Abstract
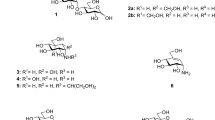
Glycosylation is an effective way to increase the polarity of natural products. UDP-glucuronyltransferases (UGTs) are commonly observed and extensively studied in phase II drug metabolism. However, UGTs in microorganisms are not well studied, which hampered the utilization of this type of enzyme in microbial glucuronidation of natural products. Screening of five actinomycete strains showed that Streptomyces chromofuscus ATCC 49982 can convert diverse plant polyphenols into more polar products, which were characterized as various glucuronides based on their spectral data. Analysis of the genome of this strain revealed a putative glucuronidation gene cluster that contains a UGT gene (gcaC) and two UDP-glucuronic acid biosynthetic genes (gcaB and gcaD). The gcaC gene was cloned and heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Incubation of the purified enzyme with resveratrol and UDP-glucuronic acid led to the production of resveratrol-4′-O-β-D-glucuronide and resveratrol-3-O-β-D-glucuronide, allowing GcaC to be characterized as a flexible UGT. The optimal in vitro reaction pH and temperature for GcaC are 7.5 and 30 °C, respectively. Its activity can be stimulated by Ca2+, Mg2+, and Mn2+, whereas Zn2+, Cu2+, and Fe2+ showed inhibitory effects. Furthermore, GcaC has a broad substrate specificity, which can glucuronidate various substrates besides resveratrol, including quercetin, ferulic acid, vanillic acid, curcumin, vanillin, chrysin, zearalenone, and apigenin. The titers of resveratrol-4′-O-β-D-glucuronide and resveratrol-3-O-β-D-glucuronide in E. coli-GcaC were 78.381 ± 0.366 mg/L and 14.991 ± 0.248 mg/L from 114.125 mg/L resveratrol within 3 h. Therefore, this work provides an effective way to produce glucuronides of resveratrol and other health-benefitting natural products.
Key points
• A novel versatile microbial UDP-glucuronyltransferase was discovered and characterized from Streptomyces chromofuscus ATCC 49982.
• The UDP-glucuronyltransferase was expressed in Escherichia coli and can convert resveratrol into two glucuronides both in vitro and in vivo.
• The UDP-glucuronyltransferase has a highly flexible substrate specificity and is an effective tool to prepare mono- or diglucuronides of bioactive molecules.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Almeida AF, Santos CuN, Ventura MR (2017) Synthesis of new sulfated and glucuronated metabolites of dietary phenolic compounds identified in human biological samples. J Agric Food Chem 65(31):6460–6466. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05629
Bezalel L, Hadar Y, Cerniglia CE (1997) Enzymatic mechanisms involved in phenanthrene degradation by the white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(7):2495–2501. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.63.7.2495-2501.1997
Bowles D, Isayenkova J, Lim E-K, Poppenberger B (2005) Glycosyltransferases: managers of small molecules. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8(3):254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2005.03.007
Cai Z, Huang J, Luo H, Lei X, Yang Z, Mai Y, Liu Z (2013) Role of glucose transporters in the intestinal absorption of gastrodin, a highly water-soluble drug with good oral bioavailability. J Drug Target 21(6):574–580. https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2013.778263
Chung SY, Seki H, Fujisawa Y, Shimoda Y, Hiraga S, Nomura Y, Saito K, Ishimoto M, Muranaka T (2020) A cellulose synthase-derived enzyme catalyses 3-O-glucuronosylation in saponin biosynthesis. Nat Commun 11(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19399-0
Clarke DJ, George SG, Burchell B (1991) Glucuronidation in fish. Aquat Toxicol 20(1–2):35–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(91)90040-G
De Bruyn F, Maertens J, Beauprez J, Soetaert W, De Mey M (2015) Biotechnological advances in UDP-sugar based glycosylation of small molecules. Biotechnol Adv 33(2):288–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.02.005
De Wildt SN, Kearns GL, Leeder JS, van den Anker JN (1999) Glucuronidation in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet 36(6):439–452. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199936060-00005
DeAngelis PL, White CL (2002) Identification and molecular cloning of a heparosan synthase from Pasteurella multocida type D. J Biol Chem 277(9):7209–7213. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112130200
Engstrom KM, Daanen JF, Wagaw S, Stewart AO (2006) Gram scale synthesis of the glucuronide metabolite of ABT–724. J Org Chem 71(22):8378–8383. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo0611972
Fidan O, Yan R, Zhu D, Zhan J (2019) Improved production of antifungal angucycline Sch47554 by manipulating three regulatory genes in Streptomyces sp. SCC-2136. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 66(4):517–526. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1748
Francioso A, Mastromarino P, Restignoli R, Boffi A, d’Erme M, Mosca L (2014) Improved stability of trans-resveratrol in aqueous solutions by carboxymethylated (1,3/1,6)-β-D-glucan. J Agric Food Chem 62(7):1520–1525. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404155e
Gachon CM, Langlois-Meurinne M, Saindrenan P (2005) Plant secondary metabolism glycosyltransferases: the emerging functional analysis. Trends Plant Sci 10(11):542–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.09.007
Gould S, Guo J (1994) Cytosylglucuronic acid synthase (cytosine: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase) from Streptomyces griseochromogenes, the first prokaryotic UDP-glucuronosyltransferase. J Bacteriol 176(5):1282–1286. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.176.5.1282-1286.1994
Harborne JB, Baxter H (1999) The handbook of natural flavonoids, vol 1 and 2. John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken
Hmidene AB, Hanaki M, Murakami K, Irie K, Isoda H, Shigemori H (2017) Inhibitory activities of antioxidant flavonoids from Tamarix gallica on amyloid aggregation related to Alzheimer’s and type 2 diabetes diseases. Biol Pharm Bull 40(2):238–241. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b16-00801
Imai H, Kitagawa M, Ishihara K, Masuoka N, Shimoda K, Nakajima N, Hamada H (2012) Glycosylation of trans-resveratrol by plant-cultured cells. Biosci Biotech Bioch 76(8):1552–1554. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.120126
Jeon YO, Lee J-S, Lee HG (2016) Improving solubility, stability, and cellular uptake of resveratrol by nanoencapsulation with chitosan and γ-poly (glutamic acid). Colloids Surf B 147:224–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.07.062
Kaminaga Y, Nagatsu A, Akiyama T, Sugimoto N, Yamazaki T, Maitani T, Mizukami H (2003) Production of unnatural glucosides of curcumin with drastically enhanced water solubility by cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus. FEBS Lett 555(2):311–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01265-1
Kim S-K (2016) Marine enzymes biotechnology: production and industrial applications, Part II-Marine Organisms Producing Enzymes, Volume 79, 1st edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
King RE, Bomser JA, Min DB (2006) Bioactivity of resveratrol. Compr Rev Food Sci F 5(3):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2006.00001.x
Kren V, Martínková L (2001) Glycosides in medicine: “the role of glycosidic residue in biological activity.” Curr Med Chem 8(11):1303–1328. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867013372193
Li X, Wang L, Bai L, Yao C, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Li Y (2010) Cloning and characterization of a glucosyltransferase and a rhamnosyltransferase from Streptomyces sp. 139. J Appl Microbiol 108(5):1544–1551. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04550.x
Marvalin C, Azerad R (2011a) Microbial glucuronidation of polyphenols. J Mol Catal B Enzym 73(1–4):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2011.07.015
Mehnaz D, Abdulla K, Aiysha D, Zaheer A, Mukhtar S (2017) Actinomycetes: a source of industrially important enzymes. J Proteom Bioinform 10:12. https://doi.org/10.4172/JPB.1000456
Nagashima S, Hirotani M, Yoshikawa T (2000) Purification and characterization of UDP-glucuronate: baicalein 7-O-glucuronosyltransferase from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. cell suspension cultures. Phytochemistry 53(5):533–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00593-2
Nawani N, Aigle B, Mandal A, Bodas M, Ghorbel S, Prakash D (2013) Actinomycetes: role in biotechnology and medicine. BioMed Res Int 2013:687190. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/687190
Osmani SA, Halkjær Hansen E, Malien-Aubert C, Olsen C-E, Bak S, Lindberg Møller B (2009) Effect of glucuronosylation on anthocyanin color stability. J Agric Food Chem 57(8):3149–3155. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8034435
Pandey RP, Parajuli P, Shin JY, Lee J, Lee S, Hong Y-S, Park YI, Kim JS, Sohng JK (2014) Enzymatic biosynthesis of novel resveratrol glucoside and glycoside derivatives. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(23):7235–7243. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02076-14
Paul D, Standifer KM, Inturrisi CE, Pasternak G (1989) Pharmacological characterization of morphine-6 β-glucuronide, a very potent morphine metabolite. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251(2):477–483
Pervaiz S (2003) Resveratrol: from grapevines to mammalian biology. FASEB J 17(14):1975–1985. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-0168rev
Prakash D, Nawani N, Prakash M, Bodas M, Mandal A, Khetmalas M, Kapadnis B (2013) Actinomycetes: a repertory of green catalysts with a potential revenue resource. Biomed Res Int 2013:264020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/264020
Priyadharsini P, Dhanasekaran D (2015) Diversity of soil allelopathic Actinobacteria in Tiruchirappalli district, Tamilnadu. India J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 14(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2013.07.001
Radominska-Pandya A, Czernik PJ, Little JM, Battaglia E, Mackenzie PI (1999) Structural and functional studies of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab Rev 31(4):817–899. https://doi.org/10.1081/DMR-100101944
Regev-Shoshani G, Shoseyov O, Bilkis I, Kerem Z (2003) Glycosylation of resveratrol protects it from enzymic oxidation. Biochem J 374(1):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20030141
Remya M, Vijayakumar R (2008) Isolation and characterization of marine antagonistic actinomycetes from west coast of India. Med Biol 15(1):13–19
Ren J, Tang W, Barton CD, Price OM, Mortensen MW, Phillips A, Wald B, Hulme SE, Stanley LP, Hevel J (2022) A highly versatile fungal glucosyltransferase for specific production of quercetin-7-O-β-d-glucoside and quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucoside in different hosts. Appl Microbiol Biotech 106(1):227–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11716-x
Rice-Evans C (2001) Flavonoid antioxidants. Curr Med Chem 8(7):797–807. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867013373011
Ridder L, van der Hooft JJ, Verhoeven S, de Vos RC, van Schaik R, Vervoort J (2012) Substructure-based annotation of high-resolution multistage MSn spectral trees. Rapid Commun Mass Sp 26(20):2461–2471. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.6364
Romero-Pérez AI, Ibern-Gómez M, Lamuela-Raventós RM, de la Torre-Boronat MC (1999) Piceid, the major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. J Agric Food Chem 47(4):1533–1536. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf981024g
Sauer S, Plauth A (2017) Health-beneficial nutraceuticals-myth or reality? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(3):951–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8068-5
Sawada SY, Suzuki H, Ichimaida F, Yamaguchi M-A, Iwashita T, Fukui Y, Hemmi H, Nishino T, Nakayama T (2005) UDP-glucuronic acid: anthocyanin glucuronosyltransferase from red daisy (Bellis perennis) flowers: enzymology and phylogenetics of a novel glucuronosyltransferase involved in flower pigment biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 280(2):899–906. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M410537200
Sharipova R, Andreeva O, Strobykina IY, Voloshina A, Strobykina A, Kataev V (2017) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of glucuronosyl derivatives of steviolbioside from Stevia rebaudiana. Chem Nat Compd 53(6):1107–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-017-2211-0
Shimoda K, Hamada M, Hamada H, Takemoto M, Hamada H (2013) Synthesis of resveratrol glycosides by cultured plant cells. Nat Prod Commun 8(7):907–909. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1300800713
Smith MT, Watt JA, Cramond T (1990) Morphine-3-glucuronide-a potent antagonist of morphine analgesia. Life Sci 47(6):579–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(90)90619-3
Stachulski AV, Harding JR, Lindon JC, Maggs JL, Park BK, Wilson ID (2006) Acyl glucuronides: biological activity, chemical reactivity, and chemical synthesis. J Med Chem 49(24):6931–6945. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm060599z
Sugiura N, Baba Y, Kawaguchi Y, Iwatani T, Suzuki K, Kusakabe T, Yamagishi K, Kimata K, Kakuta Y, Watanabe H (2010) Glucuronyltransferase activity of KfiC from Escherichia coli strain K5 requires association of KfiA: KfiC and KfiA are essential enzymes for production of K5 polysaccharide. N-Acetylheparosan J Biol Chem 285(3):1597–1606. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.023002
Thilakarathna SH, Rupasinghe H (2013) Flavonoid bioavailability and attempts for bioavailability enhancement. Nutrients 5(9):3367–3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5093367
Thorson JS, Barton WA, Hoffmeister D, Albermann C, Nikolov DB (2004) Structure-based enzyme engineering and its impact on in vitro glycorandomization. ChemBioChem 5(1):16–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200300620
Thuan NH, Trung NT, Cuong NX, Van Cuong D, Van Quyen D, Malla S (2018) Escherichia coli modular coculture system for resveratrol glucosides production. World J Microb Biot 34(6):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2458-z
Tracy BS, Avci FY, Linhardt RJ, DeAngelis PL (2007) Acceptor specificity of the Pasteurella hyaluronan and chondroitin synthases and production of chimeric glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem 282(1):337–344. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M607569200
Tsao R (2010) Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients 2(12):1231–1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2121231
Uesugi D, Hamada H, Shimoda K, Kubota N, Ozaki S-i, Nagatani N (2017) Synthesis, oxygen radical absorbance capacity, and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of glycosides of resveratrol, pterostilbene, and pinostilbene. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81(2):226–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2016.1240606
Van der Hooft JJ, de Vos RC, Mihaleva V, Bino RJ, Ridder L, de Roo N, Jacobs DM, van Duynhoven JP, Vervoort J (2012) Structural elucidation and quantification of phenolic conjugates present in human urine after tea intake. Anal Chem 84(16):7263–7271. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac3017339
Wackett L, Gibson D (1982) Metabolism of xenobiotic compounds by enzymes in cell extracts of the fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Biochem J 205(1):117–122. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2050117
Wang Y, Catana F, Yang Y, Roderick R, Van Breemen R (2002) Analysis of resveratrol in grape products, cranberry juice and wine using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 50:431–435. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010812u
Wang L-X, Heredia A, Song H, Zhang Z, Yu B, Davis C, Redfield R (2004) Resveratrol glucuronides as the metabolites of resveratrol in humans: characterization, synthesis, and anti-HIV activity. J Pharm Sci 93(10):2448–2457. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20156
Wang T-T, Zhu C-Y, Zheng S, Meng C-C, Wang T-T, Meng D-H, Li Y-J, Zhu H-M, Wang F-S, Sheng J-Z (2018) Identification and characterization of a chondroitin synthase from Avibacterium paragallinarum. Appl Microbiol Biotech 102(11):4785–4797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8926-4
Wang T-T, Deng J-Q, Chen L-Z, Sun L, Wang F-S, Ling P-X, Sheng J-Z (2020) The second member of the bacterial UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine: heparosan alpha-1, 4-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase superfamily: GaKfiA from Gallibacterium anatis. Int J Biol Macromol 147:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.016
Weymouth-Wilson AC (1997) The role of carbohydrates in biologically active natural products. Nat Prod Rep 14(2):99–110. https://doi.org/10.1039/NP9971400099
Wilkinson SM, Liew CW, Mackay JP, Salleh HM, Withers SG, McLeod MD (2008) Escherichia coli glucuronylsynthase: an engineered enzyme for the synthesis of β-glucuronides. Org Lett 10(8):1585–1588. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol8002767
Wilkinson SM, Watson MA, Willis AC, McLeod MD (2011) Experimental and kinetic studies of the Escherichia coli glucuronylsynthase: an engineered enzyme for the synthesis of glucuronide conjugates. J Org Chem 76(7):1992–2000. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo101914s
Xu G, Cai W, Gao W, Liu C (2016) A novel glucuronosyltransferase has an unprecedented ability to catalyse continuous two-step glucuronosylation of glycyrrhetinic acid to yield glycyrrhizin. New Phytol 212(1):123–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14039
Yonekura K, Hanada K (2011) An evolutionary view of functional diversity in family 1 glycosyltransferases. Plant J 66(1):182–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04493.x
Yu C, Shin YG, Chow A, Li Y, Kosmeder JW, Lee YS, Hirschelman WH, Pezzuto JM, Mehta RG, van Breemen RB (2002) Human, rat, and mouse metabolism of resveratrol. Pharm Res 19(12):1907–1914. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021414129280
Yu D, Xu F, Zhang S, Shao L, Wang S, Zhan J (2013) Characterization of a methyltransferase involved in herboxidiene biosynthesis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23(20):5667–5670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.08.023
Zakim D, Vessey DA (1974) Membrane dependence of uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase: effect of the membrane on kinetic properties. Biochem Soc Trans 2(6):1165–1167. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0021165
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Award CBET-2044558. The Bruker Avance III HD Ascend-500 NMR instrument used in this research was funded by the National Science Foundation Award CHE-1429195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JR and JZ conceived and designed research. JR, CB, and KS conducted experiments. JR and JZ analyzed data. JR, CB, KS, and JZ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Barton, C., Sorenson, K. et al. Identification of a novel glucuronyltransferase from Streptomyces chromofuscus ATCC 49982 for natural product glucuronidation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 1165–1183 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11789-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11789-2