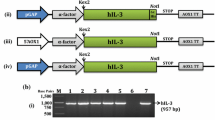
Abstract
Human interleukin-7 (hIL-7) is a therapeutically important cytokine involved in lymphocyte development and survival. In previous reports, a uniformly poor expression of hIL-7 has been shown in Escherichia coli host with the problem of inclusion body formation. In this study, the role of codon optimization and N-terminus blocking using various solubility enhancer fusion tags was explored to improve its soluble expression. The use of codon optimization strategy improved its expression to 80 ± 5 mg/L at shake flask level. The utilization of pelB leader sequence resulted in an unprocessed protein in the form of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies with lower expression yields. The N-terminus fusion of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO), thioredoxin (Trx), and NusA tags increased the expression in the range of 90–140 mg/L, where >90 % of the fusion protein was obtained in soluble form. The fed-batch fermentation of SUMO-tagged hIL-7 protein was optimized at bioreactor level, where a high volumetric product concentration of 2.65 g/L was achieved by controlling the plasmid segregation instability using high antibiotic concentration. The specific product yield (YP/X) and volumetric product concentration were 1.38 and 2.55-fold higher compared to batch results, respectively. A preparative scale affinity chromatography resulted in a high recovery yield of 50.6 mg/L with ∼90 % purity. The conformational property of purified recombinant hIL-7 from CD spectroscopy showed a typical helical structure with 31.5 % α-helix and 26.43 % β-sheet. The biological activity of purified protein was tested using IL-7-dependent murine immature B lymphocyte (2E8) cell line by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide salt (MTT) assay, where it showed a similar biological activity as standard control.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adivitiya, Dagar VK, Devi N, Khasa YP (2016) High level production of active streptokinase in Pichia pastoris fed-batch culture. Int J Biol Macromol 83:50–60
Babaeipour V, Shojaosadati SA, Khalilzadeh R, Maghsoudi N, Tabandeh F (2008) A proposed feeding strategy for the overproduction of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 49:141–147
Bhattacharya P, Pandey G, Srivastava P, Mukherjee KJ (2005) Combined effect of protein fusion and signal sequence greatly enhances the production of recombinant human GM-CSF in Escherichia coli. Mol Biotechnol 30:103–116
Burgess-Brown NA, Sharma S, Sobott F, Loenarz C, Oppermann U, Gileadi O (2008) Codon optimization can improve expression of human genes in Escherichia coli: a multi-gene study. Protein Expr Purif 59(1):94–102
Butt TR, Edavettal SC, Hall JP, Mattern MR (2005) SUMO fusion technology for difficult-to-express proteins. Protein Expr Purif 43(1):1–9
Choi JH, Lee SY (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64(5):625–635
Choi JH, Keum KC, Lee SY (2006) Production of recombinant proteins by high cell density culture of Escherichia coli. Chem Eng Sci 61:876–885
Cosenza L, Murphy JR, Smith T, Rosenbach A, White JV (2000) Comparative model building of interleukin-7 using interleukin-4 as a template: a structural hypothesis that displays atypical surface chemistry in helix D important for receptor activation. Protein Sci 9(5):916–926
Cosenza L, Sweeney E, Murphy JR (1997) Disulfide bond assignment in human interleukin-7 by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectroscopy and site-directed cysteine to serine mutational analysis. J Biol Chem 272:32995–33000
Costa S, Almeida A, Castro A, Domingues L (2014) Fusion tags for protein solubility, purification, and immunogenicity in Escherichia coli: the novel Fh8 system. Front Microbiol 5:63
Eiteman MA, Altman E (2006) Overcoming acetate in Escherichia coli recombinant protein fermentations. Trends Biotechnol 24(11):530–536
Gao J, Zhao L, Wan YY, Zhu B (2015) Mechanism of action of IL-7 and its potential applications and limitations in cancer immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci 16(5):10267–10280
Hofmeister R, Khaled AR, Benbernou N, Rajnavolgyi E, Muegge K, Durum SK (1999) Interleukin-7: physiological roles and mechanisms of action. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 10(1):41–60
Hu Z, Chen Z, Huang N, Teng X, Zhang J, Wang Z, Wei X, Qin K, Liu X, Wu X, Tang H (2015) Expression, purification of IL-38 in Escherichia coli and production of polyclonal antibodies. Protein Expr Purif 107:76–82
Jeong KJ, Lee SY (1999) High-level production of human leptin by fed-batch cultivation of recombinant Escherichia coli and its purification. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(7):3027–3032
Khaled AR, Durum SK (2002) Lymphocide: cytokines and the control of lymphoid homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol 2(11):817–830
Khasa YP, Khushoo A, Mukherjee KJ (2013) Enhancing toxic protein expression in Escherichia coli fed-batch culture using kinetic parameters: human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as a model system. J Biosci Bioeng 115(3):291–297
Khasa YP, Khushoo A, Tapryal S, Mukherjee KJ (2011) Optimization of human granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) expression using asparaginase and xylanase gene’s signal sequences in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165(2):523–537
Khushoo A, Pal Y, Mukherjee KJ (2005) Optimization of extracellular production of recombinant asparaginase in Escherichia coli in shake-flask and bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68(2):189–197
Khushoo A, Pal Y, Singh BN, Mukherjee KJ (2004) Extracellular expression and single step purification of recombinant Escherichia coli asparaginase II. Protein Expr Purif 38(1):29–36
Kong B, Guo GL (2014) Soluble expression of disulfide bond containing proteins FGF15 and FGF19 in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. PLoS One 9(1):e85890
Lee CM, McGuire H, Basten A, King C, Christ D (2010) Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant interleukin-21. J Immunol Methods 362(1):185–189
Li Y, Chen CX, von Specht BU, Hahn HP (2002) Cloning and hemolysin-mediated secretory expression of a codon-optimized synthetic human interleukin-6 gene in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 25(3):437–447
Li A, Kato Z, Ohnishi H, Hashimoto K, Matsukuma E, Omoya K, Yamamoto Y, Kondo N (2003) Optimized gene synthesis and high expression of human interleukin-18. Protein Expr Purif 32(1):110–118
Lundstrom W, Fewkes N, Mackall CL (2012) IL-7 in human health and disease. Semin Immunol 24(3):218–224
Luo Y, Kong X, Xu A, Jin S, Wu D (2009) Expression, purification, and functional characterization of recombinant human interleukin-7. Protein Expr Purif 63(1):1–4
Mackall CL, Fry TJ, Gress RE (2011) Harnessing the biology of IL-7 for therapeutic application. Nat Rev Immunol 11(5):330–342
Mirzaei M, Jardin B, Elias CB, Prakash S (2008) Expression and production of human interleukin-7 in insect cells using baculovirus expression vector system (BEVS). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 151(1):93–103
Ouellette T, Destrau S, Ouellette T, Zhu J, Roach JM, Coffman JD, Hecht T, Lynch JE, Giardina SL (2003) Production and purification of refolded recombinant human IL-7 from inclusion bodies. Protein Expr Purif 30(2):156–166
Peciak K, Tommasi R, Choi JW, Brocchini S, Laurine E (2014) Expression of soluble and active interferon consensus in SUMO fusion expression system in E. coli. Protein Expr Purif 99:18–26
Quax TE, Claassens NJ, Söll D, van der Oost J (2015) Codon bias as a means to fine-tune gene expression. Mol Cell 59(2):149–161
Rosano GL, Ceccarelli EA (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5:341
Sletta H, Tondervik A, Hakvag S, Aune TV, Nedal A, Aune R, Evensen G, Valla S, Ellingsen TE, Brautaset T (2007) The presence of N-terminal secretion signal sequences leads to strong stimulation of the total expression levels of three tested medically important proteins during high-cell-density cultivations of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(3):906–912
Studier FW (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high-density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):207–234
Tileva M, Krachmarova E, Ivanov I, Maskos K, Nacheva G (2016) Production of aggregation prone human interferon gamma and its mutant in highly soluble and biologically active form by SUMO fusion technology. Protein Expr Purif 117:26–34
Venyaminov SY, Yang JT (1996) Determination of protein secondary structure. In Circular dichroism and the conformational analysis of biomolecules. Springer US, p 69–107
Vera A, González-Montalbán N, Arís A, Villaverde A (2007) The conformational quality of insoluble recombinant proteins is enhanced at low growth temperatures. Biotechnol Bioeng 96(6):1101–1106
Wang H, Xiao Y, Fu L, Zhao H, Zhang Y, Wan X, Qin Y, Huang Y, Gao H, Li X (2010) High-level expression and purification of soluble recombinant FGF21 protein by SUMO fusion in Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol 10(1):1
Waugh DS (2005) Making the most of affinity tags. Trends Biotechnol 23(6):316–320
Wickham J, Walsh ST (2007) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction of human interleukin-7 bound to unglycosylated and glycosylated forms of its α-receptor. Acta Crystallogr Sect F: Struct Biol Cryst Commun 63(10):865–869
Wu X, Nie C, Huang Z, Nie Y, Yan Q, Xiao Y, Su Z, Huang Y, Xiao J, Zeng Y, Tan Y (2009) Expression and purification of human keratinocyte growth factor 2 by fusion with SUMO. Mol Biotechnol 42(1):68–74
Zaremba-Czogalla M, Stumpp C, Bonifacio E, Paul R (2015) Comparison of the purification of biologically active IL-7 cytokine expressed in Escherichia coli and Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 110:65–71
Zhang M, Jiang X, Su Z, Lin J, Xiang Q, Yang Z, Huang Y, Li X (2012) Large-scale expression, purification, and glucose uptake activity of recombinant human FGF21 in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(2):613–621
Acknowledgements
Nirmala Devi and Adivitiya are the recipients of a senior research fellowship from the University Grants Commission (UGC) and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Govt. of India, New Delhi, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, New Delhi, through grant number BT/PR15076/GBD/27/299/2011.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, N., Adivitiya & Khasa, Y.P. A combinatorial approach of N-terminus blocking and codon optimization strategies to enhance the soluble expression of recombinant hIL-7 in E. coli fed-batch culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 9979–9994 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7683-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7683-5