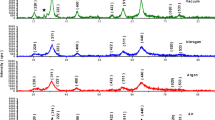
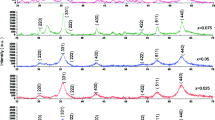
This paper describes for the first time two processing routes—the precursor method and the two-step wet chemical process—for the synthesis of magnetic cobalt ferrite using the Tamarindus indica fruit extract. These green approaches are eco-friendly, safe and efficient alternatives to classical chemical methods. The aqueous extract from tamarind fruit contains numerous metabolites (organic acids, aminoacids). All these bioactive components are able to chelate metal ions leading to the formation of the multimetallic complex (precursor of cobalt ferrite). The obtained precursor was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) and magnetic measurements. The structure, morphology and magnetic behavior of the cobalt ferrite samples prepared through both synthesis routes were investigated by various characterization techniques: FTIR, XRD, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), Mössbauer spectroscopy and magnetic measurements. XRD data confirmed that a cubic spinel structure was obtained for both ferrite powders with average crystallite size of 13 and 5 nm, respectively. The microstructure study by SEM revealed the formation of nanocrystallites assemblies using the precursor method and carbon-rich particles forming granulated micron-sized agglomerates, embedding ferrite nanocrystallites obtained through the two-step wet chemical process. Mössbauer spectroscopy results evidenced relaxation processes in the CoFe2O4 samples at room temperature, and the main characteristics of the involved sublattices were derived. The magnetic investigation revealed a typical magnetic behavior for a spinel, with CoFe2O4 nanoparticles ferrimagnetic at low temperature and superparamagnetic at room temperature.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Ansari, B.B. Sinha, D. Phase, D. Sen, P.U. Sastry, Y.D. Kolekar, C.V. Raman, Particle size, morphology, and chemical composition controlled CoFe2O4 nanoparticles with tunable magnetic properties via oleic acid based solvothermal synthesis for application in electronic devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 1828–1843 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b02009
O.K. Mmelesi, N. Masunga, A. Kuvarega, T.T. Nkambule, B.B. Mamba, K.K. Kefeni, Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites: Photocatalytic, antimicrobial activity and toxicity in water treatment. Mat. Sci. Semiconduct. Proc. 123, 105523 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105523
M. Ghanbari, F. Davar, A.E. Shalan, Effect of rosemary extract on the microstructure, phase evolution, and magnetic behavior of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and its application on anti-cancer drug delivery. Ceram. Int. 47, 9409–9417 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.073
D. Gheidari, M. Mehrdad, S. Maleki, S. Hosseini, Synthesis and potent antimicrobial activity of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles under visible light. Heliyon 6, e05058 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05058
R. Eivazzadeh-Keihan, S. Asgharnasl, M.S. Bani, F. Radinekiyan, A. Maleki, M. Mahdavi, P. Babaniamansour, H. Bahreinizad, A.E. Shalan, S. Lanceros-Méndez, Magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles functionalized by aromatic polyamide chains for hyperthermia applications. Langmuir 37(29), 8847–8854 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c01251
J. Kudr, Y. Haddad, L. Richtera, Z. Heger, M. Cernak, V. Adam, O. Zitka, Magnetic nanoparticles: From design and synthesis to real world applications. Nanomaterials 7, 243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090243
M. Suljagic, P. Vulic, D. Jeremic, V. Pavlovic, S. Filipovic, L. Kilanski, S. Lewinska, A. Slawska-Waniewska, M.R. Milenkovic, A.S. Nikolic, L. Andjelkovic, The influence of the starch coating on the magnetic properties of nanosized cobalt ferrites obtained by different synthetic methods. Mater. Res. Bull. 134, 111117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.111117
K.V. Chandekar, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, A structural, elastic, mechanical, spectroscopic, thermodynamic, and magnetic properties of polymer coated CoFe2O4 nanostructures for various applications. J. Mol. Struct. 1205, 127681 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.1276
D. Gingasu, I. Mindru, L. Patron, A. Ianculescu, E. Vasile, G. Marinescu, S. Preda, L. Diamandescu, O. Oprea, M. Popa, C. Saviuc, M.C. Chifiriuc, Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity. J. Inor. Organomet. Polym. 28, 1932–1941 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0870-3
H. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Zeng, G. Wang, S. Han, Z. Yang, B. Li, X. Wang, J. Gao, L. Zheng, X. Liu, Z. Huo, R. Yu, Leucine-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and potential biomedical applications for drug delivery. Phys. Lett. A 384, 126600 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2020.126600
D.C. Culita, L. Patron, V.S. Teodorescu, I. Balint, Synthesis and characterization of spinelic ferrites obtained from coordination compounds as precursors. J. Alloys Compd. 432, 211–216 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.05.104
G. Lavorato, M. Alzamora, C. Contreras, G. Burlandy, F.J. Litterst; E. Baggio-Saitovitch, Internal structure and magnetic properties in cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Influence of the synthesis method. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 1900061 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.201900061
A.I. Alharthi, I.U. Din, M.A. Alotaibi, G. Centi, Application of cobalt ferrite nano-catalysts for methanol synthesis by CO2 hydrogenation: deciphering the role of metals cations distribution. Ceram. Int. 47, 19234–19240 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.149
M.V. Gerbaldo, S.G. Marchetti, V.R. Elías, S. Nazaret Mendieta, M. Elsie Crivello, Degradation of anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac using cobalt ferrite as photocatalyst. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 166, 237–247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2020.12.009
G.R. Patta, V. Ravi Kumar, B.V. Ragavaiah, N. Veeraiah, A critical study on the magnetic properties of ultrafine cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by polyethylene glycol assisted sol–gel method. Appl. Phys. A 126, 64 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3253-x
F. Ansari, A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Simple sol-gel synthesis and characterization of new CoTiO3/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite by using liquid glucose, maltose and starch as fuel, capping and reducing agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 514, 723–732 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.12.083
S. Das, M. Bououdina, C. Manoharan, The influence of cationic surfactant CTAB on optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 46, 11705–11716 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.202
I. Anila, M.J. Mathew, Study on the physico-chemical properties, magnetic phase resolution and cytotoxicity behavior of chitosan-coated cobalt ferrite nanocubes. Appl. Surface Sci. 556, 149791 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149791
P. Palade, C. Comanescu, A. Kuncser, D. Berger, C. Matei, N. Iacob, V. Kuncser, Mesoporous cobalt ferrite nanosystems obtained by surfactant-assisted hydrothermal method: Tuning morpho-structural and magnetic properties via pH-variation. Nanomaterials 10, 476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030476
I. Mindru, D. Gingasu, L. Diamandescu, L. Patron, G. Marinescu, D.C. Culita, J.M. Calderon-Moreno, S. Preda, O. Oprea, V. Parvulescu, CoFe2−xCrxO4 ferrites: synthesis, characterization and their catalytic activity. Chem. Paper 72, 3203–3213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0553-0
D. Gingasu, L. Diamandescu, I. Mindru, G. Marinescu, D.C. Culita, J.M. Calderon-Moreno, S. Preda, C. Bartha, L. Patron, Chromium substituted cobalt ferrites by glycine-nitrates process. Croat. Chem. Acta 88, 445–451 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5562/cca2743
I.H. Karakas, The effects of fuel type onto the structural, morphological, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of nanoparticles in the synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with microwave assisted combustion method. Ceram. Int. 47, 5597–5609 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.144
M. Hashim, N. Boda, A. Ahmed, S.K. Sharma, D. Ravinder, E. Sumalatha, A. Ul-Hamid, M.M. Ismail, M. Chaman, S.E. Shirsath, R. Kumar, S. Kumar, S.S. Meena, M. Nasir, Influence of samarium doping on structural, elastic, magnetic, dielectric, and electrical properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. Appl. Phys. A 127, 526 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04686-4
K. Vasundhara, S.N. Achary, S.K. Deshpande, P.D. Babu, S.S. Meena, A.K. Tyagi, Size dependent magnetic and dielectric properties of nano CoFe2O4 prepared by a salt assisted gel-combustion method. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 194101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4804946
S. Shanmugam, B. Subramanian, Evolution of phase pure magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles by varying the synthesis conditions of polyol method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 252, 114451 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2019.114451
R. El-Sayed, H.K. Abdelhakim, Z. Zakaria, Extracellular biosynthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles by Monascus purpureus and their antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial activities: Yield enhancement by gamma irradiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 107, 110318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110318
S. Ahmadian-Fard-Fini, M. Salavati-Niasari, D. Ghanbari, Hydrothermal green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4-carbon dots by lemon and grape fruit extracts and as a photoluminescence sensor for detecting of E. coli bacteria, Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 203, 481–493 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.06.021
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshira, M.S. Morassaei, M. Salavati-Niasari, Eco-friendly synthesis of Nd2Sn2O7–based nanostructure materials using grape juice as green fuel as photocatalyst for the degradation of erythrosine. Compos. B Eng. 167, 643–653 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.045
A. Manikandan, R. Sridhar, S. Arul Antony, S. Ramakrishna, A simple aloe vera plant-extracted microwave and conventional combustion synthesis: Morphological, optical, magnetic and catalytic properties of CoFe2O4 nanostructures. J. Mol. Struct. 1076, 188–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.07.054
D. Gingasu, I. Mindru, L. Patron, J.M. Calderon-Moreno, O.C. Mocioiu, S. Preda, N. Stanica, S. Nita, N. Dobre, M. Popa, G. Gradisteanu, M.C. Chifiriuc, Green synthesis methods of CoFe2O4 and Ag-CoFe2O4 nanoparticles using hibiscus extracts. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2106756 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2106756
D. Gingasu, I. Mindru, O.C. Mocioiu, S. Preda, N. Stanica, L. Patron, A. Ianculescu, O. Oprea, S. Nita, I. Paraschiv, M. Popa, C. Saviuc, C. Bleotu, M.C. Chifiriuc, Synthesis of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite through soft chemistry methods: A green chemistry approach using sesame seed extract. Mater. Chem. Phys. 182, 219–230 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.07.026
D. Gingasu, I. Mindru, S. Preda, J.M. Calderon-Moreno, D.C. Culita, L. Patron, L. Diamandescu, Green synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles using plant extract. Rev. Roum. Chim. 62, 647–655 (2017)
P. Mahajan, A. Sharma, B. Kaur, N. Goyal, S. Gautam, Green synthesized (Ocimum sanctum and Allium sativum) Ag-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for antibacterial application. Vacuum 161, 389–397 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.12.021
E.B.S. Da Silva; S.R. Da Silva Ferreira, A.O. Da Silva; J.A. Lopes Matias, A.R. Albuquerque, J.B.L. De Oliveira, M.A. Morales, Cashew gum as a sol-gel precursor for green synthesis of nanostructured Ni and Co ferrites, Int. J. Biol. Macromolec. 164, 4245–4251 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.252
M.K. Satheeshkumar, E. Ranjith Kumar, C. Srinivasc, N. Suriyanarayanan, M. Deepty, C.L. Prajapat, T.V.C. Rao, D.L. Sastry, Study of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Ag substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey assisted combustion method and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469, 691–697 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.039
E. De Caluwe, K. Halamova, P. Van Damme, Tamarindus indica L.—A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Afrika Focus 23, 53–83 (2010)
A.O.E.E. Ahmed, S.M.H. Ayoub, Chemical composition and antimalarial activity of extracts of Sudanese Tamarindus indica L. (Fabaceae), The Pharma Innov. J. 4, 90–93 (2015)
A.M.E. Sulieman, S.M. Alawad, M.A. Osman, E.A. Abdelmageed, Physicochemical characteristics of local varieties of tamarind (Tamarindus indica L) Sudan. Int. J. Plant Res. 5, 13–18 (2015)
N. Jayaprakash, J.J. Vijaya, K. Kaviyarasu, K. Kombaiah, L.J. Kennedy, R.J. Ramalingam, M.A. Munusamy, H.A. Al-Lohedan, Green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles using Tamarind fruit extract for the antibacterial studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 169, 178–185 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.03.013
I. Mindru, D. Gingasu, L. Patron, A. Ianculescu, V.A. Surdu, D.C. Culita, S. Preda, C.D. Negut, O. Oprea, A new approach: Synthesis of cobalt aluminate nanoparticles using tamarind fruit extract. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 246, 42–48 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2019.05.031
M.B. Zaman, R. Poolla, P. Singh, T. Gudipat, Biogenic synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Tamarindus indica L. and a study of their photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 14, 100346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100346
R.A. Brand, Improving the validity of hyperfine field distributions from magnetic alloys: Part I: Unpolarized source. Nuclear Instrum. Method Phys. Res. B 28, 398–416 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583X(87)90182-0
D. Gingasu, I. Mindru, D.C. Culita, L. Patron, J.M. Calderon-Moreno, P. Osiceanu, S. Preda, O. Oprea, V. Parvulescu, V. Teodorescu, J.P.S. Walsh, Structural, magnetic and catalytic properties of cobalt chromite obtained through precursor method. Mater. Res. Bull. 62, 52–64 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.11.009
D. Gingasu, I. Mindru, L. Patron, S. Stoleriu, Synthesis of lithium ferrites from polymetallic carboxylates. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 73, 979–988 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC0810979G
M. Razavi, S. Nyamathulla, H. Karimian, S.Z. Moghadamtousi, M.I. Noordin, Hydrogel polysaccharides of tamarind and xanthan to formulate hydrodynamically balanced matrix tablets of famotidine. Molecules 19, 1390–13931 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913909
P.G.K. Kumar, G. Battu, K.N.S.L. Raju, Isolation and evaluation of tamarind seed polysaccharide being used as a polymer in pharmaceutical dosage forms. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2, 274–290 (2011)
J.A. Rood, B.C. Noll, K.W. Henderson, Homochiral frameworks derived from magnesium, zinc and copper salts of l-tartaric acid. J. Solid State Chem. 123, 270–275 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2009.11.003
G. Concas, G. Spano, C. Cannas, A. Musinu, D. Peddis, G. Piccaluga, Inversion degree and saturation magnetization of different nanocrystalline cobalt ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1893–1897 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.12.001
R. Gans, Regarding the magnetic behaviour of isotropic ferromagnetic. Ann. Phys. 15, 28–34 (1932)
Q. Li, C.W. Kartikowati, S. Horie, T. Ogi, T. Iwaki, K. Okuyama, Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 7, 9894 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09897-5
S.R. Naik, A.V. Salker, S.M. Yusuf, S.S. Meena, Influence of Co2+ distribution and spin–orbit coupling on the resultant magnetic properties of spinel cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J. Alloy Compd. 566, 54–61 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.02.163
M. Grigorova, H.J. Blythe, V. Blaskov, V. Rusanov, V. Petkov, V. Masheva, D. Nihtianova, L. Martinez, J.S. Munoz, M. Mikhov, Magnetic properties and Mössbauer spectra of nanosized CoFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 183, 163–172 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(97)01031-7
S. Chikazumi, Physics of Ferromagnetism (Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1997)
S. Xu, Y. Ma, B. Geng, X. Sun, M. Wang, The remanence ratio in CoFe2O4 nanoparticles with approximate single-domain sizes. Nanoscale Res. Let. 11, 471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1691-3
Acknowledgements
The work benefited from the support of the “Materials Science and Advanced Characterization Methods” Programme of the “Ilie Murgulescu” Institute of Physical Chemistry, financed by the Romanian Academy. C. Bartha, S. Greculeasa and N. Iacob would like to acknowledge the financial support from the Romanian Ministry of Research and Innovation through projects Core Program PN030101 (21N/2019) (C.B, S.G. and N.I.) and PN-III-P1-1.1.-PD-2019-0724 (S.G.). D. Gingasu and I. Mindru would like to thank Dr. Luminita Patron for her support and expertise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gingasu, D., Mindru, I., Culita, D.C. et al. Structural, morphological and magnetic investigations on cobalt ferrite nanoparticles obtained through green synthesis routes. Appl. Phys. A 127, 892 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05044-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05044-0