Abstract
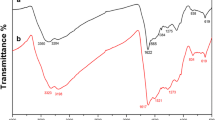
In this work, a novel nanocomposite containing silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) embedded poly(1-naphthylamine) nanospheres (Ag/PNA) was prepared by in situ chemical reduction of silver nitrate. The structure, composition, and morphology of the prepared Ag/PNA nanocomposites were established by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the PNA and Ag/PNA-modified carbon paste electrodes were analyzed using cyclic voltammetry (cyclic voltammogram) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. It is observed that the electrochemical and charge transfer characteristics of PNA have significantly enhanced upon the incorporation of AgNPs. The prepared Ag/PNA nanocomposite has shown impressive electrocatalytic and electrochemical sensing performance toward H2O2. Remarkably, the present Ag/PNA-based enzymeless voltammetric H2O2 sensor showed a wide detection range in the concentration range of 1–3000 μM with a lower detection limit of 0.972 μM. The study revealed that Ag/PNA-modified carbon paste electrodes are an ideal platform for the fabrication of low-cost non-enzymatic H2O2 sensor with high sensitivity, good reproducibility, better selectivity, and stability.
Graphic abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luo X, Morrin A, Killard AJ, Smyth MR (2006) Application of nanoparticles in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Electroanalysis 18:319–326
Murphy CJ, Sau TK, Gole AM, Orendorff CJ, Gao J, Gou L, Hunyadi SE, Li T (2005) Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J Phys Chem B 109:13857–13870
Francis S, Joseph S, Koshy EP, Mathew B (2017) Synthesis and characterization of multifunctional gold and silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of: naregamia alata and their applications in the catalysis and control of mastitis. New J Chem 41:14288–14298
Suchomel P, Kvitek L, Prucek R et al (2018) Simple size-controlled synthesis of Au nanoparticles and their size-dependent catalytic activity. Sci Rep 8:1–11
Choudhary M, Brink R, Nandi D et al (2017) Gold nanoparticle within the polymer chain, a multi-functional composite material, for the electrochemical detection of dopamine and the hydrogen atom-mediated reduction of Rhodamine-B, a mechanistic approach. J Mater Sci 52:770–781
Sagitha P, Sarada K, Muraleedharan K (2016) One-pot synthesis of poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) supported silver nanoparticles and its efficiency in catalytic reduction of methylene blue. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 26:2693–2700
Chamoli P, Das MK, Kar KK (2017) Green synthesis of silver-graphene nanocomposite-based transparent conducting film. Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostruct 90:76–84
Horiguchi Y, Kanda T, Torigoe K et al (2014) Preparation of gold/silver/titania trilayered nanorods and their photocatalytic activities. Langmuir 30:922–928
Stejskal J (2013) Conducting polymer-silver composites. Chem Pap 67:814–848
Spain E, Keyes TE, Forster RJ (2013) Polypyrrole-gold nanoparticle composites for highly sensitive DNA detection. Electrochim Acta 109:102–109
Upadhyay J, Kumar A, Gogoi B, Buragohain AK (2015) Antibacterial and hemolysis activity of polypyrrole nanotubes decorated with silver nanoparticles by an in situ reduction process. Mater Sci Eng, C 54:8–13
Kim J, Ju H, Inamdar AI et al (2014) Synthesis and enhanced electrochemical supercapacitor properties of Ag–MnO2-polyaniline nanocomposite electrodes. Energy 70:473–477
Park E, seok Kwon O, joo Park S et al (2012) One-pot synthesis of silver nanoparticles decorated poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanotubes for chemical sensor application. J Mater Chem 22:1521–1526
Yuan C, Xu Y, Zhong L et al (2013) Heterogeneous silver-polyaniline nanocomposites with tunable morphology and controllable catalytic properties. Nanotechnology 24:185602–185612
Reda SM, Al-Ghannam SM (2012) Synthesis and electrical properties of polyaniline composite with silver nanoparticles. Adv Mater Phys Chem 02:75–81
Dan LI, Huang J, Kaner RB (2009) Polyaniline nanofibers: a unique polymer nanostructure for versatile applications. Acc Chem Res 42:135–145
Ma B, Wang M, Tian D et al (2015) Micro/nano-structured polyaniline/silver catalyzed borohydride reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv 5:41639–41645
Bober P, Stejskal J, Trchová M, Prokeš J (2014) In-situ prepared polyaniline-silver composites: single- and two-step strategies. Electrochim Acta 122:259–266
Blinova NV, Stejskal J, Trchová M et al (2009) The oxidation of aniline with silver nitrate to polyaniline-silver composites. Polymer (Guildf) 50:50–56
Bober P, Stejskal J, Trchová M, Prokeš J (2011) Polyaniline-silver composites prepared by the oxidation of aniline with mixed oxidants, silver nitrate and ammonium peroxydisulfate: the control of silver content. Polymer (Guildf) 52:5947–5952
Stejskal J, Trchová M, Brožová L, Prokeš J (2009) Reduction of silver nitrate by polyaniline nanotubes to produce silver-polyaniline composites. Chem Pap 63:77–83
Nesher G, Aylien M, Sandaki G et al (2009) Polyaniline entrapped in silver: structural properties and electrical conductivity. Adv Funct Mater 19:1293–1298
Massoumi B, Fathalipour S, Massoudi A et al (2013) Ag/polyaniline nanocomposites: synthesize, characterization, and application to the detection of dopamine and tyrosine. J Appl Polym Sci 130:2780–2789
Bober P, Stejskal J, Trchová M et al (2010) Oxidation of aniline with silver nitrate accelerated by p-phenylenediamine: a new route to conducting composites. Macromolecules 43:10406–10413
Tang L, Duan F, Chen M (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded in polyaniline nanofibers via vitamin C for supercapacitor applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:7769–7777
Chen S, Yuan R, Chai Y, Hu F (2013) Electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide using metal nanoparticles: a review. Microchim Acta 180:15–32
Ansari AA, Sumana G, Khan R, Malhotra BD (2009) Polyaniline-cerium oxide nanocomposite for hydrogen peroxide sensor. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:4679–4685
Barman K, Jasimuddin S (2016) Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose and hydrogen peroxide using a bis(acetylacetonato)oxovanadium(iv) complex modified gold electrode. RSC Adv 6:20800–20806
Tian K, Prestgard M, Tiwari A (2014) A review of recent advances in nonenzymatic glucose sensors. Mater Sci Eng, C 41:100–118
Hatchett DW, Josowicz M (2008) Composites of intrinsically conducting polymers as sensing nanomaterials. Chem Rev 108:746–769
Malhotra B, Dhand C, Lakshminarayanan R et al (2015) Polyaniline-based biosensors. Nanobiosensors Dis Diagnosis 4:25
Kabomo TM, Scurrell MS (2016) The effects of ring substituents in aniline on the reactivity of PANI with hydrogen tetrachloroaurate and the dispersion of gold nanoparticles. Polym Adv Technol 27:759–764
Refat MS, Adam AM (2014) Research and reviews. J Mater Sci 2:90–93
Jadoun S, Verma A, Ashraf SM, Riaz U (2017) A short review on the synthesis, characterization, and application studies of poly(1-naphthylamine): a seldom explored polyaniline derivative. Colloid Polym Sci 295:1443–1453
Riaz U, Ashraf SM, Aleem S et al (2016) Microwave-assisted green synthesis of some nanoconjugated copolymers: characterisation and fluorescence quenching studies with bovine serum albumin. New J Chem 40:4643–4653
Liu Y (2013) Poly(1-naphthylamine)-nickel modified glassy carbon electrode for electrocatalytic oxidation of formaldehyde in alkaline medium. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:4776–4784
Huang SS, Lin HG, Yu RQ (1992) Electrocatalysis of a chemically modified poly(1-naphthylamine) film electrode. Anal Chim Acta 262:331–337
Syafiuddin A, Salmiati Salim MR et al (2017) A review of silver nanoparticles: research trends, global consumption, synthesis, properties, and future challenges. J Chin Chem Soc 64:732–756
Kumar THV, Sundramoorthy AK (2018) Non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of urea on silver nanoparticles anchored nitrogen-doped single-walled carbon nanotube modified electrode. J Electrochem Soc 165:B3006–B3016
Anderson K, Poulter B, Dudgeon J et al (2017) A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose biosensor based on the regulatory effect of glucose on electrochemical behaviors of colloidal silver nanoparticles on MoS2. Sensors 17:1807
Lorestani F, Shahnavaz Z, Nia PM et al (2015) One-step preparation of silver-polyaniline nanotube composite for non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide detection. Appl Surf Sci 347:816–823
Huang SS, Li J, Lin HG, Yu RQ (1995) Electropolymerization of 1-naphthylamine and the structure of the polymer film. Microchim Acta 117:145–152
Riaz U, Ahmad S, Ashraf SM (2008) Effect of dopant on the nanostructured morphology of poly (1-naphthylamine) synthesized by template free method. Nanoscale Res Lett 3:45–48
Ding J, Zhang K, Wei G, Su Z (2015) Fabrication of polypyrrole nanoplates decorated with silver and gold nanoparticles for sensor applications. RSC Adv 5:69745–69752
Prabhakar PK, Raj S, Anuradha PR et al (2011) Biocompatibility studies on polyaniline and polyaniline-silver nanoparticle coated polyurethane composite. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 86:146–153
Tamboli MS, Kulkarni MV, Patil RH et al (2012) Nanowires of silver-polyaniline nanocomposite synthesized via in situ polymerization and its novel functionality as an antibacterial agent. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 92:35–41
Riaz U, Ahmad S, Ashraf SM (2008) Pseudo template synthesis of poly (1-naphthylamine): effect of environment on nanostructured morphology. J Nanoparticle Res 10:1209–1214
Ciric-Marjanovic G, Marjanović B, Stamenković V et al (2002) Structure and stereochemistry of electrochemically synthesized poly-(1-naphthylamine) from neutral acetonitrile solution. J Serbian Chem Soc 67:867–877
Na Z, Wang X, Yin D, Wang L (2017) Tin dioxide as a high-performance catalyst towards Ce(vi)/Ce(iii) redox reactions for redox flow battery applications. J Mater Chem A 5:5036–5043
Sherino B, Mohamad S, Abdul Halim SN, Abdul Manan NS (2018) Electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide on a new microporous Ni-metal organic framework material-carbon paste electrode. Sens Actuators, B Chem 254:1148–1156
Abbasi A (2018) Hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on carbon paste modified electrode with hemoglobin and copper(II) oxide nanoparticles. Int J Electrochem Sci 13:3986–3996
Habibi B, Azhar FF, Fakkar J, Rezvani Z (2017) Ni–Al/layered double hydroxide/Ag nanoparticle composite modified carbon-paste electrode as a renewable electrode and novel electrochemical sensor for hydrogen peroxide. Anal Methods 9:1956–1964
Mahanthappa M, Kottam N, Yellappa S (2018) Electrocatalytic performance of a zinc sulphide nanoparticles-modified carbon paste electrode for the simultaneous determination of acetaminophen, guanine and adenine. Anal Methods 10:1362–1371
Nia PM, Meng WP, Alias Y (2015) Hydrogen peroxide sensor: uniformly decorated silver nanoparticles on polypyrrole for wide detection range. Appl Surf Sci 357:1565–1572
Shamkhalichenar H, Choi J (2017) An inkjet-printed non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor on paper. J Electrochem Soc 164:B3101–B3106
Wang P, Xiao J, Guo M et al (2014) Voltammetric determination of 4-nitrophenol at graphite nanoflakes modified glassy carbon electrode. J Electrochem Soc 162:H72–H78
Kazici HC, Salman F, Caglar A et al (2018) Synthesis, characterization, and voltammetric hydrogen peroxide sensing on novel monometallic (Ag, Co/MWCNT) and bimetallic (AgCo/MWCNT) alloy nanoparticles. Fullerenes Nanotub Carbon Nanostruct 26:145–151
Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhong Y, Li S (2015) Enzyme-free hydrogen peroxide sensor based on Au@Ag@C core-double shell nanocomposites. Appl Surf Sci 347:428–434
Habibi B, Azhar FF, Fakkar J, Rezvani Z, Aguirre MJ, Ruiz-león D et al (2017) Ni-Al/layered double hydroxide/Ag nanoparticles composite modified carbon-2 paste electrode as a renewable electrode and novel electrochemical sensor for 3 hydrogen peroxide. Anal Methods 42:3986–3996
Karthik R, Vinoth Kumar J, Chen SM et al (2018) Simple sonochemical synthesis of novel grass-like vanadium disulfide: a viable non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor for the detection of hydrogen peroxide. Ultrason Sonochem 48:473–481
Achari DS, Santhosh C, Deivasegamani R et al (2017) A non-enzymatic sensor for hydrogen peroxide based on the use of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles deposited on the surface of NiO nanosheets. Microchim Acta 184:3223–3229
Ma P, Zhu H, Wei J, Zhang M (2015) Facile fabrication of Au nanoparticles immobilized on polyaniline nanofibers: high sensitive nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 7:1–7
Yang Z, Zheng X, Zheng J (2016) Non-enzymatic sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with Ag nanoparticles/polyaniline/halloysite nanotube nanocomposites for hydrogen peroxide sensing. RSC Adv 6:58329–58335
Chang G, Luo Y, Lu W et al (2012) Ag nanoparticles decorated polyaniline nanofibers: synthesis, characterization, and applications toward catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and electrochemical detection of H2O2 and glucose. Catal Sci Technol 2:800–806
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledged the financial assistance to Femina K.S. granted by University Grants Commission (under Faculty Development Program: Grant No. FIP/12th Plan/KLMG 009 TF 12 dated 20/04/2017), Government of India. The authors thank SAIF STIC, CUSAT, and Kerala, India, for characterization facilities. We acknowledge the SARD scheme of Kerala State Council for Science, Technology, and Environment for the grant received (Grant No. 002/SARD/2015/KSCSTE) by Dr.Alex Joseph, Newman College, Thodupuzha, Kerala, India. The authors thank Dr. Neena George, Assistant professor, Maharajas College, Kochi, India, for her valuable support during the manuscript writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to publish the paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saidu, F.K., Joseph, A., Varghese, E.V. et al. Silver nanoparticles-embedded poly(1-naphthylamine) nanospheres for low-cost non-enzymatic electrochemical H2O2 sensor. Polym. Bull. 77, 5825–5846 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03053-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03053-x