Abstract
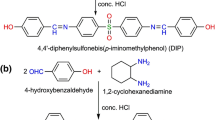
In this work, a series of isovanillin-or syringaldehyde-based new Schiff base monomers were synthesized and polymerized using terephthaloyl chloride by solution condensation polymerization technique. Both the monomers and polymers were characterized by FT-IR, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR. The thermal and molecular weight properties were determined by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Gel permeation chromatography (GPC). The antimicrobial activities of the polyesters were evaluated based on minimum inhibition concentration against bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and staphylococcus aureus as well as fungi such as Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger. The results of inhibition zones showed that new Schiff base polyesters had good antimicrobial activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiliopoulos IK, Mikroyannidis JA (1996) Soluble, rigid-rod polyamide, polyimides, and polyazomethine with phenyl pendent groups derived from 4,4‘‘-Diamino-3,5,3‘‘,5‘‘-tetraphenyl-p-terphenyl. Macromolecules 29:5313–5319
Cerrada P, Oriol L, Piñol M, Serrano JL, Alonso PJ, Puértolas JA, Iribarren I, Muñoz Guerra S (1999) Influence of hydroxy functionalization and metal cross-linking on fiber properties of liquid-crystalline polyazomethines. Macromolecules 32:3565–3573
Shukla U, Rao KV, Rakshit AK (2003) Thermotropic liquid-crystalline polymers: synthesis, characterization and properties of polyazomethine esters. J Appl Polym Sci 88:153–160
Aly KI, Khalaf A (2000) New polymer syntheses. IX. Synthesis and properties of new conducting polyazomethine polymers containing main chain cycloalkanone and pyridine moieties. J Appl Polym Sci 77:1218–1229
Jung SH, Lee TW, Kim YC, Suh DH, Cho HN (2003) Synthesis and characterization of fluorene-based poly(azomethines). Opt Mater 21:169–173
Rasool R, Hasnain S, Nishat N (2014) Metal-based Schiff base polymers: preparation, spectral, thermal and their in vitro biological investigation. Des Monomers Polym 17:217–226
Jenekhe SA, Yang CJ, Vanherzeele H, Meth JS (1991) Cubic nonlinear optics of polymer thin films. Effects of structure and dispersion on the nonlinear optical properties of aromatic Schiff base polymers. Chem Mater 3:985–987
Iwan A, Boharewicz B, Tazbir I, Malinowski M, Filapek M, Kłąb T, Luszczynska B, Glowacki I, Korona KP, Kaminska M, Wojtkiewicz J, Lewandowska M, Hreniak A (2015) New environmentally friendly polyazomethines with thiophene rings for polymer solar cells. Sol Energy 117:246–259
Niu H, Huang Y, Bai X, Li X, Zhang G (2004) Study on crystallization, thermal stability and hole transport properties of conjugated polyazomethine materials containing 4,4′-bisamine-triphenylamine. Mater Chem Phys 86:33–37
Jae-Wook K, Jang-Joo K, Jinkyu K, Xiangdan L, Myong-Hoon L (2002) Low-loss and thermally stable TE-mode selective polymer waveguide using photosensitive fluorinated polyimide. IEEE Photonic Tech Let 14:1297–1299
Iwan A, Palewicz M, Chuchmala A, Sikora A, Gorecki L, Sek D (2013) Opto(electrical) properties of triphenylamine-based polyazomethine and its blend with [6,6]-phenyl C61 butyric acid methyl ester. High Perform Polym 25:832–842
Kamacı M, Kaya I (2017) A highly selective, sensitive and stable fluorescent chemo sensorbased on Schiff base and poly(azomethine-urethane) for Fe3+ ions. J Ind Eng Chem 46:234–243
Marin L, Cozan V, Bruma M, Grigoras VC (2006) Synthesis and thermal behaviour of new poly(azomethine-ether). Eur Polym J 42(5):1173–1182
Sȩk D (1984) Liquid crystalline properties of new poly(azomethine esters). Eur Polym J20:923–926
Yılmaz Baran N, Karakışla M, Demir HO, Saçak M (2016) Synthesis, characterization, conductivity and antimicrobial study of a novel thermally stable polyphenol containing azomethine group. J Mol Struct 1123:153–161
Kaya I, Çöpür S, Karaer H (2017) Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical properties of poly(phenoxy-imine)s containing carbazole unit. Int J Ind Chem 8:1–15
Yıldırım M, Kaya I (2014) Synthesis and characterizations of poly(ether)/poly(phenol)s including azomethine coupled benzothiazole side chains: the effect of reaction conditions on the structure, optical, electrochemical, electrical and thermal properties. Polym Bull 71:3067–3084
Yılmaz Baran N, Demir HO, Kostekçi S, Sacak M (2015) Poly‐2‐[(4‐methylbenzylidene) amino] phenol: Investigation of thermal degradation and antimicrobial properties. J Appl Polym Sci 132
Kaya I, Emdi D, Saçak M (2009) Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of Oligomer and Monomer/Oligomer–Metal Complexes of 2-[(Pyridine-3-yl-methylene)amino]phenol. J Inorg Organomet Polym 19:286–297
McConkey BJ, Sobolev V, Edelman M (2002) The performance of current methods in ligand–protein docking. Curr Sci 83:845–855
Francolini I, Donelli G, Crisante F, Taresco V, Piozzi A (2015) Antimicrobial polymers for anti-biofilm medical devices: state-of-art and perspectives. Adv Exp Med Biol 831:93–117
Sedlarik V (2013) Antimicrobial modifications of polymers. In: Chamy R, Rosenkranz F (eds) Biodegradation-Life of Science. InTech, Rijeka, Croatia, pp 187–204
Martins AF, Facchi SP, Follmann HD, Pereira AG, Rubira AF, Muniz EC (2014) Antimicrobial activity of chitosan derivatives containing N-quaternized moieties in its backbone: a review. Int J Mol Sci 15:20800–20832
Deka SR, Sharma AK, Kumar P (2015) Cationic polymers and their self-assembly for antibacterial applications. Curr Top Med Chem 15(13):1179–1195
Chung D, Papadakis SE, Yam KL (2003) Evaluation of a polymer coating containing triclosan as the antimicrobial layer for packaging materials. Int J Food Sci Technol 38(2):165–169
da Silva CM, da Silva DL, Modolo LV, Alves RB, de Resende MA, Martins CVB, de Fatima A (2011) Schiff bases: a short review of their antimicrobial activities. Journal of Advanced Research 2:1–8
Al-Balakocy NG, Shalaby SE (2017) Imparting antimicrobial properties to polyester and polyamide fibers-state of the art. Journal of Textile Association 78(3):179–201
Subramani A, Mohammed Mustaque K, Shabeer TK (2017) Synthesis and characterization of new polyesters using Schiff base monomer. Asian J Chem 29(5):1168–1170
Fred W, Billmeyer JR (1965) Characterization of molecular weight distributions in high polymers. J Polym Sci Polym Symp 8:161–178
Aly KI, Khalaf AA, Alkskas IA (2003) New polymer syntheses XII. Polyketones based on diarylidenecycloalkanones. Eur Polym J 39:1273–1279
Deanin RD (1972) Polymer structure, properties and applications. Canners book, Boston 8:457
Yılmaz Baran N, Demir HO, Kostekçi S, Sacak M (2015) Poly-2-[(4-methylbenzylidene) amino] phenol: investigation of thermal degradation and antimicrobial properties. J Appl Polym Sci 132:41758
Kaya I, Emdi D, Saçak M (2009) Oxidative polymerization of N2O2 type Schiff base monomer and its metal complexes: synthesis and thermal, optical and electrochemical properties. J Inorg Organomet Polym 19:286–297
Selvi C, Nartop D (2012) Novel polymer anchored Cr(III) Schiff base complexes: synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial properties. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 95:165–171
Bellamy LJ (1980) The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules, Chapman and Hall, 3rd Edition Vol. 2, London
Narasimhan B (2001) Mathematical models describing polymer dissolution: consequences for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 48:195–210
Brandrup J, Immergut EH, Grulke EA (1999) editors, 4th ed. Polymer handbook, Vol. 7. New York, NY: Wiley, 675–714
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, A.M., Shabeer, T.K. Antimicrobial new Schiff base polyesters: design, thermal, and structural characterizations. Polym. Bull. 79, 1119–1132 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03548-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03548-6