Abstract
Objectives
We proposed a strategy for the creation of a 6-mm transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) and to assess its effectiveness compared to a conventional 8-mm shunt for TIPS-induced hepatic encephalopathy (HE).
Methods
Patients were reviewed retrospectively using propensity score matching (1:1) and divided into 6-mm and 8-mm shunt groups based on shunt diameter. The stent patency, HE incidence, and rebleeding rate between the two groups were then compared.
Results
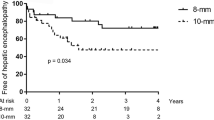
From January 2018 to June 2021, both 6-mm shunt group and 8-mm shunt group included 58 patients. The 6-mm shunt group had significantly smaller liver volumes (879.3 ± 237.1 vs. 1008.8 ± 293.0; p = 0.010), and the median stent patency times were 30.7 and 33.8 months in the 6-mm and 8-mm groups, respectively (p = 0.124). No statistically significant difference was found between the two groups in the 1-year (8.6% vs. 3.4%; p = 0.242) and 2-year (17.2% vs. 12.1%; p = 0.242) rebleeding rates. The 1-year cumulative incidences of overt HE were 12.1% and 27.6% in the 6-mm and 8-mm groups, respectively (p = 0.040), and the 2-year cumulative overt HE incidences in these groups were 19.0% and 36.2%, respectively (p = 0.038). Notably, patients with a 6-mm shunt also experienced less hepatic impairment.
Conclusions
For patients with variceal bleeding and a small liver volume, the 6-mm shunt significantly reduced the incidence of overt HE, protected perioperative liver function, and did not affect stent patency or rebleeding rate.
Clinical relevance statement
For patients with variceal bleeding with small liver volume, the 6-mm transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) significantly reduced the incidence of overt hepatic encephalopathy after TIPS, protected perioperative liver function, and did not affect stent patency and rebleeding rate.
Key Points.
• A strategy for the creation of a 6-mm transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for patients with variceal bleeding and a small liver volume was proposed.
• The 6-mm transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt significantly reduced the incidence of overt hepatic encephalopathy.
• The 6-mm transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt did not affect stent patency or rebleeding rate.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALB:
-
Albumin
- CDUS:
-
Color Doppler ultrasound
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- C-P:
-
Child-Pugh
- HE:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- MELD:
-
Model for end-stage liver disease
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PPG:
-
Portal pressure gradient
- PT:
-
Prothrombin time
- TIPS :
-
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
References
Ezequiel M, Adrián G (2020) What’s new in portal hypertension? Liver Int 40(Suppl. 1):122–127
Marta M, Anna B, Virginia H-G (2020) Precision medicine in variceal bleeding: are we there yet? J Hepatol 72(4):774–784
European Association for the Study of the Liver (2018) EASL clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol 69(2):406–460
Danielle A, Fong NS, Florence W (2019) Refractory ascites in liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 114(1):40–47
Christophe Bureau, Dominique Thabut, Frédéric Oberti et al (2017) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts with covered stents increase transplant-free survival of patients with cirrhosis and recurrent ascites. Gastroenterology 152:157–163
Oana N-F, Guohong H, Marika R et al (2021) Effects of early placement of transjugular portosystemic shunts in patients with high-risk acute variceal bleeding: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology 160:193-205.e10
Xuefeng Luo, Xiaoze Wang, Yongjun Zhu et al (2019) Clinical efficacy of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt created with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent-grafts: 8-mm versus 10-mm. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 42:737–743
Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J (2017) Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the american association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 65:310–335
Martin R (2013) TIPS: 25 years later. J Hepatol 59:1081–1093
Carlos García-Pagán Juan, Karel Caca, Christophe Bureau et al (2010) Early use of TIPS in patients with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 362:2370–9
Lisanne Holster I, Tjwa Eric TTL, Adriaan Moelker et al (2016) Covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic therapy + β-blocker for prevention of variceal rebleeding. Hepatology 63:581–9
Wai-Kay Seto, Ying-Ru Lo, Jean-Michel Pawlotsky et al (2018) Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 392:2313–2324
Yong Lv, Xingshun Qi, Chuangye He et al (2018) Covered TIPS versus endoscopic band ligation plus propranolol for the prevention of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients with portal vein thrombosis: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 67:2156–2168
Christian Pieper Claus, Christian Jansen, Carsten Meyer et al (2017) Prospective evaluation of passive expansion of partially dilated transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt stent grafts-a three-dimensional sonography study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 28:117–125
Zheng Kenneth I, Chuan Liu, Jia Li et al (2020) Validation of baveno VI and expanded baveno VI criteria to identify high-risk varices in patients with MAFLD-related compensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol 73:1571–1573
Qiuhe Wang, Yong Lv, Ming Bai et al (2017) Eight millimetre covered TIPS does not compromise shunt function but reduces hepatic encephalopathy in preventing variceal rebleeding. J Hepatol 67:508–516
Ashkan M, Dominik B, Martin R (2017) The underdilation of nitinol stents at TIPS implantation: solution or illusion? Eur J Radiol 89:123–128
Zongzhang Huang, Qigu Yao, Jianping Zhu et al (2021) Efficacy and safety of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) created using covered stents of different diameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagn Interv Imaging 102:279–285
Bradley Christopher R, Cox Eleanor F, Scott Robert A et al (2018) Multi-organ assessment of compensated cirrhosis patients using quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. J Hepatol 69:1015–1024
Kuhn-Fulton J, Trerotola SO, Harris VJ, Snidow JJ, Lumeng L (1996) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedure: efficacy of 10-mm versus 12-mm wallstents. Radiology 199:658–664
Oliviero Riggio, Lorenzo Ridola, Stefania Angeloni et al (2010) Clinical efficacy of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt created with covered stents with different diameters: results of a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol 53:267–72
Lopez-Lopez V, Miura K, Lopez-Conesa A, Brusadin R, Navarro A, Robles-Campos R (2023) ALPPS versus portal vein embolization for hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: a delicate balance between volume and morbidity. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 12:284–286
Jonel Trebicka, Diana Bastgen, Jonathan Byrtus et al (2019) Smaller-diameter covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt stents are associated with increased survival. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:2793-2799.e1
Miraglia R, Maruzzelli L, Tuzzolino F, Petridis I, D’Amico M, Luca A (2017) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in patients with cirrhosis with refractory ascites: comparison of clinical outcomes by using 8- and 10-mm PTFE-covered stents. Radiology 284:281–288
Riggio O, Ridola L, Lucidi C, Angeloni S (2020) Emerging issues in the use of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) for management of portal hypertension: time to update the guidelines? Dig Liver Dis 42:462–467
Trebicka J, Gu W, Ibáez-Samaniego L, Hernández-Gea V, Baares R (2020) Rebleeding and mortality risk are increased by ACLF but reduced by pre-emptive TIPS. J Hepatol 73:1082–1091
Wei Y, Liu Jia-Cheng Wu, Yong-Juan, et al (2022) Effect of underdilated transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on prognosis in patients with prior splenectomy: a propensity score-matched case-control study. Abdom Radiol (NY) 47:3615–3627
Gilberto Silva-Junior, Fanny Turon, Anna Baiges et al (2017) Timing affects measurement of portal pressure gradient after placement of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in patients with portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 152:1358–1365
Zhenkang Qiu, Wenliang Zhu, Huzheng Yan et al (2022) Single-Centre retrospective study using propensity score matching comparing left versus right internal jugular vein access for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) creation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 45:563–569
Pereira K, Carrion AF, Martin P et al (2015) Current diagnosis and management of post-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt refractory hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Int 35(12):2487–2494
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients enrolled in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation (fund No: 82072035).
Role of the Funder: The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Mingsheng Huang.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University approved the study and waived the requirement of informed consent because of its low risk.
Ethical approval
The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University approved the study and waived the requirement of informed consent because of its low risk.
Study subjects or cohorts overlap
No study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported in any elsewhere.
Methodology
• Retrospective
• case–control study
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Xiang, Z., Zhao, C. et al. 6-mm shunt transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with severe liver atrophy and variceal bleeding. Eur Radiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10346-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10346-3