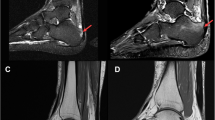
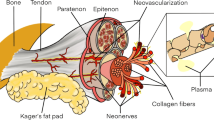
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to determine the presence of peripheral spondyloarthritis and investigate the clinical characteristics of patients with concurrent peripheral spondyloarthritis in those presenting with refractory plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendinopathy by conducting human leukocyte antigen B-27 (HLA-B27) testing.
Methods
This retrospective study aimed to investigate patients who complained of persistent pain and significant limitations in daily activities due to their respective foot pain, despite receiving conservative treatment for over one year under the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis or insertional Achilles tendinopathy. The study included 63 patients who underwent HLA-B27 testing. The patients were classified into two groups based on the presence or absence of HLA-B27 positivity. The Mann–Whitney U test assessed significant relationships between continuous variables, and the chi-square test was used to compare categorical variables.
Results
Among the 63 included patients, HLA-B27 positivity was confirmed in 11 patients (17.5%), which was significantly associated with a lower average age (22.8 years versus 31.7 years, P = 0.01) and a substantially lower proportion of females compared to HLA-B27-negative patients (9.1% vs. 25.0%, P = 0.001). Ten of the 11 patients initiated treatment with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) combined with oral steroids as the first-line medication after being diagnosed as HLA-B27 positive. Six patients experienced pain relief with the first-line medication (60%). Four patients who did not achieve pain control with the first-line medication received tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors as the second-line medication. Two patients experienced pain relief, while two experienced reduced but persistent pain.
Conclusions
Among the patients with “refractory” plantar fasciitis and insertional Achilles tendinopathy, 17.5% were diagnosed with peripheral spondyloarthritis. Patients diagnosed with peripheral spondyloarthritis had a higher proportion of men and relatively younger mean age compared to those without the diagnosis. Approximately 70% of these patients achieved symptom improvement in foot and ankle joints by taking conventional synthetic DMARDs, TNF-α inhibitors, or both appropriate for spondyloarthritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author [JSS], upon reasonable request.
References
Dougados M, Baeten D (2011) Spondyloarthritis. Lancet 377:2127–2137
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R et al (2009) The development of assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68:777–783
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R et al (2011) The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general. Ann Rheum Dis 70:25–31
Seo MR, Baek HJ (2013) The concept and overview of spondyloarthritis. Korean J Med 85(3):229–239
Romero-López JP, Elewaut D, Pacheco-Tena C, Burgos-Vargas R (2021) Inflammatory foot involvement in spondyloarthritis: from tarsitis to ankylosing tarsitis. Front Med (Lausanne) 8:730273
Mander M, Simpson JM, McLellan A, Walker D, Goodacre JA, Dick WC (1987) Studies with an enthesis index as a method of clinical assessment in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 46:197–202
Martin RL, Irrgang JJ, Burdett RG, Conti SF, Swearingen JM (2005) Evidence of validity for the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM). Foot Ankle Int 26(11):968–983
Saarinen AJ, Uimonen MM, Suominen EN, Sandelin H, Repo JP (2022) Structural and construct validity of the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) with an emphasis on pain and functionality after foot surgery: a multicenter study. J Foot Ankle Surg 61(4):872–878
Latt LD, Jaffe DE, Tang Y, Taljanovic MS (2020) Evaluation and treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Orthop 5(1):2473011419896763
Moon YS, Kim C, Ahn JH (2019) Use of ultrasonography for foot and ankle sports injuries. J Korean Orthop Assoc 54(5):402–410
Felbo SK, Østergaard M, Sørensen IJ, Terslev L (2022) Ultrasound of the heel improves diagnosis-tender entheses in the heel region rarely corresponds to inflammatory enthesitis in patients with peripheral spondyloarthritis. J Clin Med 11(9):2325
Seven S, Pedersen SJ, Østergaard M et al (2020) Peripheral enthesitis detected by ultrasonography in patients with axial spondyloarthritis-anatomical distribution, morphology, and response to tumor necrosis factor-inhibitor therapy. Front Med (Lausanne) 7:341
Lee DO, Yoo JH, Cho HI, Cho S, Cho HR (2020) Comparing effectiveness of polydeoxyribonucleotide injection and corticosteroid injection in plantar fasciitis treatment: a prospective randomized clinical study. Foot Ankle Surg 26(6):657–661
Kim JK, Chung JY (2015) Effectiveness of polydeoxyribonucleotide injection versus normal saline injection for treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: a prospective randomised clinical trial. Int Orthop 39(7):1329–1334
Riddle DL, Schappert SM (2004) Volume of ambulatory care visits and patterns of care for patients diagnosed with plantar fasciitis: a national study of medical doctors. Foot Ankle Int 25(5):303–310
Thomas JL, Christensen JC, Kravitz SR et al (2010) The diagnosis and treatment of heel pain: a clinical practice guideline-revision 2010. J Foot Ankle Surg 49(3 Suppl):S1-19
Haake M, Buch M, Schoellner C et al (2003) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis: randomised controlled multicentre trial. BMJ 327(7406):75
Sharma R, Chaudhary NK, Karki M et al (2023) Effect of platelet-rich plasma versus steroid injection in plantar fasciitis: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 24(1):172
Stania M, Juras G, Chmielewska D, Polak A, Kucio C, Król P (2019) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for Achilles tendinopathy. Biomed Res Int 2019:3086910
Schett G, Lories RJ, D’Agostino MA et al (2017) Enthesitis: from pathophysiology to treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13(12):731–741
Kehl AS, Corr M, Weisman MH (2016) Review: Enthesitis: new insights into pathogenesis, diagnostic modalities, and treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(2):312–322
Hammer RE, Maika SD, Richardson JA, Tang JP, Taurog JD (1990) Spontaneous inflammatory disease in transgenic rats expressing HLA-B27 and human beta 2m: an animal model of HLA-B27-associated human disorders. Cell 63(5):1099–1112
van der Linden SM, Valkenburg HA, de Jongh BM, Cats A (1984) The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals. A comparison of relatives of spondylitis patients with the general population. Arthritis Rheum 27(3):241–249
Carron P, De Craemer AS, Van den Bosch F (2020) Peripheral spondyloarthritis: a neglected entity-state of the art. RMD Open 6(1):e001136
Queiro-Silva R, García-Valle A, Alonso-Castro S, Alperi-López M (2021) Do NSAIDs take us away from treatment goals in axial spondyloarthritis: a story about dysbiosis or just a matter of bias? Front Med (Lausanne) 8:817884
Ward MM, Deodhar A, Gensler LS et al (2019) 2019 Update of the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network Recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 71(10):1599–1613
Callhoff J, Sieper J, Weiß A, Zink A, Listing J (2015) Efficacy of TNFα blockers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 74(6):1241–1248
Ward MM, Deodhar A, Akl EA et al (2016) American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network 2015 Recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(2):282–298
Navarro-Compán V, Ermann J, Poddubnyy D (2022) A glance into the future of diagnosis and treatment of spondyloarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 14:1759720X221111611
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YH Jung wrote the article with organizing the data, participated in the design of the study, performed the statistical analysis, and wrote the article. JS Suh sorted the involved patients with a review of medial record. JY Choi conceived of the study and participated in its design and coordination and helped to draft the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by Inje University Ilsan Paik hospital institutional ethics review committee and performed according to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki (IRB number IRB number 2023–06-009).
Informed consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients.
Consent to publication
The authors agree to publish this manuscript. This manuscript has not been published in any journals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Level of Evidence: III, Retrospective comparative study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, Y.H., Suh, J.S. & Choi, J.Y. The association between refractory plantar fasciitis and insertional Achilles tendinopathy and peripheral spondyloarthritis: a report of human leukocyte antigen B-27 investigation and treatment outcome. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 48, 711–718 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-06019-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-06019-x