Abstract
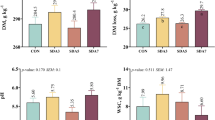
Alfalfa silage fermentation quality, metabolome, bacterial interactions, and successions as well as their predicted metabolic pathways were explored under different dry matter contents (DM) and lactic acid bacteria (LAB) inoculations. Silages were prepared from alfalfa with DM contents of 304 (LDM) and 433 (HDM) g/kg fresh weight and inoculated with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (L. plantarum, LP), Pediococcus pentosaceus (P. pentosaceus, PP), or sterile water (control). The silages were stored at a simulated hot climate condition (35°C) and sampled at 0, 7, 14, 30, and 60 days of fermentation. The results revealed that HDM significantly improved the alfalfa silage quality and altered microbial community composition. The GC-TOF-MS analysis discovered 200 metabolites in both LDM and HDM alfalfa silage, mainly consisting of amino acids, carbohydrates, fatty acids, and alcohols. Compared with LP and control, PP-inoculated silages had increased concentrations of lactic acid (P < 0.05) and essential amino acids (threonine and tryptophan) as well as decreased pH, putrescine content, and amino acid metabolism. However, alfalfa silage inoculated with LP had higher proteolytic activities than control and PP-inoculated silage, as revealed by a higher concentration of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), and also upregulated amino acid and energy metabolism. HDM content and P. pentosaceus inoculation significantly altered the composition of alfalfa silage microbiota from 7 to 60 days of ensiling. Conclusively, these results indicated that inoculation with PP exhibited great potential in enhancing the fermentation of silage with LDM and HDM via altering the microbiome and metabolome of the ensiled alfalfa, which could help in understanding and improving the ensiling practices under hot climate conditions.
Key points
• HDM improved fermentation quality and declined putrescine content of alfalfa silage
• P. pentosaceus inoculation enhanced the fermentation quality of alfalfa silage
• P. pentosaceus is an ideal inoculant for alfalfa silage under high temperature




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Raw sequencing files and associated metadata have been deposited at NCBI's Sequence Read Archive (accession PRJNA870577), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra.
References
Agarussi MCN, Pereira OG, da Silva VP, Leandro ES, Ribeiro KG, Santos SA (2019) Fermentative profile and lactic acid bacterial dynamics in non-wilted and wilted alfalfa silage in tropical conditions. Mol Biol Rep 46:451–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4494-z
Bai J, Ding Z, Ke W, Xu D, Wang M, Huang W, Zhang Y, Liu F, Guo X (2021) Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb Biotechnol 14:1171–1182. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13785
Bernardes TF, Daniel JLP, Adesogan AT, McAllister TA, Drouin P, Nussio LG, Huhtanen P, Tremblay GF, Bélanger G, Cai Y (2018) Silage review: unique challenges of silages made in hot and cold regions. J Dairy Sci 101:4001–4019. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-13703
Chen MM, Liu QH, Xin GR, Zhang JG (2013) Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their inoculating effects on the silage fermentation at high temperature. Lett Appl Microbiol 56:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12018
Da Silva TC, Smith ML, Barnard AM, Kung L (2015) The effect of a chemical additive on the fermentation and aerobic stability of high-moisture corn. J Dairy Sci 98:8904–8912. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-9640
Du Z, Sun L, Chen C, Lin J, Yang F, Cai Y (2021) Exploring microbial community structure and metabolic gene clusters during silage fermentation of paper mulberry, a high-protein woody plant. Anim Feed Sci Technol 275:114766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114766
Du Z, Lin Y, Sun L, Yang F, Cai Y (2022) Microbial community structure, co-occurrence network and fermentation characteristics of woody plant silage. J Sci Food Agric 102:1193–1204. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11457
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
Ertekin I, Kizilşimşek M (2020) Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculation in pre-harvesting period on fermentation and feed quality properties of alfalfa silage. Asian-Australasian J Anim Sci 33:245–253. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.18.0801
Fu Z, Sun L, Hou M, Hao J, Lu Q, Liu T, Ren X, Jia Y, Wang ZJ, Ge G (2022) Effects of different harvest frequencies on microbial community and metabolomic properties of annual ryegrass silage. Front Microbiol 13:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.971449
Garcia AD, Olson WG, Otterby DE, Linn JG, Hansen WP (1989) Effects of temperature, moisture, and aeration on fermentation of alfalfa silage. J Dairy Sci 72:93–103. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(89)79084-6
Guan H, Shuai Y, Ran Q, Yan Y, Wang X, Li D, Cai Y, Zhang X (2020) The microbiome and metabolome of Napier grass silages prepared with screened lactic acid bacteria during ensiling and aerobic exposure. Anim Feed Sci Technol 269:114673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114673
Gulfam A, Guo G, Tajebe S, Chen L, Liu Q, Yuan X, Bai Y, Saho T (2017) Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their effect on the fermentation quality of Napier grass silage at three high temperatures. J Sci Food Agric 97:1931–1938. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7998
Guo XS, Undersander DJ, Combs DK (2013) Effect of Lactobacillus inoculants and forage dry matter on the fermentation and aerobic stability of ensiled mixed-crop tall fescue and meadow fescue. J Dairy Sci 96:1735–1744. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2045-5786
Guo XS, Ke WC, Ding WR, Ding LM, Xu DM, Wang WW, Zhang P, Yang FY (2018) Profiling of metabolome and bacterial community dynamics in ensiled Medicago sativa inoculated without or with Lactobacillus plantarum or Lactobacillus buchneri. Sci Rep 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18348-0
Hu Z, Niu H, Tong Q, Chang J, Yu J, Li S, Zhang S, Ma D (2020) The microbiota dynamics of alfalfa silage during ensiling and after air exposure, and the metabolomics after air exposure are affected by Lactobacillus casei and cellulase addition. Front Microbiol 11:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.519121
Jia T, Yun Y, Yu Z (2021) Propionic acid and sodium benzoate affected biogenic amine formation, microbial community, and quality of oat silage. Front Microbiol 12:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.750920
Ke W, Ding Z, Li F, Xu D, Bai J, Muhammad I, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Guo X (2021) Effects of malic or citric acid on the fermentation quality, proteolysis and lipolysis of alfalfa silage ensiled at two dry matter contents. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 106(5):988. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.13630
Kim SC, Adesogan AT (2006) Influence of ensiling temperature, simulated rainfall, and delayed sealing on fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of corn silage. J Dairy Sci 89:3122–3132. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72586-3
Kung L, Shaver RD, Grant RJ, Schmidt RJ (2018) Silage review: interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J Dairy Sci 101:4020–4033. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-13909
Li D, Ni K, Zhang Y, Lin Y, Yang F (2019a) Fermentation characteristics, chemical composition and microbial community of tropical forage silage under different temperatures. Asian-Australasian J Anim Sci 32:665–674. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.18.0085
Li J, Yin L, Wang L, Li J, Huang P, Yang H, Yin Y (2019b) Effects of vitamin B6 on growth, diarrhea rate, intestinal morphology, function, and inflammatory factors expression in a high-protein diet fed to weaned piglets. J Anim Sci 97:4865–4874. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skz338
Li H, Guan H, Jia Z, Liu W, Ma X, Liu Y, Wang H, Zhou Q (2022) Freeze–thaw condition limits the fermentation process and accelerates the aerobic deterioration of oat (Avena sativa) silage in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front Microbiol 13:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.944945
Lisnahan CV, Nahak OR (2020) Growth performance and small intestinal morphology of native chickens after feed supplementation with tryptophan and threonine during the starter phase. Vet World 13:2765–2771. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2020.2765-2771
Ni K, Wang F, Zhu B, Yang J, Zhou G, Pan Y, Tao Y, Zhong J (2017) Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour Technol 238:706–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.055
Ni K, Zhao J, Zhu B, Su R, Pan Y, Ma J, Zhou G, Tao Y, Liu X, Zhong J (2018) Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour Technol 265:563–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.097
Ni K, Wang X, Lu Y, Guo L, Li X, Yang F (2020) Exploring the silage quality of alfalfa ensiled with the residues of astragalus and hawthorn. Bioresour Technol 297:122249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122249
Nishino N, Li Y, Wang C, Parvin S (2012) Effects of wilting and molasses addition on fermentation and bacterial community in guinea grass silage. Lett Appl Microbiol 54:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2011.03191.x
Oliveira AS, Weinberg ZG, Ogunade IM, Cervantes AAP, Arriola KG, Jiang Y, Kim D, Li X, Gonçalves MCM, Vyas D, Adesogan AT (2017) Meta-analysis of effects of inoculation with homofermentative and facultative heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and the performance of dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 100:4587–4603. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-11815
Saia S, Fragasso M, De Vita P, Beleggia R (2019) Metabolomics provides valuable insight for the study of Durum wheat: a review. J Agric Food Chem 67:3069–3085. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b07097
Tao L, Zhou H, Zhang N, Si B, Tu Y, Ma T, Diao Q (2017) Effects of different source additives and wilt conditions on the pH value, aerobic stability, and carbohydrate and protein fractions of alfalfa silage. Anim Sci J 88:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/asj.12599
Vendramini JMB, Aguiar AD, Adesogan AT, Sollenberger LE, Alves E, Galzerano L, Salvo P, Valente AL, Arriola KG, Ma ZX, Oliveira FCL (2016) Effects of genotype, wilting, and additives on the nutritive value and fermentation of bermudagrass silage. J Anim Sci 94:3061–3071. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2016-0306
Wang B, Yu Z (2020) Effects of moisture content and additives on the ensiling quality and vitamins changes of alfalfa silage with or without rain damage. Anim Sci J 91:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/asj.13379
Wang S, Li J, Zhao J, Dong Z, Dong D, Shao T (2021) Fermentation profile and microbial diversity of temperate grass silage inoculated with epiphytic microbiota from tropical grasses. Arch Microbiol 203:6007–6019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02555-5
Wang S, Li J, Zhao J, Dong Z, Dong D, Shao T (2022a) Dynamics of the bacterial communities and predicted functional profiles in wilted alfalfa silage. J Appl Microbiol 132:2613–2624. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15417
Wang S, Li J, Zhao J, Dong Z, Shao T (2022b) Exploring the ensiling characteristics and bacterial community of red clover inoculated with the epiphytic bacteria from temperate gramineous grasses. J Appl Microbiol 132:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15234
Wang S, Shao T, Li J, Zhao J, Dong Z (2022c) A survey of fermentation parameters, bacterial community compositions and their metabolic pathways during the ensiling of sorghum. J Appl Microbiol 132:3563–3577. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15484
Xia T, Wang T, Sun J, Shi W, Liu Y, Huang F, Zhang J, Zhong J (2022) Modulation of fermentation quality and metabolome in co-ensiling of Sesbania cannabina and sweet sorghum by lactic acid bacterial inoculants. Front Microbiol 13:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.851271
Xu D, Ding W, Ke W, Li F, Zhang P, Guo X (2019) Modulation of metabolome and bacterial community in whole crop corn silage by inoculating homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum and heterofermentative Lactobacillus buchneri. Front Microbiol 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.03299
Xu D, Wang N, Rinne M, Ke W, Weinberg ZG, Da M, Bai J, Zhang Y, Li F, Guo X (2021) The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb Biotechnol 14:561–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13623
Yang L, Yuan X, Li J, Dong Z, Shao T (2019) Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour Technol 275:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.067
Yang F, Wang Y, Zhao S, Feng C, Fan X (2022) Dynamics of the fermentation products, residual non-structural carbohydrates, and bacterial communities of wilted and non-wilted alfalfa silage with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculation. Front Microbiol 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.824229
Yin L, Li J, Wang H, Yi Z, Wang L, Zhang S, Li X, Wang Q, Li J, Yang H, Yin Y (2020) Effects of vitamin B6 on the growth performance, intestinal morphology, and gene expression in weaned piglets that are fed a low-protein diet. J Anim Sci 98:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skaa022
Yuan XJ, Li JF, Dong ZH, Shao T (2020) The reconstitution mechanism of Napier grass microiota during the ensiling of alfalfa and their contributions to fermentation quality of silage. Bioresour Technol 297:122391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122391
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant number 2022YFD1301002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XG, RS, WK, and JB conceived and designed the research. RS, WK, and JB conducted the experiments. RS and WK analyzed the data. RS wrote the manuscript. XG, US, JB, and ZA revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1:
Supplementary tables (PDF 967 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, R., Ke, W., Usman, S. et al. Dry matter content and inoculant alter the metabolome and bacterial community of alfalfa ensiled at high temperature. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 3443–3457 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12535-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12535-y