Abstract
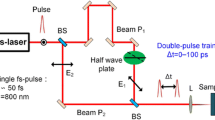
In this paper, the Mach Zehnder interferometer is utilized to generate a collinear dual optical path with 800-nm center wavelength, 1 kHz repetition rate, 120-fs pulse duration and an energy ratio of 1:1 to scan 6H-SiC crystal at a scanning speed of 500 μm/s, resulting in laser-induced periodic surface structure (LIPSS). From the perspective of instantaneous electron density level, variation of the period of low spatial frequency LIPSS (LSFL) with interpulse delay time and polarization angle is studied. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) characterization of the line-scanned ablation zone combined with fast Fourier transformation (FFT) spectrum analysis shows that the period of LSFL decreases with the increase of delay time, and remains stable when the delay exceeds 240 fs. Meanwhile, the period of LSFL increases with the increase of polarization angle under the same delay time, showing an anisotropy that dependent on the polarization angle. The variation trend of the maximum electron density level with delay time calculated by electron rate equation is roughly consistent with the periodic variation trend. Interaction between incident light and transient metal-like SiC surface is simulated based on finite-difference time-domain method (FDTD). The simulation results show that the surface of the sample has a periodic light field enhancement structure controlled by the transient electron density, which explains the phenomenon that the period decreases with increasing delay time. It is further confirmed that the formation of LSFL is due to the interference of incident light and surface plasmon, and the period of LSFL can be controlled by adjusting the electron density level by delay time. The periodic polarization dependence of LSFL may be related to the relative orientation change of the laser pulse front tilt (PFT) and laser polarization.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.E. Sipe, J.F. Young, J.S. Preston, H.M. van Driel, Laser-induced periodic surface structure. I. Theory. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 27, 1141–1154 (1983)
M. Huang, F. Zhao, Y. Cheng, N. Xu, Z. Xu, Origin of laser-induced near-subwavelength ripples: interference between surface plasmons and incident laser. ACS Nano 3, 4062–4070 (2009)
J. Bonse, S. Höhm, S.V. Kirner, A. Rosenfeld, J. Krüger, Laser-induced periodic surface structures—a scientific evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron 23(3), 9000615 (2017)
T.Q. Jia, F.L. Zhao, M. Huang, H.X. Chen, J.R. Qiu, R.X. Li, Z.Z. Xu, H. Kuroda, Alignment of nanoparticles formed on the surface of 6H-SiC crystals irradiated by two collinear femtosecond laser beams. Appl. Phys. Let. 88(11), 3668 (2006)
X.J. Wu, T.Q. Jia, F.L. Zhao, M. Huang, N.S. Xu, H. Kuroda, Z.Z. Xu, Formation mechanisms of uniform arrays of periodic nanoparticles and nanoripples on 6H-SiC crystal surface induced by femtosecond laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 86, 491–495 (2007)
G. Obara, H. Shimizu, T. Enami, E. Mazur, M. Terakawa, M. Obara, Growth of high spatial frequency periodic ripple structures on SiC crystal surfaces irradiated with successive femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 21, 26324–26334 (2013)
G. Li, J. Li, Y. Hu, C. Zhang, X. Li, J. Chu, W. Huang, Femtosecond laser color marking stainless steel surface with different wavelengths. Appl. Phys. A 118(4), 1189–1196 (2015)
N. Tagawa, M. Takada, A. Mori, H. Sawada, K. Kawahara, Development of contact sliders with nanotextures by femtosecond laser processing. Tribol. Lett. 24(2), 143–149 (2006)
B. Wu, M. Zhou, J. Li, X. Ye, G. Li, L. Cai, Superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated by microstructuring of stainless steel using a femtosecond laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(1), 61–66 (2009)
M. Martínez-Calderon, M. Manso-Silván, A. Rodríguez, M. Gómez-Aranzadi, J.P. García-Ruiz, S.M. Olaizola, R.J. Martín-Palma, Surface micro- and nano-texturing of stainless steel by femtosecond laser for the control of cell migration. Sci. Rep. 6, 36296 (2016)
H. Mustafa, M. Jalaal, W. Ya, N. Ur Rahman, D.T.A. Matthews, G.R.B.E. Römer, Short and ultrashort pulsed laser processing of zinc : resolidification morphology of ablated craters. J. of Laser Micro Nanoen. 13(3), 178–188 (2018)
M. Barberoglou, G.D. Tsibidis, D. Gray, E. Magoulakis, C. Fotakis, E. Stratakis, P.A. Loukakos, The influence of ultra-fast temporal energy regulation on the morphology of Si surfaces through femtosecond double pulse laser irradiation. Appl. Phys. A 113(2), 273–283 (2013)
W. Han, L. Jiang, X. Li, Q. Wang, H. Li, Y. Lu, Anisotropy modulations of femtosecond laser pulse induced periodic surface structures on silicon by adjusting double pulse delay. Opt. Express 22(13), 15820–15828 (2014)
S. Xu, H. Dou, K. Sun, Y. Ye, Z. Li, H. Wang, W. Liao, H. Liu, X. Miao, X. Yuan, X. Jiang, X. Zu, Scan speed and fluence effects in femtosecond laser induced micro/nano-structures on the surface of fused silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 492, 56–62 (2018)
J. Song, W. Tao, M. Gong, J. Ye, Y. Dai, G. Ma, J. Qiu, The three-level ripples induced by femtosecond laser on a 6H-SiC single crystal and the formation mechanism. Appl. Phys. A 122(4), 450 (2016)
J. Bonse, S. Höhm, A. Rosenfeld, J. Krüger, Sub-100-nm laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of titanium by Ti:sapphire femtosecond laser pulses in air. Appl. Phys. A 110(3), 547–551 (2013)
F. Meng, J. Hu, W. Han, P. Liu, Q. Wang, Morphology control of laser-induced periodic surface structure on the surface of nickel by femtosecond laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 13(6), 062201–062201 (2015)
K. Zhang, J. Zhang, L. Jiang, X. Li, Y. Liu, B. Li, Y. Lu, Ablation enhancement of metal in ultrashort double-pulse experiments. Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 261906 (2018)
J. Zhang, S. Wang, M. Wang, Z. Chu, Femtosecond Laser Double Pulses Nanofabrication on Silicon. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 565, 012018 (2019)
M. Barberoglou, D. Gray, E. Magoulakis, C. Fotakis, E. Stratakis, Controlling ripples’ periodicity using temporally delayed femtosecond laser double pulses. Opt. Express 21, 18501–18508 (2013)
W.J. Choyke, G. Pensl, Physical properties of SiC. MRS Bull 22, 25–29 (1997)
Q.Z. Zhao, F. Ciobanu, S. Malzer, L.J. Wang, Enhancement of optical absorption and photocurrent of 6H-SiC by laser surface nanostructuring. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 283 (2007)
M. Deki, T. Ito, M. Yamamoto, T. Tomita, S. Matsuo, S. Hashimoto, T. Kitada, T. Isu, S. Onoda, T. Ohshima, Enhancement of local electrical conductivities in SiC by femtosecond laser modification. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98(13), 697 (2011)
J. Song, Y. Dai, W. Tao, M. Gong, G. Ma, Q. Zhao, J. Qiu, Surface birefringence of self-assembly periodic nanostructures induced on 6H-SiC surface by femtosecond laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 363, 664–669 (2016)
F. Fraggelakis, E. Stratakis, P.A. Loukakos, Control of periodic surface structures on silicon by combined temporal and polarization shaping of femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 444, 154–160 (2018)
F. Keilmann, Y.H. Bai, Periodic surface structures frozen into CO2 laser-melted quartz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 29, 9–18 (1982)
G. Zhou, P.M. Fauchet, A.E. Siegman, Growth of spontaneous periodic surface structures on solids during laser illumination. Phys. Rev. B 26(10), 5366–5381 (1982)
A.Q. Wu, I.H. Chowdhury, X. Xu, Femtosecond laser absorption in fused silica: Numerical and experimental investigation. Phys. Rev. B 72(8), 085128 (2005)
T.E. Tiwald, J.A. Woollam, S. Zollner, J. Christiansen, R.B. Gregory, T. Wetteroth, S.R. Wilson, A.R. Powell, Carrier concentration and lattice absorption in bulk and epitaxial silicon carbide determined using infrared ellipsometry. Phys. Rev. B 60, 11464–11474 (1999)
A.A. Borshch, M.S. Brodyn, V.Y. Gayvoronsky, Diagnostics of optical nonlinearities: spatial beam distortion technique and its application to semiconductors and novel materials. Proc. SPIE 5024, 128–136 (2003)
K. Xie, J.H. Zhao, J.R. Flemish, T. Burke, W.R. Buchwald, G. Lorenzo, H. Singh, Electron. Device Lett. IEEE 17, 142–144 (1996)
A. Galeckas, J. Linnros, V. Grivickas, U. Lindefelt, C. Hallin, Auger recombination in 4H-SiC: unusual temperature behavior. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 3269–3271 (1997)
J.Y. Derrien, J. Krüger, T.E. Itina, S. HöHm, A. Rosenfeld, J.R. Bonse, Rippled area formed by surface plasmon polaritons upon femtosecond laser double-pulse irradiation of silicon. Opt. Express 21(24), 29643 (2013)
J. Song, W. Tao, H. Song, M. Gong, G. Ma, Y. Dai, Q. Zhao, J. Qiu, Laser-induced periodic surface structures on 6H-SiC single crystals using temporally delayed femtosecond laser double-pulse trains. Appl. Phys. A 122(4), 341 (2016)
S. Ramo, J. Whinnery, T. Duzer, Fields and Waves in Communication Electronics (Wiley, New York, 1993), p. 684
W.J. Choyke, L. Patrick, Refractive Index and Low-Frequency Dielectric Constant of 6H-SiC. JOSA 58, 377–379 (1968)
A. Collins, D. Rostohar, C. Prieto, Y. Chan, G.M. O’Connor, Laser scribing of thin dielectrics with polarized ultrashort pulses. Opt. Laser Eng. 60, 18–24 (2014)
X. Li, W. Rong, L. Jiang, K. Zhang, C. Li, Q. Cao, G. Zhang, Y. Lu, Generation and elimination of polarization-dependent ablation of cubic crystals by femtosecond laser radiation. Opt. Express 22(24), 30170–30176 (2014)
H.P. Iwata, Determination of the in-plane anisotropy of the electron effective mass tensor in 6H–SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82(4), 598–600 (2003)
Y. Dai, J. Ye, M. Gong, X. Ye, X. Yan, G. Ma, J. Qiu, Forced rotation of nanograting in glass by pulse-front tilted femtosecond laser direct writing. Opt. Express 22, 28500–28505 (2014)
Y. Dai, G. Wu, X. Lin, G. Ma, J. Qiu, Femtosecond laser induced rotated 3D self-organized nanograting in fused silica. Opt. Express 20(16), 18072–18078 (2012)
P. Liu, L. Jiang, J. Hu, W. Han, Y. Lu, Direct writing anisotropy on crystalline silicon surface by linearly polarized femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 38, 1969–1971 (2013)
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11974147, 11774220, 61205128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, L., Kong, D., Zhang, X. et al. Ripple period adjustment on SiC surface based on electron dynamics control and its polarization anisotropy. Appl. Phys. A 127, 22 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04181-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04181-2