Abstract
The prognosis of relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is poor. The efficacy of salvage therapy with ICE (ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide) is limited. DLBCL can evade immune surveillance by upregulating programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1). The purpose of this study was to explore the efficacy and safety of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) blockade combined with ICE regimen (P-ICE) in the treatment of R/R DLBCL patients. In this study, we retrospectively explored efficacy and toxicity in R/R DLBCL patients treated with P-ICE. Prognostic biomarkers, including clinical features and molecular markers related to efficacy, were explored. From February 2019 to May 2020, a total of 67 patients treated with the P-ICE regimen were analyzed. The median follow-up time was 24.7 months (range: 1.4–39.6 months), with an objective response rate (ORR) of 62.7% and a complete response rate (CRR) of 43.3%. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates were 41.1% (95% CI: 35.0–47.2%) and 65.6% (95% CI: 59.5–71.7%), respectively. Age, Ann Arbor stage, international prognostic index (IPI) score, and response to first-line chemotherapy were correlated with the ORR. Grade 3 and 4 adverse events (AEs) related to the P-ICE regimen were reported in 21.5% of patients. The most common AE was thrombocytopenia (9.0%). No treatment-related deaths occurred. In patients with R/R DLBCL, the P-ICE regimen has promising efficacy and mild toxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
These data are available by individual application to corresponding author.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2022) Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 72(1):7–33
Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, Lefort S, Marit G, Macro M, Sebban C, Belhadj K, Bordessoule D, Fermé C, Tilly H (2010) Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood 116(12):2040–5
Westin JR, Kersten MJ, Salles G, Abramson JS, Schuster SJ, Locke FL, Andreadis C (2021) Efficacy and safety of CD19-directed CAR-T cell therapies in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas: observations from the JULIET, ZUMA-1, and TRANSCEND trials. Am J Hematol 96(10):1295–1312
Gisselbrecht C, Glass B, Mounier N, Singh Gill D, Linch DC, Trneny M, Bosly A, Ketterer N, Shpilberg O, Hagberg H, Ma D, Brière J, Moskowitz CH, Schmitz N (2010) Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin Oncol 28(27):4184–4190
Matasar MJ, Czuczman MS, Rodriguez MA, Fennessy M, Shea TC, Spitzer G, Lossos IS, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Joyce R, Fayad L, Henkel K, Liao Q, Edvardsen K, Jewell RC, Fecteau D, Singh RP, Lisby S, Moskowitz CH (2013) Ofatumumab in combination with ICE or DHAP chemotherapy in relapsed or refractory intermediate grade B-cell lymphoma. Blood 122(4):499–506
Pascual M, Mena-Varas M, Robles EF, Garcia-Barchino MJ, Panizo C, Hervas-Stubbs S, Alignani D, Sagardoy A, Martinez-Ferrandis JI, Bunting KL, Meier S, Sagaert X, Bagnara D, Guruceaga E, Blanco O, Celay J, Martínez-Baztan A, Casares N, Lasarte JJ, MacCarthy T, Melnick A, Martinez-Climent JA, Roa S (2019) PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint and p53 loss facilitate tumor progression in activated B-cell diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 133(22):2401–2412
Kiyasu J, Miyoshi H, Hirata A, Arakawa F, Ichikawa A, Niino D, Sugita Y, Yufu Y, Choi I, Abe Y, Uike N, Nagafuji K, Okamura T, Akashi K, Takayanagi R, Shiratsuchi M, Ohshima K (2015) Expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 is associated with poor overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 126(19):2193–2201
Smith SD, Till BG, Shadman MS, Lynch RC, Cowan AJ, Wu QV, Voutsinas J, Rasmussen HA, Blue K, Ujjani CS, Shustov A, Cassaday RD, Fromm JR, Gopal AK (2020) Pembrolizumab with R-CHOP in previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: potential for biomarker driven therapy. Br J Haematol 189(6):1119–1126
Lesokhin AM, Ansell SM, Armand P, Scott EC, Halwani A, Gutierrez M, Millenson MM, Cohen AD, Schuster SJ, Lebovic D, Dhodapkar M, Avigan D, Chapuy B, Ligon AH, Freeman GJ, Rodig SJ, Cattry D, Zhu L, Grosso JF, Bradley Garelik MB, Shipp MA, Borrello I, Timmerman J (2016) Nivolumab in patients with relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancy: preliminary results of a phase Ib study. J Clin Oncol 34(23):2698–2704
Ansell SM, Minnema MC, Johnson P, Timmerman JM, Armand P, Shipp MA, Rodig SJ, Ligon AH, Roemer MGM, Reddy N, Cohen JB, Assouline S, Poon M, Sharma M, Kato K, Samakoglu S, Sumbul A, Rigg A (2019) Nivolumab for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients ineligible for or having failed autologous transplantation: a single-arm, phase II study. J Clin Oncol 37(6):481–489
Fucikova J, Kepp O, Kasikova L, Petroni G, Yamazaki T, Liu P, Zhao L, Spisek R, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2020) Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis 11(11):1013
Moskowitz CH, Bertino JR, Glassman JR, Hedrick EE, Hunte S, Coady-Lyons N, Agus DB, Goy A, Jurcic J, Noy A, O’Brien J, Portlock C, Straus DS, Childs B, Frank R, Yahalom J, Filippa D, Louie D, Nimer SD, Zelenetz AD (1999) Ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide: a highly effective cytoreduction and peripheral-blood progenitor-cell mobilization regimen for transplant-eligible patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 17(12):3776–3785
Wang X, Gao Y, Shan C, Lai M, He H, Bai B, Ping L, Rong Q, Ai R, Wen L, Zhou Z, Yu R, Ou Q, Wu X, Wang X, Shao YW, Cai L, Huang H (2021) Association of circulating tumor DNA from the cerebrospinal fluid with high-risk CNS involvement in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Transl Med 11(1):e236
Luo H, Lu J, Bai Y, Mao T, Wang J, Fan Q, Zhang Y, Zhao K, Chen Z, Gao S, Li J, Fu Z, Gu K, Liu Z, Wu L, Zhang X, Feng J, Niu Z, Ba Y, Zhang H, Liu Y, Zhang L, Min X, Huang J, Cheng Y, Wang D, Shen Y, Yang Q, Zou J, Xu RH (2021) Effect of camrelizumab vs placebo added to chemotherapy on survival and progression-free survival in patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the ESCORT-1st Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 326(10):916–925
Crump M, Kuruvilla J, Couban S, MacDonald DA, Kukreti V, Kouroukis CT, Rubinger M, Buckstein R, Imrie KR, Federico M, Di Renzo N, Howson-Jan K, Baetz T, Kaizer L, Voralia M, Olney HJ, Turner AR, Sussman J, Hay AE, Djurfeldt MS, Meyer RM, Chen BE, Shepherd LE (2014) Randomized comparison of gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin versus dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin chemotherapy before autologous stem-cell transplantation for relapsed and refractory aggressive lymphomas: NCIC-CTG LY.12. J Clin Oncol 32(31):3490–6
Moccia AA, Hitz F, Hoskins P, Klasa R, Power MM, Savage KJ, Shenkier T, Shepherd JD, Slack GW, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM, Sehn LH (2017) Gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP) is an effective and well-tolerated salvage therapy for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 58(2):324–332
Hong JY, Yoon DH, Suh C, Kim WS, Kim SJ, Jo JC, Kim JS, Lee WS, Oh SY, Park Y, Kim SY, Lee MH, Lee HS, Do YR (2018) Bendamustine plus rituximab for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Ann Hematol 97(8):1437–1443
Manconi L, Coviello E, Canale F, Giannoni L, Minetto P, Guolo F, Clavio M, Marcolin R, Cea M, Cagnetta A, Gobbi M, Miglino M, Ballerini F, Lemoli RM (2020) Dexamethasone, oxaliplatin and cytarabine (R-DHAOx) as salvage and stem cells mobilizing therapy in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma 61(1):84–90
Matsumoto T, Hara T, Shibata Y, Nakamura N, Nakamura H, Ninomiya S, Kitagawa J, Kanemura N, Goto N, Kito Y, Kasahara S, Yamada T, Sawada M, Miyazaki T, Takami T, Takeuchi T, Moriwaki H, Tsurumi H (2017) A salvage chemotherapy of R-P-IMVP16/CBDCA consisting of rituximab, methylprednisolone, ifosfamide, methotrexate, etoposide, and carboplatin for patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma who had previously received R-CHOP therapy as first-line chemotherapy. Hematol Oncol 35(3):288–295
Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Deeb G, Zinzani PL, Pileri SA, Malik F, Macon WR, Goy A, Witzig TE, Czuczman MS (2011) Higher response to lenalidomide in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in nongerminal center B-cell-like than in germinal center B-cell-like phenotype. Cancer 117(22):5058–5066
Bratman SV, Yang SYC, Iafolla MAJ, Liu Z, Hansen AR, Bedard PL, Lheureux S, Spreafico A, Razak AA, Shchegrova S, Louie M, Billings P, Zimmermann B, Sethi H, Aleshin A, Torti D, Marsh K, Eagles J, Cirlan I, Hanna Y, Clouthier DL, Lien SC, Ohashi PS, Xu W, Siu LL, Pugh TJ (2020) Personalized circulating tumor DNA analysis as a predictive biomarker in solid tumor patients treated with pembrolizumab. Nat Cancer 1(9):873–881
Kim ST, Cristescu R, Bass AJ, Kim KM, Odegaard JI, Kim K, Liu XQ, Sher X, Jung H, Lee M, Lee S, Park SH, Park JO, Park YS, Lim HY, Lee H, Choi M, Talasaz A, Kang PS, Cheng J, Loboda A, Lee J, Kang WK (2018) Comprehensive molecular characterization of clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition in metastatic gastric cancer. Nat Med 24(9):1449–1458
Funding
This study was supported by the National Science & Technology Major Project (2017ZX09304021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in this research, including conception and design (PLQ, WXX, HHQ), data acquisition (PLQ, GY, HYX, BB, HC, SLN, WXX, HHQ), data analysis and interpretation (PLQ, HYX, SLN, HHQ), material support (PLQ, WXX, HHQ), study supervision (PLQ, WXX, HHQ), and drafting the article or critically revising (PLQ, WXX, HHQ). The final version was ensured and approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Our study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center Health Authority (identifier: B2021-093).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Liqin Ping, Yan Gao, and Yanxia He contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

277_2023_5292_Fig8_ESM.png
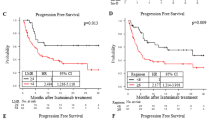
Supplementary file1 Supplementary Figure 1. The status of plasma ctDNA after the P-ICE regimen did not affect the prognosis of patients. Undetectable ctDNA was not related to PFS (A) or OS (B) (PNG 67 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ping, L., Gao, Y., He, Y. et al. PD-1 blockade combined with ICE regimen in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 102, 2189–2198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05292-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05292-5