Abstract
Background
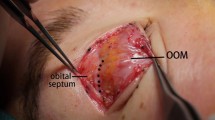
With an increasing number of East Asians undergoing blepharoplasty, the number of patients with secondary upper eyelid deformities is increasing. The sunken eyelid deformity is a common deformity after upper blepharoplasty in Asians due to over-resection, retraction, or atrophy of the nasal and central orbital fat pads. Herein, we present a novel procedure, the pendulum movement of orbital fat and retro-orbicularis oculi fat (“POR” technique), for correction of sunken eyelid deformity in secondary Asian blepharoplasty.
Methods
Patients who underwent secondary upper blepharoplasty with the POR technique by the senior author between January 2020 and October 2021 were identified retrospectively. Those with fewer than 6 months of follow-up were excluded. Patient charts and images were reviewed for demographic data, comorbidities, concomitant eyelid deformities, and postoperative complications. Pre- and postoperative aesthetics, including degree of sunken eyelid deformity, were assessed by two independent raters and by self-reported patient satisfaction.
Results
Forty-nine consecutive patients were identified, all of whom were female and had grade I or II sunken eyelid deformity. Median follow-up was 8 months. Concomitant deformities included high tarsal crease (N = 31 patients, 63.3%), ptosis (N = 13, 26.5%), and upper eyelid retraction (N = 5, 10.2%). Almost patients had improvement in their eyelid volume, and 95.9% had improvement in their aesthetic rating. Approximately 93.9% of patients were satisfied with the outcome.
Conclusions
The POR technique is an effective technique for correction of sunken eyelid deformity and can be utilized in conjunction with other techniques during secondary blepharoplasty.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suo LL, Li JQ, Fu R et al (2020) A four-step technique for creating individual double-eyelid crease shapes: a free-style design. Plast Reconstr Surg 146:756–765
Rohrich RJ, Coberly DM, Fagien S et al (2004) Current concepts in aesthetic upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 113(3):32e–42e
Cho IC (2015) Revision upper blepharoplasty. Semin Plast Surg 29:201–208
Zhu Z, Yuan ZQ, Lu L et al (2021) Unsatisfactory upper blepharoplasty revision technique: reconstruction of the upper orbital septum and its fusion point. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(6):2790–2797
Mangan MS, Cakir A, Ercalik NY et al (2021) Efficacy of the Müller muscle-conjunctival resection for the correction of unilateral ptosis following external levator operations in patients with bilateral involutional ptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 148:195e–199e
Tonnard PL, Verpaele AM, Zeltzer AA (2013) Augmentation blepharoplasty: a review of 500 consecutive patients. Aesthet Surg J 33(3):341–352
Kim BG, Youn DY (2006) Management of adhesion using a pretarsal fibromuscular flap or graft in secondary blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:782–789
Lee W, Kwon SB, Oh SK et al (2017) Correction of sunken upper eyelid with orbital fat transposition flap and dermofat graft. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 70:1768–1775
Bremond-Gignac D, Copin H, Cussenot O et al (2004) Anatomical histological and mesoscopic study of the adipose tissue of the orbit. Surg Radiol Anat 26:297–302
Wang X, Wang H (2020) Anatomical study and clinical observation of retro-orbicularis oculi fat (ROOF). Aesthetic Plast Surg 44:89–92
Blandford AD, Bachour SP, Chen R et al (2019) Dimensions and Morphologic Variability of the Retro-Orbicularis Oculi and Frontalis Muscle Fat Pad. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 35(5):447–450
Jin R, Shen YR, Yu WJ et al (2020) Tarsal-fixation with aponeurotic flap linkage in blepharoplasty: bridge technique. Aesthet Surg J 40:NP648–NP654
Shen YR, Yu WJ, Ding FX et al (2022) Aesthetic correction of mild-to-moderate blepharoptosis among Asians: the bridge technique. Ophthalmol Ther 11:151–160
Park S, Kim B (2011) Correction of superior sulcus deformity with orbital fat anatomic repositioning and fat graft applied to retro-orbicularis oculi fat for Asian eyelids. Aesthet Plast Surg 35:162–170
Lee W, Kwon SB, Oh SK et al (2017) Correction of sunken upper eyelid with orbital fat transposition flap and dermofat graft. J Plast Reconstr Aes 70(12):1768–1775
Hwang K (2013) Surgical anatomy of the upper eyelid relating to upper blepharoplasty or blepharoptosis surgery. Anat Cell Biol. 46:93–100
Guo S, Yang M, Zhou C et al (2019) Corrective strategies for a complex deformity caused by “European-Style Double Eyelid” blepharoplasty in Asians. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43(2):395–403
Kim KK, Kim WS, Oh SK et al (2017) High double eyelid fold correction using wide dual-plane dissection. Ann Plast Surg 78:365–370
Jiang L, Li H, Yin N et al (2020) Free orbital fat grafting during upper blepharoplasty in Asians to prevent multiple upper eyelid folds and sunken upper eyelids. J Craniofac Surg 31:685–688
Saonanon P, Sithanon S (2018) External levator advancement versus muller muscle-conjunctival resection for aponeurotic blepharoptosis: a randomized clinical trial. Plast Reconstr Surg 141:213e–219e
Cohen LM, Rootman DB (2021) Blepharoptosis repair: external versus posterior approach surgery: why I select one over the other. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 29:195–208
Acknowledgements
The all authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 82102319).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
We received informed consent from the patients for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
266_2023_3827_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Table 1: Correction results of upper eyelid depression. Supplementary Table 2: The Photographic analysis of the results regarding meeting patient expectations. Supplementary Table 3: Postoperative Complications. (PPTX 46 KB)
Video 1: This video partially shows the surgical procedure of separating and resetting orbital fat and ROOF. (MP4 97344 KB)
Video 2: This video reveals the procedure of fixing orbital fat and ROOF at the position as they overlap. (MP4 55860 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Li, R., Qiu, C.S. et al. The Pendulum Movement of Orbital Fat and Retro-Orbicularis Oculi Fat: A New Strategy for Correction of Sunken Eyelid Deformity in Revision Upper Blepharoplasty for Asian Patients. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 1104–1110 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03827-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03827-9