Abstract
Background
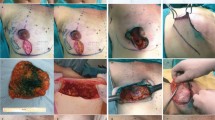
Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) and implant-based immediate breast reconstruction are becoming preferred options with improved outcomes. However, reconstruction in patients with large and ptotic breasts is challenging. When mastectomy and skin reduction are combined in a single-staged procedure, the vasculature of the skin is disturbed leading to increased complication rates. This paper aims to compare complication rates of NSM and immediate implant-based reconstruction with or without reduction to determine the safety of reduction in this patient group.
Methods
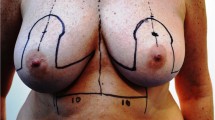
Breast cancer patients that underwent NSM and implant-based immediate breast reconstruction between November 2010 and 2018 were analyzed. All implants were placed submuscularly. Patients with skin reduction and nipple–areolar complex transposition were matched in a 1:1 fashion with patients without reduction.
Results
There were 50 patients (72 procedures) in each group. Demographics of the groups were similar as a part of matching process. Mean implant volume in the reduction group was higher (399.93 ± 97.54 vs. 360.21 ± 82.54, p = 0.009). Full thickness skin necrosis rate was higher in the reduction group [12/72 (%17) vs. 2/72 (3%), p = 0.009], and the most common site was over the suture line [6/12 (50%)]. Complications in the reduction group were more common in reconstructions with implant volumes greater than 500 cc (p = 0.008).
Conclusions
When compared with no reduction, the skin necrosis rate of NSM and immediate implant-based reconstruction with skin reduction is higher. The described technique can only be considered in patients with moderate breast volumes, grade II–III ptosis, and when the planned implant volume is low (< 500 cc).
Level of Evidence
IV. This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CM, Disa JJ, Sacchini V et al (2009) Nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:1772–1780. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181bd05fd
Spear SL, Willey SC, Feldman ED et al (2011) Nipple-sparing mastectomy for prophylactic and therapeutic indications. Plast Reconstr Surg 128:1005–1014. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31822b6456
Endara M, Chen D, Verma K et al (2013) Breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy: a systematic review of the literature with pooled analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:1043–1054. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182a48b8a
De La Cruz L, Moody AM, Tappy EE et al (2015) Overall survival, disease-free survival, local recurrence, and nipple-areolar recurrence in the setting of nipple-sparing mastectomy: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Ann Surg Oncol 22:3241–3249. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4739-1
Choi M, Frey JD, Alperovich M et al (2016) “Breast in a day”: examining single-stage immediate, permanent implant reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 138:184e–e191. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002333
De Vita R, Zoccali G, Buccheri EM et al (2017) Outcome evaluation after 2023 nipple-sparing mastectomies: our experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 139:335e–347e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000003027
Galimberti V, Vicini E, Corso G et al (2017) Nipple-sparing and skin-sparing mastectomy: review of aims, oncological safety and contraindications. Breast 34(Suppl 1):S82–S84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2017.06.034
Albornoz CR, Bach PB, Mehrara BJ et al (2013) A paradigm shift in U.S. Breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plast Reconstr Surg 131:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182729cde
Panchal H, Matros E (2017) Current trends in postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 140:7S–13S. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000003941
Rodriguez-Feliz J, Codner MA (2015) Embrace the change: incorporating single-stage implant breast reconstruction into your practice. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:221–231. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001448
Dietz J, Lundgren P, Veeramani A et al (2012) Autologous inferior dermal sling (autoderm) with concomitant skin-envelope reduction mastectomy: an excellent surgical choice for women with macromastia and clinically significant ptosis. Ann Surg Oncol 19:3282–3288. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2549-2
della Rovere GQ, Nava M, Bonomi R et al (2008) Skin-reducing mastectomy with breast reconstruction and sub-pectoral implants. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:1303–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2007.06.032
DellaCroce FJ, Blum CA, Sullivan SK et al (2015) Nipple-sparing mastectomy and ptosis: perforator flap breast reconstruction allows full secondary mastopexy with complete nipple areolar repositioning. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:1e–9e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001325
Carlson GW, Bostwick J 3rd, Styblo TM et al (1997) Skin-sparing mastectomy. Oncol Reconstr Cons Ann Surg 225:570–578. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-199705000-00013
Nava MB, Cortinovis U, Ottolenghi J et al (2006) Skin-reducing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:603. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000233024.08392.14
Losken A, Collins BA, Carlson GW (2010) Dual-plane prosthetic reconstruction using the modified wise pattern mastectomy and fasciocutaneous flap in women with macromastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:731–738. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181e3b38a
Gentileschi S, Bracaglia R, Garganese G et al (2013) Immediate definitive prosthetic reconstruction in patients with ptotic breasts. Ann Plast Surg 70:144–148. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182367bfd
Chang L-Y, Hargreaves W, Segara D, Moisidis E (2013) Experience in dermomyofascial pouch coverage of immediate implants following skin sparing reduction mastectomy. ANZ J Surg 83:135–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-2197.2012.06313.x
Di Candia M, Lie KH, Forouhi P, Malata CM (2011) Experience with the Wise mammaplasty skin resection pattern in skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for large breast volumes. Int J Surg 9:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.08.004
Bonomi S, Sala L, Gennaro M et al (2019) Skin-Reducing Mastectomy and Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction With Submuscular-Dermal-Mesh Pocket. Ann Plast Surg 82:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000001614
Salgarello M, Visconti G, Barone-Adesi L et al (2012) Inverted-T skin-reducing mastectomy with immediate implant reconstruction using the submuscular-subfascial pocket. Plast Reconstr Surg 130:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182547d42
Korwar V, Skillman J, Matey P (2014) Skin reducing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction: the effect of radiotherapy on complications and patient reported outcomes. Eur J Surg Oncol 40:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2014.01.003
Nair A, Jaleel S, Abbott N et al (2010) Skin-reducing mastectomy with immediate implant reconstruction as an indispensable tool in the provision of oncoplastic breast services. Ann Surg Oncol 17:2480–2485. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1058-4
Ross GL (2012) One stage breast reconstruction following prophylactic mastectomy for ptotic breasts: the inferior dermal flap and implant. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 65:1204–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2012.03.040
Rammos CK, Mammolito D, King VA, Yoo A (2018) Two-stage reconstruction of the large and ptotic breasts: skin reduction mastectomy with prepectoral device placement. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob open 6:e1853. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000001853
De Vita R, Pozzi M, Zoccali G et al (2015) Skin-reducing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction in patients with macromastia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 34:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0227-5
Bayram Y, Kulahci Y, Irgil C et al (2010) Skin-reducing subcutaneous mastectomy using a dermal barrier flap and immediate breast reconstruction with an implant: a new surgical design for reconstruction of early-stage breast cancer. Aesthet Plast Surg 34:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-009-9452-7
Irwin GW, Black A, Refsum SE, McIntosh SA (2013) Skin-reducing mastectomy and one-stage implant reconstruction with a myodermal flap: a safe and effective technique in risk-reducing and therapeutic mastectomy. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66:1188–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2013.04.048
Spear SL, Rottman SJ, Seiboth LA, Hannan CM (2012) Breast reconstruction using a staged nipple-sparing mastectomy following mastopexy or reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:572–581. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318241285c
Rochlin DH, Nguyen DH (2018) Deepithelialized skin reduction preserves skin and nipple perfusion in immediate reconstruction of large and ptotic breasts. Ann Plast Surg 81:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000001427
Al-Mufarrej FM, Woods JE, Jacobson SR (2013) Simultaneous mastopexy in patients undergoing prophylactic nipple-sparing mastectomies and immediate reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66:747–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2013.02.007
Rivolin A, Kubatzki F, Marocco F et al (2012) Nipple-areola complex sparing mastectomy with periareolar pexy for breast cancer patients with moderately ptotic breasts. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 65:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2011.09.023
Folli S, Mingozzi M, Curcio A et al (2015) Nipple-sparing mastectomy: an alternative technique for large ptotic breasts. J Am Coll Surg 220:e65–e69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.028
Letterman G, Schurter M (1975) Inframammary-based dermofat flaps in mammary reconstruction following a subcutaneous mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 55:156–159
Woods JE (1987) Detailed technique of subcutaneous mastectomy with and without mastopexy. Ann Plast Surg 18:51–61
Mosharrafa AM, Mosharrafa TM, Zannis VJ (2020) Direct-to-implant breast reconstruction with simultaneous nipple-sparing mastopexy utilizing an inferiorly based adipodermal flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 145:1125–1133. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006781
Khalil HH, Malahias MN, Youssif S et al (2019) Nipple-sparing mastectomy and prepectoral implant/acellular dermal matrix wrap reconstruction in large ptotic breasts. Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open 7:e2289. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002289
Salibian AA, Frey JD, Karp NS, Choi M (2019) Does Staged breast reduction before nipple-sparing mastectomy decrease complications? a matched cohort study between staged and nonstaged techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 144:1023–1032. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006121
Pontell ME, Saad N, Brown A et al (2018) Single stage nipple-sparing mastectomy and reduction mastopexy in the ptotic breast. Plast Surg Int 2018:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9205805
Yazar S, Karadag EC, Altinkaya A et al (2018) Risk factor analysis for survival of becker-type expander in immediate breast reconstruction. Aesthet Plast Surg 42:971–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1111-4
Yazar S, Altinkaya A, Bengur FB et al (2019) Factors associated with complications in immediate breast reconstruction in 1 stage with completely submuscular implants. Ann Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000001808
Nanigian BR, Wong GB, Khatri VP (2007) Inframammary crease: positional relationship to the pectoralis major muscle origin. Aesthet Surg J 27:509–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2007.06.002
Cordeiro PG, Jazayeri L (2016) Two-stage implant-based breast reconstruction: an evolution of the conceptual and technical approach over a two-decade period. Plast Reconstr Surg 138:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002243
Yazar S, Altinkaya A, Karadag EC et al (2018) A Simple Flap Design for the Salvage of Immediate Implant-Based Breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 80:109–112. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000001196
Spear SL, Hannan CM, Willey SC, Cocilovo C (2009) Nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 123:1665–1673. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181a64d94
Algaithy ZK, Petit JY, Lohsiriwat V et al (2012) Nipple sparing mastectomy: can we predict the factors predisposing to necrosis? Eur J Surg Oncol 38:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2011.10.007
Ahn SJ, Woo TY, Lee DW et al (2018) Nipple-areolar complex ischemia and necrosis in nipple-sparing mastectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol 44:1170–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2018.05.006
de Alcantara FP, Capko D, Barry JM et al (2011) Nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer and risk-reducing surgery: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center experience. Ann Surg Oncol 18:3117–3122. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1974-y
Headon HL, Kasem A, Mokbel K (2016) The oncological safety of nipple-sparing mastectomy: a systematic review of the literature with a pooled analysis of 12,358 procedures. Arch Plast Surg 43:328–338. https://doi.org/10.5999/aps.2016.43.4.328
Maruccia M, Elia R, Gurrado A et al (2020) Skin-reducing mastectomy and pre-pectoral breast reconstruction in large ptotic breasts. Aesthet Plast Surg 44:664–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01616-2
Wagner RD, Braun TL, Zhu H, Winocour S (2019) A systematic review of complications in prepectoral breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 72:1051–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2019.04.005
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was given by the IRB with the reference number, ATADEK-2019–13/2.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 323858 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazar, S., Bengur, F., Altinkaya, A. et al. Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Implant-Based Reconstruction with or Without Skin Reduction in Patients with Large Ptotic Breasts: A Case-Matched Analysis. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 956–967 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-02000-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-02000-w