Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) intra-articular injective treatments for ankle osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods
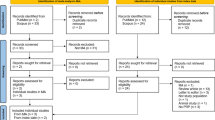
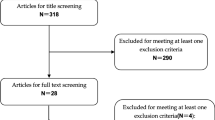
A systematic literature search was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines in PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane library until May 2022. Both randomized and non-randomized studies were included with the assessment of the risk of bias. We recorded the participant’s age, gender, type of PRP, injection volume, the kit used, and activating agent. We subsequently assessed the short-term and long-term efficacy of PRP using the functional scores and visual analog scale (VAS).
Results
We included four studies with a total of 127 patients, with a mean age of 56.1 years. 47.2% were male (60/127), according to eligibility criteria. There were three cohort studies and one randomized controlled trial (RCT) study, and no study reported severe adverse events. All included studies used the Leukocyte-poor PRP. Short-term follow-up results suggested significant improvement of the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) score in the PRP injection group compared to the control group (n = 87 patients; MD: 6.94 [95% CI: 3.59, 10.29]; P < 0.01). Consistently, there was a statistical difference in AOFAS score between PRP injection and control groups in the final follow-up (≥ 6 months) (n = 87 patients; MD: 9.63 [95% CI: 6.31, 12.94]; P < 0.01). Furthermore, we found a significant reduction in VAS scores in the PRP groups at both the short-term follow-up (n = 59 patients; MD, − 1.90 [95% CI, − 2.54, − 1.26]; P < 0.01) and the ≥ six months follow-up (n = 79 patients; MD, − 3.07 [95% CI, − 5.08, − 1.05]; P < 0.01). The improvement of AOFAS and VAS scores at ≥ six months follow-up reached the minimal clinically important difference (MCID). Nevertheless, the treatment effect of AOFAS and VAS scores offered by PRP at short-term follow-up did not exceed the MCID. Substantial heterogeneity was reported at the ≥ six months follow-up in VAS scores (I2: 93%, P < 0.01).
Conclusion
This meta-analysis supports the safety of PRP intra-articular injection for ankle OA. The improvements of AOFAS and VAS scores in the PRP group at short-term follow-up do not exceed the MCID to be clinically significant. PRP injection provides significant improvement of AOFAS score and reduced pain at ≥ six months follow-up. The efficacy of PRP should be interpreted with caution regarding the high heterogeneity and the scarcity of available literature, which urges large-scale RCTs with longer follow-up to confirm the potential efficacy of PRP injection for ankle OA.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are reported within this manuscript, additional information will be available upon request to the corresponding author.
Code availability
All computer codes required to generate these results will be available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Cushnaghan J, Dieppe P (1991) Study of 500 patients with limb joint osteoarthritis. I. Analysis by age, sex, and distribution of symptomatic joint sites. Ann Rheum Dis 50(1):8–13. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.50.1.8
Akoh CC, Fletcher AN, Chen J, Wang J, Adams SA, DeOrio JK et al (2021) Economic analysis and clinical outcomes of short-stay versus inpatient total ankle replacement surgery. Foot Ankle Int 42(1):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100720949200
Boffa A, Previtali D, Di Laura FG, Vannini F, Candrian C, Filardo G (2021) Evidence on ankle injections for osteochondral lesions and osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop 45(2):509–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04689-5
Daniels T, Thomas R (2008) Etiology and biomechanics of ankle arthritis. Foot Ankle Clin 13(3):341–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcl.2008.05.002
Kim J, Kim JB, Lee WC (2021) Clinical and radiographic results of ankle joint preservation surgery in posterior ankle arthritis. Foot Ankle Int 42(10):1260–1269. https://doi.org/10.1177/10711007211011182
Coetzee JC, McGaver RS, Seiffert KJ, Giveans MR (2020) Management of ankle arthritis after severe ankle trauma. J Orthop Trauma 34(Suppl 1):S26-s31. https://doi.org/10.1097/bot.0000000000001697
Chen X, Jones IA, Park C, Vangsness CT Jr (2018) The efficacy of platelet-rich plasma on tendon and ligament healing: a systematic review and meta-analysis with bias assessment. Am J Sports Med 46(8):2020–2032. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546517743746
Liao HT, Marra KG, Rubin JP (2014) Application of platelet-rich plasma and platelet-rich fibrin in fat grafting: basic science and literature review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 20(4):267–276. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2013.0317
Everts P, Onishi K, Jayaram P, Lana JF, Mautner K (2020) Platelet-rich plasma: new performance understandings and therapeutic considerations in 2020. Int J Mol Sci 21(20):7794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207794
Andia I, Maffulli N (2018) A contemporary view of platelet-rich plasma therapies: moving toward refined clinical protocols and precise indications. Regen Med 13(6):717–728. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2018-0042
Szwedowski D, Szczepanek J, Paczesny Ł, Zabrzyński J, Gagat M, Mobasheri A et al (2021) The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the intra-articular microenvironment in knee osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci 22(11):5492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115492
Bennell KL, Paterson KL, Metcalf BR, Duong V, Eyles J, Kasza J et al (2021) Effect of intra-articular platelet-rich plasma vs placebo injection on pain and medial tibial cartilage volume in patients with knee osteoarthritis: the RESTORE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 326(20):2021–2030. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.19415
Keene DJ, Alsousou J, Harrison P, Hulley P, Wagland S, Parsons SR et al (2019) Platelet rich plasma injection for acute Achilles tendon rupture: PATH-2 randomised, placebo controlled, superiority trial. Bmj 367:l6132. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l6132
Guney A, Akar M, Karaman I, Oner M, Guney B (2015) Clinical outcomes of platelet rich plasma (PRP) as an adjunct to microfracture surgery in osteochondral lesions of the talus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(8):2384–2389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2784-5
Giannini S, Buda R, Battaglia M, Cavallo M, Ruffilli A, Ramponi L et al (2013) One-step repair in talar osteochondral lesions: 4-year clinical results and t2-mapping capability in outcome prediction. Am J Sports Med 41(3):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546512467622
Fukawa T, Yamaguchi S, Akatsu Y, Yamamoto Y, Akagi R, Sasho T (2017) Safety and efficacy of intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma in patients with ankle osteoarthritis. Foot Ankle Int 38(6):596–604. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100717700377
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP et al (2019) Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:Ed000142. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.Ed000142
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2535
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25(9):603–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Boffa A, Previtali D, Altamura SA, Zaffagnini S, Candrian C, Filardo G (2020) Platelet-rich plasma augmentation to microfracture provides a limited benefit for the treatment of cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis. Orthop J Sports Med 8(4):2325967120910504. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967120910504
Lin L, Chu H (2018) Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 74(3):785–794. https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.12817
Angthong C, Khadsongkram A, Angthong W (2013) Outcomes and quality of life after platelet-rich plasma therapy in patients with recalcitrant hindfoot and ankle diseases: a preliminary report of 12 patients. J Foot Ankle Surg 52(4):475–480. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2013.04.005
Stiene H (2021) Safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cells and platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of moderately advanced post-traumatic arthritis of the ankle. Biol Orthop J 3(1):e9-e18. https://doi.org/10.22374/boj.v3i1.14
Repetto I, Biti B, Cerruti P, Trentini R, Felli L (2017) Conservative treatment of ankle osteoarthritis: can platelet-rich plasma effectively postpone surgery? J Foot Ankle Surg 56(2):362–365. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2016.11.015
Paget LDA, Reurink G, de Vos RJ, Weir A, Moen MH, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA et al (2021) Effect of platelet-rich plasma injections vs placebo on ankle symptoms and function in patients with ankle osteoarthritis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 326(16):1595–1605. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.16602
Sun SF, Hsu CW, Lin GC, Lin HS, Chou YJ, Wu SY et al (2021) Efficacy and safety of a single intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma on pain and physical function in patients with ankle osteoarthritis-a prospective study. J Foot Ankle Surg 60(4):676–682. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2020.12.003
Matheus HR, Ozdemir SD, SemeghiniGuastaldi FP (2022) Stem cell-based therapies for temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis and regeneration of cartilage/osteochondral defects: a systematic review of preclinical experiments. Osteoarthr Cartil 30(9):1174–1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2022.05.006
Gadelkarim M, Elmegeed AA, Hafez A, Awad AK, Shehata MA, AbouEl-Enein A et al (2022) Safety and efficacy of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Joint Bone Spine 89(5):105404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2022.105404
Evans A, Ibrahim M, Pope R, Mwangi J, Botros M, Johnson SP et al (2020) Treating hand and foot osteoarthritis using a patient’s own blood: a systematic review and meta-analysis of platelet-rich plasma. J Orthop 18:226–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2020.01.037
Al-Moraissi EA, Wolford LM, Ellis E 3rd, Neff A (2020) The hierarchy of different treatments for arthrogenous temporomandibular disorders: a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 48(1):9–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2019.10.004
Ornetti P, Nourissat G, Berenbaum F, Sellam J, Richette P, Chevalier X (2016) Does platelet-rich plasma have a role in the treatment of osteoarthritis? Joint Bone Spine 83(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.05.002
Sánchez M, Anitua E, Azofra J, Aguirre JJ, Andia I (2008) Intra-articular injection of an autologous preparation rich in growth factors for the treatment of knee OA: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 26(5):910–913
Anitua E, Sánchez M, Nurden AT, Zalduendo MM, de la Fuente M, Azofra J et al (2007) Platelet-released growth factors enhance the secretion of hyaluronic acid and induce hepatocyte growth factor production by synovial fibroblasts from arthritic patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46(12):1769–1772. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kem234
Doganay Erdogan B, Leung YY, Pohl C, Tennant A, Conaghan PG (2016) Minimal clinically important difference as applied in rheumatology: an OMERACT Rasch Working Group Systematic Review and Critique. J Rheumatol 43(1):194–202. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.141150
Beitzel K, Allen D, Apostolakos J, Russell RP, McCarthy MB, Gallo GJ et al (2015) US definitions, current use, and FDA stance on use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine. J Knee Surg 28(1):29–34. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1390030
Eymard F, Ornetti P, Maillet J, Noel É, Adam P, Legré-Boyer V et al (2021) Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a consensus statement from French-speaking experts. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 29(10):3195–3210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-06102-5
Zhou Y, Wang JH (2016) PRP treatment efficacy for tendinopathy: a review of basic science studies. Biomed Res Int 2016:9103792. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9103792
Fitzpatrick J, Bulsara M, Zheng MH (2017) The effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of tendinopathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Am J Sports Med 45(1):226–233. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546516643716
Price DD, McGrath PA, Rafii A, Buckingham B (1983) The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain 17(1):45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(83)90126-4
Everts PA, Devilee RJ, Brown Mahoney C, van Erp A, Oosterbos CJ, Stellenboom M et al (2008) Exogenous application of platelet-leukocyte gel during open subacromial decompression contributes to improved patient outcome. A prospective randomized double-blind study. Eur Surg Res 40(2):203–210. https://doi.org/10.1159/000110862
Odem MA, Bavencoffe AG, Cassidy RM, Lopez ER, Tian J, Dessauer CW et al (2018) Isolated nociceptors reveal multiple specializations for generating irregular ongoing activity associated with ongoing pain. Pain 159(11):2347–2362. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001341
Kuffler DP (2015) Platelet-rich plasma promotes axon regeneration, wound healing, and pain reduction: fact or fiction. Mol Neurobiol 52(2):990–1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9251-x
Lin MT, Wei KC, Wu CH (2020) Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injection in rotator cuff tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diagnostics (Basel) 10(4):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040189
Urits I, Smoots D, Franscioni H, Patel A, Fackler N, Wiley S et al (2020) Injection techniques for common chronic pain conditions of the foot: a comprehensive review. Pain Ther 9(1):145–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40122-020-00157-5
Madeley NJ, Wing KJ, Topliss C, Penner MJ, Glazebrook MA, Younger AS (2012) Responsiveness and validity of the SF-36, Ankle Osteoarthritis Scale, AOFAS Ankle Hindfoot Score, and Foot Function Index in end stage ankle arthritis. Foot Ankle Int 33(1):57–63. https://doi.org/10.3113/fai.2012.0057
Smith PA (2016) Intra-articular autologous conditioned plasma injections provide safe and efficacious treatment for knee osteoarthritis: an FDA-sanctioned, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Am J Sports Med 44(4):884–891. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546515624678
Lin KY, Yang CC, Hsu CJ, Yeh ML, Renn JH (2019) Intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma is superior to hyaluronic acid or saline solution in the treatment of mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, triple-parallel, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arthroscopy 35(1):106–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2018.06.035
Juras V, Zbýň Š, Mlynarik V, Szomolanyi P, Hager B, Baer P et al (2016) The compositional difference between ankle and knee cartilage demonstrated by T2 mapping at 7 Tesla MR. Eur J Radiol 85(4):771–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.01.021
Shepherd D, Seedhom B (1999) Thickness of human articular cartilage in joints of the lower limb. Ann Rheum Dis 58(1):27–34
Xiong G, Lingampalli N, Koltsov JCB, Leung LL, Bhutani N, Robinson WH et al (2018) Men and women differ in the biochemical composition of platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med 46(2):409–419. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546517740845
Taniguchi Y, Yoshioka T, Sugaya H, Gosho M, Aoto K, Kanamori A et al (2019) Growth factor levels in leukocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma and correlations with donor age, gender, and platelets in the Japanese population. J Exp Orthop 6(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40634-019-0175-7
Breddin HK (2005) Can platelet aggregometry be standardized? Platelets 16(3–4):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537100400020161
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81773091), the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (Grant No. 7212020), Science and Technology Planning Project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KM202110025013), and the Beijing Municipal Excellent Talents Project (Grant No. 2020A43).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sheng-Long Ding: study design, data acquisition, and drafting the manuscript. Lin-Feng Ji: data acquisition and interpretation, drafting the manuscript. Wei Xiong and Cheng-Yi Sun: data acquisition and editing of the manuscript. Ze-Yu Han and Chao Wang: data interpretation. Ming-Zhu Zhang: study design, reviewing & editing of the manuscript, and project funding. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The ethical approval was not applicable because this research was a systematic review. Furthermore, this systematic review has been registered with International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) database (ID: CRD42022334564).
Consent to participate
This systematic review analyzed published studies and no human participants were involved, so the consent to participate was not applicable.
Consent to publish
This review analyzed published studies and no human participants were involved, so the consent to publish was not applicable. All authors confirm that the work has not been published before and it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Sheng-Long Ding and Lin-Feng Ji contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, SL., Ji, LF., Zhang, MZ. et al. Safety and efficacy of intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of ankle osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 1963–1974 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05773-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05773-2