Abstract
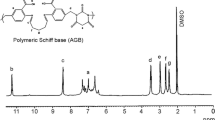
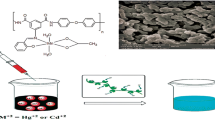
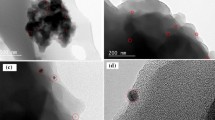
A novel polymeric resin was synthesized by condensing a Schiff base of 6-chloro-2-aminobenzothiazole and salicyldehyde with formaldehyde, which may have multidimensional application. First step of the synthesis of novel polymeric material is synthesis of Schiff base, which is the monomer of the resin. The Schiff base was synthesize by using greener method to reduce hazardous chemical waste and reaction time, so that reduction of environmental pollution and conservation of energy can be achieved. The greener method is compared with the conventional method. The metal polychelates of the polymeric resin with Cu2+ and Fe3+ were synthesized. The Schiff base, resin and its polychelates were converted to nanodimension and its dimension is measured by DLS method. The structure of the Schiff base, resin and polychelates are ascertained by FTIR, 1H NMR spectroscopy. The experimental data are compared with the computational data obtained from Gaussian software to ascertain the synthesis of these materials. These materials have a very wide range of application starting from analytical chemistry to biochemistry. The antibacterial activities of Schiff base, resin and metal polychelates were studied against pathogenic bacteria Escherichia coli by turbidity measurement method. All these materials are found to be effective against the tested bacterial species, whereas the polychelates are shown exceptional results.

Optimization structure of Schiff base
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagla P, Kaiser J (1996) Epidemiology: India’s spreading health crisis draws global arsenic experts. Science 274:174–175
Lepkowski W (1998) Arsenic crisis in Bangladesh. C&EN News November 16:27–29
Bearak D (1998) New Bangladesh disaster: wells that pumps poison. The New York Times, November 10
Chowdhury UK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury TR, Samanta G, Mandal BK, Basu GC, Chanda CR, Lodh D, Saha KC, Mukherjee SK, Roy S, Kabir S, Quamruzzman Q, Chakraborti D (2000) Groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh and West Bengal, India. Environ Health Perspect 108:393–397
Prociv P (1987) Palm Island Reconsidered. Was it Copper poisoning? Int Med J 17:3
Fenwich A (2006) Water borne infectious diseases- could they be consigned to history? Science 4:1077–1081
Craun GE (2006) FraunMF, Calderon RL, beach MJ, water borne out breaks reported in the united states. J Water Health 4:19–30
World Health Organization (WHO) Water Quality and Health. Drinking water chlorination – A review of disinfection practices and issues. 2014. http://www.waterandhealth.org/drinkingwater/wp.html. Accessed 28 Apr 2014
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manage 62(3):407–418
Ueno K, Martell AE (1955) Infrared study of metal chelates of bisacetylacetoneethylenediimine and related compounds. J Phys Chem 59:998
Ueno K, Martell AE (1956) Infrared studies on synthetic oxygen carriers. J Phys Chem 60:1270
Che CM, Cheng WK (1986) Manganese(III) amide complexes as a new class of catalyst for efficient alkene epoxidation. J Chem Soc Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/C39860001443
Johnson DK, Murphy TB, Rose TB, Goodwin WH, Pickart L (1982) Cytotoxic chelators and chelates 1. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in cultured rodent and human cells by aroylhydrazones and by a copper(II) complex of salicylaldehyde benzoyl hydrazine. Inorg Chim Acta 67:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1693(00)85058-6
Alzuet G, Ferrer S, Borras J, Supuran CT (1994) Complexes of heterocyclic sulfonamides-a class of dual carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Roum Chem Quart Rev 2(4):283–300
Almajan GL, Barbuceanu SF, Innocenti A, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT (2008) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of the cytosolic and tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II and IX with some 1,3,4-oxadiazole- and 1,2,4-triazole-thiols. J Enzym Inhib Med Chem 23:101–107
Supuran CT (1995) Metal complexes of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-disulfonamide are strong dual carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, although the ligand possesses very weak such properties. Met Based Drugs 2:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1155/MBD.1995.331
Supuran CT, Scozzafava A (1997) Novel aromatic/heterocyclic sulfonamides and their metal complexes as inhibitors of carbonic anhydraseisozymes I, II and IV. J Enz Inhib 12(1):37–51
Alzuet G, Casanova J, Borras J, Garcia-Granda S, Gutierrez-Rodriguez A, Supuran CT (1998) Copper complexes modelling the interaction between benzolamide and Cu-substituted carbonic anhydrase. Crystal structure of Cu(bz)(NH3)4 complex. Inorg Chim Acta 273(1–2):334–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1693(97)06020-9
Chohan ZH, Jaffery MF, Supuran CT (2001) Antibacterial Co(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes of Thiadiazoles Schiff bases. Met Based Drugs 8(2):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1155/MBD.2001.95
Komis G (1984) Comprehensive heterocyclic chemistry. Katritzky AR (ed), Pergamon, New York, vol 6, Part 4B
Kornis G (1984) 1,3,4-Thiadiazoles. In: Katritzky AR (ed) Comprehensive heterocyclic chemistry. Pergamon, New York, vol 6, Part 4B, p 545
Chohan ZH, Kausar S (2000) Synthesis, characterization and biological properties of tridentate NNO, NNS and NNN donor thiazole-derived furanyl, thiophenyl and pyrrolyl schiff bases and their Co(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) metal chelates. Met Based Drugs 7(1):17–22. https://doi.org/10.1155/MBD.2000.17
Chohan ZH, Pervez H, Rauf A, Scozzafava A, Claudiu T, Supuran CT (2002) Isatin-derived antibacterial and antifungal compounds and their transition metal complexes. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 17(2):117–122
Vukovic N, Sukdolak S, Solujic S, Milosevic T (2008) Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of some novel 2-aminothiazole derivatives of 4-hydroxy-chromene-2-one. Arch Pharm Chem Life Sci 341(8):491–496. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.200700215
Chohan ZH, Praveen M (2000) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of symmetric 1,1′‐ferrocene derived Schiff‐base ligands and their Co(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) chelates. Appl Organomet Chem 14(6):376–382. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-0739(200007)14:7%3c376::AID-AOC995%3e3.0.CO;2-5
Chohan ZH (1999) Ni (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II) metal chelates with some thiazole derived schiff-bases: their synthesis, characterization and bactericidal properties. Met Based Drugs 6(2):75–90. https://doi.org/10.1155/MBD.1999.75
Mohanty D (2014) Antibacterial studies of the polymeric phenolic schiff bases containing aminothiazole moiety. Int J Res Pharm Nano Sci. 3(3):215–221
Helfferich FG (1961) Ligand exchange: a novel separation technique. Nature 189:1001–1002
Helfferich FG (1962) Ion exchange. McGraw-Hill Book Company, London
Bruno Urbano; Bernabé L. Rivas, (2014) Sorption properties of chelating polymer-clay nano-composite resin based on iminodiacetic acid and montmorillonite: Water absorbency, metal ion uptake, selectivity, and kinetics. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4109
Ricco R, Konstas K, Styles MJ, Richardson JJ, Babarao R, Suzuki K, Scopece P, Falcaro P (2015) Lead(II) uptake by aluminium based magnetic framework composites (MFCs) in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 3:19822–19831
Yang J, Hou B, Wang J, Tian B, Bi J, Wang N, Li X, Huang X (2019) Nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Nanomaterials 9:424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030424
Kuehne ME (1959) The applications of enamines to a new synthesis of b-ketonitriles. J Am Chem Soc 81:5400–5404
Taguchi K, Westheimer FH (1971) Catalysis by molecular sieves in the preparation of ketimines and enamines. J Org Chem 36:1570–1572
Billman JH, Tai KMJ (1958) Reduction of Schiff bases II: Benzhydrylamines and structurally related compounds. J Org Chem 23:535–539
White WA, Weingarten H (1967) A versatile new enamine synthesis. J Org Chem 32:213–214
Texier-Boullet F (1985) A simple, convenient, and mild synthesis of imines on alumina surface without solvent. Synthesis, 679–681.
Naeimi H, Salimi F, Rabiei K (2006) Mild and convenient one-pot synthesis of Schiff bases in the presence of P2O5=Al2O3 as new catalyst under solvent-free conditions. J Mol Cat A: Chem 260:100–104
Chakraborti AK, Bhagat S, Rudrawar S (2004) Magnesium perchlorate as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of imines and phenylhydrazones. Tetrahedron Lett 45:7641–7644
Vazquez MA, Landa M, Reyes L, Miranda R, Tamariz J, Delgado F (2004) Infrared irradiation: effective promoter in the formation of N-benzylideneanilines in the absence of solvent. Synth Commun 34:2705–2718
Touchelte KM (2006) Reductive amination: A remarkable experiment for the organic laboratory. J Chem Educ 83:929–931
Varma RS, Dahiya R, Kumar S (1997) Clay-catalyzed synthesis of imines and enamines under solvent-free conditions using microwave irradiation. Tetrahedron Lett 38:2039–2042
Gopalakrishnan M, Sureshkumar P, Kanagarajan V, Thanusu J (2007) New environmentally friendly, solvent-free synthesis of imines using calcium oxide under microwave irradiation. J Res Chem Intermed. 33:541–548
Bennett JS, Charles KL, Miner MR, Heuberger CF, Spina EJ, Bartels MF, Foreman T (2009) Ethyl lactate as a tunable solvent for greener synthesis of arylaldimines. Green Chem 11:166–168
Silverstein RM, Bassler GC, Morrill TC (1981) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. Wiley, New York, p 130
Thamizharasi S, Reddy AVR (1992) Polymer 33(11):2421
Chen H, Cronin JA, Archer RD (1994) Supramolecular polymers. Macromolecules 27:2174
Antony R, Pillai CKS (1994) Synthesis and thermal characterization of chemically modified phenolic resins. J Appl Polym Sci 54(4):429–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1994.070540403
Hafi N, Kolli M, Vergnaud JM, Montheard JP (1991) Amines release from Schiff bases polymers and diffusion from dosage forms with eudragit RL in acidic medium. J Appl Polym Sci 43(10):1837–1847. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1991.070431007
Azarudeen RS, Burkanudeen AR (2012) Synthesis, spectral, morphology, thermal degradation kinetics and antibacterial studies of terpolymer metal complexes. J Inorg Organometa Polym Mater 22:791–806
He Y, Cai C (2011) Polymer-supported macrocyclic Schiff base palladium complex as an efficient catalyst for the Heck reaction. Appl Organomet Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.1839
Tamami B, Ghasemi S (2015) Catalytic activity of Schiff-base transition metal complexes supported on crosslinked polyacrylamides for hydrogen peroxide decomposition. J Organomet Chem 794:311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2015.05.041
Elmali A, Kabak M, Elerman Y (1999) Keto–enol tautomerism, conformations and structure of N-(2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl), 2-hydroxybenzaldehydeimine J Mol Struct 477:151–158
Patel PR, Thaker BT, Zele S (1999) Preparation and characterisation of some lanthanide complexes involving a heterocyclic β – diketone Ind J Chem 38A:563–567
Misra PK, Mishra BK, Behera GB (1988) Determination of dissociation constants of salicylidene- 2-aminobenzothiazole & p-hydroxybenzylidene-2-aminobenzothiazole in different surfactant systems. Ind J Chem 27A:889–892
Panigrahi S, Misra PK (2016) The effect of solvent on electronic absorption bands of some Benzylideneanilines. J Mol Liq 224:53–61
Perry BF, Beezer AE, Miles RJ, Smith BW, Miller J, Nascimento MG (1988) Evaluation of microcalorimetry as a drug bioactivity screening procedure, application to a series of novel Schiff base compounds. Microbois 45:181
Cimerman Z, Miljanic S, Galic N (2000) Schiff bases derived from aminopyridines as spectrofluorimetric analytical reagent. Cro Chem Acta 73:81
Demircioglu Z, Kastas CA, Buyukgungor O (2015) Theoretical analysis (NBO, NPA, Mulliken Population Method) and molecular orbital studies (hardness, chemical potential, electrophilicity and Fukui function analysis) of (E)-2-((4-hydroxy-2-methylphenylimino)methyl)-3-methoxyphenol. J Mol Struct 1091:183–195
Sorrosa AA, Gonzalez JIH, Arellano AR, Toscano RA, Martinez RR, Mendoza JRP, Morales DM (2015) Synthesis, structural characterization and biological activity of fluorinated Schiff-bases of the type [C6H4-1-(OH)-3-(CH NArF)]. J Mol Struct 1085:249–257
Minkin VI, Tsukanov AV, Dubonosov AD, Bren VA (2011) Tautomeric Schiff bases: Iono-, solvato-, thermo- and photochromism. J Mol Struct 998:179–191
Shepelenko EN, Tsukanov AV, Revinskii YV, Dubonosov AD, Bren VA, Minkin VI (2007) Benzoid-quinoid tautomerism of schiff bases and their structural analogs: LIII. Schiff bases derived from 5-hydroxy- and 5-hydroxy-6-nitro-2,3-diphenyl-1-benzofuran-4-carbaldehydes. Russ J Org Chem 43:559–562
Hadjoudis E, Rontoyianni A, Ambroziak K, Dziembowska T, Mavridis IM (2004) Photochromism and thermochromism of solid trans-N,N′-bis-(salicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamines and trans-N,N′-bis-(2-hydroxy-naphylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine. J Photochem Photobiol A 162:521–530
Alaghaz AMA, Zayed ME, Alharbi SA (2015) Synthesis, spectral characterization, molecular modeling, biological activity and potentiometric studies of 4-amino-5-mercapto-3-methyl-S-triazole Schiff’s base complexes. J Mol Struct 1083:430–440
Hota P, Biswal SP, Panigrahi S, Misra PK (2019) Vibrational and electronic spectral analyses of substituted N-benzylideneanilines for Possible application as material for a functional Dyad: theoretical and experimental explorations. Mater Today: Proc 9:680–688
Temel E, Albayrak C, Buyukgungor O, Odabasoglu M (2006) Zwitterionic (E)-2-hy¬droxy-6-[(o-tolyl¬iminio)meth¬yl]phenolate 0.07-hydrate. Acta Crystallogr E 62:04484–04486
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge HOD and other faculty of Ravenshaw University, VSSUT for providing their various analytical facilities. The authors especially express their gratitude towards Prof. S. K. Swain of VSSUT and his research scholars for providing technical support to carry out various analytical studies. The Principal, Dhenkanal (Auto) college is highly acknowledged for providing facilities to carry out the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, S.R., Mohapatra, P. & Mohanty, D. Green synthesis, characterisation and antibacterial activity studies of new multifunctional nano polymeric material, which may have multidimensional application in water purification. Polym. Bull. 80, 703–723 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04046-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04046-5