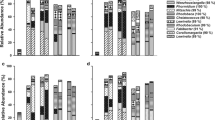
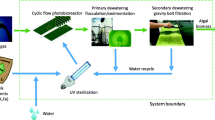
Abstract
Phototrophic microorganisms have been proposed as an alternative to capture carbon dioxide (CO2) and to produce biofuels and other valuable products. Low CO2 absorption rates, low volumetric productivities, and inefficient downstream processing, however, currently make algal biotechnology highly energy intensive, expensive, and not economically competitive to produce biofuels. This mini-review summarizes advances made regarding the cultivation of phototrophic microorganisms at highly alkaline conditions, as well as other innovations oriented toward reducing the energy input into the cultivation and processing stages. An evaluation, in terms of energy requirements and energy return on energy invested, is performed for an integrated high-pH, high-alkalinity growth process that uses biofilms. Performance in terms of productivity and expected energy return on energy invested is presented for this process and is compared to previously reported life cycle assessments (LCAs) for systems at near-neutral pH. The cultivation of alkaliphilic phototrophic microorganisms in biofilms is shown to have a significant potential to reduce both energy requirements and capital costs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acién FG, Fernández JM, Magán JJ, Molina E (2012) Production cost of a real microalgae production plant and strategies to reduce it. Biotechnol Adv 30:1344–1353. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.02.005
Acién FG, Fernández JM, Sánchez JA, Molina E, Chisti Y (2001) Airlift-driven external-loop tubular photobioreactors for outdoor production of microalgae: assessment of design and performance. Chem Eng Sci 56:2721–2732. doi:10.1016/S0009-2509(00)00521-2
Baba M, Shiraiwa Y (2012) High-CO2 response mechanisms in microalgae. In: Najafpour M (ed) Advances in photosynthesis—fundamental aspects. InTech, Rijeka, pp. 299–320. doi:10.5772/27737
Bagnoud-Velásquez M, Schmid-Staiger U, Peng G, Vogel F, Ludwig C (2015) First developments towards closing the nutrient cycle in a biofuel production process. Algal Res 8:76–82. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2014.12.012
Ballot A, Krienitz L, Kotut K, Wiegand C, Metcalf JS, Codd G, Pflugmacher S (2004) Cyanobacteria and cyanobacterial toxins in three alkaline Rift Valley lakes of Kenya—lakes Bogoria, Nakuru and Elmenteita. J Plankton Res 26:925–935. doi:10.1093/plankt/fbh084
Ballot A, Krienitz L, Kotut K, Wiegand C, Pflugmacher S (2005) Cyanobacteria and cyanobacterial toxins in the alkaline crater lakes Sonachi and Simbi, Kenya. Harmful Algae 4:139–150. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2004.01.001
Benemann J (1997) CO2 mitigation with microalgae systems. Energ Convers Manage 38:S475–S479. doi:10.1016/S0196-8904(96)00313-5
Berner F, Heimann K, Sheehan M (2014) Microalgal biofilms for biomass production. J Appl Phycol. doi:10.1007/s10811-014-0489-x
Bernstein H, Kesaano M, Moll K, Smith T, Gerlach R, Carlson R, Miller C, Peyton B, Cooksey K, Gardner R, Sims R (2014) Direct measurement and characterization of active photosynthesis zones inside wastewater remediating and biofuel producing microalgal biofilms. Bioresour Technol 156:206–215. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.001
Blanken W, Janssen M, Cuaresma M, Libor Z, Bhaiji T, Wijffels R (2014) Biofilm growth of Chlorella sorokiniana in a rotating biological contactor based photobioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:2436–2445. doi:10.1002/bit.25301
Canter C, Blowers P, Handler R, Shonnard D (2015) Implications of widespread algal biofuels production on macronutrient fertilizer supplies: nutrient demand and evaluation of potential alternate nutrient sources. Appl Energ 143:71–80. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.065
Carvalho AP, Meireles LA, Malcata FX (2006) Microalgal reactors: a review of enclosed system designs and performances. Biotechnol Prog 22:1490–1506. doi:10.1021/bp060065r
Cheng-Wu Z, Zmora O, Kopel R, Richmond A (2001) An industrial-size flat plate glass reactor for mass production of Nannochloropsis sp. (Eustigmatophyceae). Aquaculture 195:35–49. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00533-0
Chi Z, Elloy F, Yuxiao X, Hu Y, Chen S (2014) Selection of microalgae and cyanobacteria strains for bicarbonate-based integrated carbon capture and algae production system. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:447–457. doi:10.1007/s12010-013-0515-5
Chi Z, Xie Y, Elloy F, Zheng Y, Hu Y, Shulin C (2013) Bicarbonate-based integrated carbon capture and algae production system with alkalihalophilic cyanobacterium. Bioresour Technol 133:513–521. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.150
Christenson L, Sims R (2012) Rotating algal biofilm reactor and spool harvester for wastewater treatment with biofuels by-products. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:1674–1684. doi:10.1002/bit.24451
Collet P, Hélias A, Lardon L, Ras M, Goy RA, Steyer JP (2011) Life-cycle assessment of microalgae culture coupled to biogas production. Bioresour Technol 102:207–214. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.154
Crowe B, Attalah S, Agrawal S, Waller P, Ryan R, Van Wagenen J, Chavis A, Kyndt J, Kacira M, Ogden K, Huesemann M (2012) A comparison of Nannochloropsis salina growth performance in two outdoor pond designs: conventional raceways versus the arid pond with superior temperature management. Int J Chem Eng. doi:10.1155/2012/920608
Davis R, Aden A, Pienkos PT (2011) Techno-economic analysis of autotrophic microalgae for fuel production. Appl Energ 88:3524–3531. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.04.018
Delrue F, Setier P, Sahut C, Cournac L, Roubaud A, Peltier G, Froment K (2012) An economic, sustainability, and energetic model of biodiesel production from microalgae. Bioresour Technol 111:191–200. doi:10.1016/j.biortech. 2012.02.020
Dickson AG, Goyet C (1997) Handbook of methods for the analysis of the carbon dioxide system in sea water; version 2.13. U.S. Department of Energy, ORNL/CDIAC-74
Doucha J, Livansky K (2006) Productivity, CO2/O2 exchange and hydraulics in outdoor open high density microalgal (Chlorella sp.) photobioreactors operated in a Middle and Southern European climate. J Appl Phycol 18:811–826. doi:10.1007/s10811-006-9100-4
Doucha J, Livansky K (2014) High density outdoor microalgal culture. In: Bajpai R, Prokop A, Zappi M (eds) Algal biorefineries. Springer, New York, pp. 147–173
Fields M, Hise A, Lohman E, Bell T, Gardner R, Corredor L, Moll K, Peyton B, Characklis G, Gerlach R (2014) Sources and resources: importance of nutrients, resource allocation, and ecology in microalgal cultivation for lipid accumulation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:4805–4816. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5694-7
Flora J, Suidan M, Biswas P, Sayles G (1995) Modeling algal biofilms: role of carbon, light, cell surface charge, and ionic species. Water Environ Res 67:87–94
Gross M, Henry W, Michael C, Wen Z (2013) Development of a rotating growth system for attached microalgae with in situ biomass harvest. Bioresour Technol 150:195–201. doi:10.1016/j.biortech. 2013.10.016
Guzzon A, Bohn A, Diociaiutic M, Albertano P (2008) Cultured phototrophic biofilms for phosphorous removal in wastewater treatment. Water Res 42:4357–4367. doi:10.1016/j.watres. 2008.07.029
Hempel N, Petrick I, Behrendt F (2012) Biomass productivity and productivity of fatty acids and amino acids of microalgae strains as key characteristics of suitability for biodiesel production. J Appl Phycol 24:1407–1418. doi:10.1007/s10811-012-9795-3
Hirano A, Ueda R, Hirayama S, Ogushi Y (1997) CO2 fixation and ethanol production with microalgal photosynthesis and intracellular anaerobic fermentation. Energy 22:137–142. doi:10.1016/S0360-5442(96)00123-5
Irving T, Allen G (2011) Species and material considerations in the formation and development of microalgal biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:283–294. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3341-0
Johnson M, Wen Z (2010) Development of an attached microalgal growth system for biofuel production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:525–534. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2133-2
Jorquera O, Kiperstok A, Sales E, Embiruçu M, Ghirardi ML (2010) Comparative energy life-cycle analyses of microalgal biomass production in open ponds and photobioreactors. Bioresour Technol 101:1406–1413. doi:10.1016/j.biortech. 2009.09.038
Kesaano M, Sims R (2014) Algal biofilm based technology for wastewater treatment. Algal Res 5:231–240. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2014.02.003
Kesaano M, Gardner R, Moll K, Lauchnor E, Gerlach R, Peyton B, Sims R (2015) Dissolved inorganic carbon enhanced growth, nutrient uptake, and lipid accumulation in wastewater grown microalgal biofilms. Bioresour Technol 180:7–15. doi:10.1016/j.biortech. 2014.12.082
Kupriyanova E, Villarejo A, Markelova A, Gerasimenko L, Zavarzin G, Samuelsson G, Pronina NA (2007) Extracellular carbonic anhydrases of the stromatolite-forming cyanobacterium Microcoleus chthonoplastes. Microbiology (Moscow, Russ Fed) 153:1149–1156. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2006/003905-0
Kupriyanova EV, Lebedeva NV, Dudoladova MV, Gerasimenko LM, Alekseeva SG, Pronina NA, Zavarzin GA (2003) Carbonic anhydrase activity of alkalophilic cyanobacteria from soda lakes. Russ J Plant Physiol 50:532–539. doi:10.1023/A:1024733109767
Kupriyanova EV, Markelova AG, Lebedeva NV, Gerasimenko LM, Zavarzin GA, Pronina NA (2004) Carbonic anhydrase of the alkaliphilic cyanobacterium Microcoleus chthonoplastes. Microbiology (Moscow, Russ Fed) 73:307–311. doi:10.1023/B:MICI.0000032233.36705.5a
Liu T, Wang J, Hu Q, Cheng P, Ji B, Liu J, Chen Y, Zhang W, Chen X, Chen L, Gao L, Ji C, Wang H (2013) Attached cultivation technology of microalgae for efficient biomass feedstock production. Bioresour Technol 127:216–222. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.100
Livansky K, Doucha J (1996) CO2 and O2 gas exchange in outdoor thin-layer high density microalgal cultures. J Appl Phycol 8:353–358. doi:10.1007/BF02178578
Mahapatra DM, Chanakya HN, Ramachandra TV (2013) Treatment efficacy of algae-based sewage treatment plants. Environ Monit Assess 185:7145–7164. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3090-x
Medeiros DL, Sales EA, Kiperstok A (2014) Energy production from microalgae biomass: carbon footprint and energy balance. J Clean Prod 96:493–500. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.07.038
Melack J (1981) Photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton in tropical African soda lakes. Hydrobiologia 81:71–85. doi:10.1007/BF00048707
Melack J, Kilham P (1974) Photosynthetic rates of phytoplankton in East African alkaline, saline lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 19:743–755. doi:10.4319/lo.1974.19.5.0743
Mesbah N, Abou-El-Ela S, Wiegel J (2007) Novel and unexpected prokaryotic diversity in water and sediments of the alkaline, hypersaline lakes of Wadi-an-Natrun, Egypt. Microb Ecol 54:598–617. doi:10.1007/s00248-006-9193-y
Meyer M, Weiss A (2014) Life cycle costs for the optimized production of hydrogen and biogas from microalgae. Energy 78:84–93. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2014.08.069
Mikhodiuk O, Zavarzin G, Ivanovski R (2008a) Transport systems for carbonate in the extremely natronophilic cyanobacterium Euhalothece sp. Microbiology (Moscow, Russ Fed) 77:465–471. doi:10.1134/S002626170804005X
Mikhodyuk O, Gerasimenko L, Akimov V, Ivanovsky R, Zavarzin G (2008b) Ecophysiology and polymorphism of the unicellular extremely natronophilic cyanobacterium Euhalothece sp. Z-M001 from lake Magadi. Microbiology (Moscow, Russ Fed) 77:717–725. doi:10.1134/S0026261708060106
Moll B, McCool B, Drake W, Purobsky W, Adams R, Enke H, Metzner J, Knuth K (2014) Biofilm photobioreactor system and method of use. United States Patent US 8,691,538 B1
Nolla-Ardèvol V, Strous M, Sorokin DY, Merkel AY, Tegetmeyer HE (2012) Activity and diversity of haloalkaliphilic methanogens in Central Asian soda lakes. J Biotechnol 161:167–173. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.04.003
Nolla-Ardèvol V, Strous M, Tegetmeyer H (2015) Anaerobic digestion of the microalga Spirulina at extreme alkaline conditions: biogas production, metagenome, and metatranscriptome. Front Microbiol 6:597. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00597
Norsker NH, Barbosa MJ, Vermuë MH, Wijffels RH (2011) Microalgal production—a close look at the economics. Biotechnol Adv 29:24–27. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.08.005
Ono E, Cuello J (2006) Feasibility assessment of microalgal carbon dioxide sequestration technology with photobioreactor and solar collector. Biosys Eng 95:597–606. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2006.08.005
Ozkan A, Kinney K, Katz L, Berberoglu H (2012) Reduction of water and energy requirement of algae cultivation using an algae biofilm photobioreactor. Bioresour Technol 114:542–548. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.055
Pancha I, Chokshi K, Ghosh T, Paliwal C, Maurya R, Mishra S (2015) Bicarbonate supplementation enhanced biofuel production potential as well as nutritional stress mitigation in the microalgae Scenedesmus sp. CCNM 1077. Bioresour Technol 193:315–323. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.107
Picard C, Logette S, Schrotter J, Aimar P, Remigy J (2012) Mass transfer in membrane aerated biofilm. Water Res 46:4761–4769. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.05.056
Raes EJ, Isdepsky A, Muylaert K, Borowitzka MA, Moheimani NR (2014) Comparison of growth of Tetraselmis in a tubular photobioreactor (Biocoil) and a raceway pond. J Appl Phycol 26:247–255. doi:10.1007/s10811-013-0077-5
Razon LF, Tan RR (2011) Net energy analysis of the production of biodiesel and biogas from the microalgae: Haematococcus pluvialis and Nannochloropsis. Appl Energ 88:3507–3514. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.12.052
Richardson JW, Johnson MD, Outlaw JL (2012) Economic comparison of open pond raceways to photo bio-reactors for profitable production of algae for transportation fuels in the Southwest. Algal Res 1:93–100. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2012.04.001
Santos A, Lamers P, Janssen M, Wijfels R (2013) Biomass and lipid productivity of Neochloris oleoabundans under alkaline–saline conditions. Algal Res 2:204–211. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2013.04.007
Schnurr P, Espie G, Allen G (2013) Algae biofilm growth and the potential to stimulate lipid accumulation through nutrient starvation. Bioresour Technol 136:337–344. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.036
Schragerl M, Oduor S (2008) Phytoplankton community relationship to environmental variables in three Kenyan Rift Valley saline-alkaline lakes. Mar Freshwat Res 59:125–136. doi:10.1071/MF07095
Seckbach J (2007) Algae and cyanobacteria in extreme environments, Springer
Singh A, Nigam P, Murphy J (2011) Mechanism and challenges in commercialization of algal biofuels. Bioresour Technol 102:26–34. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.057
Sorokin D, Kuenen J (2005) Chemolithotrophic haloalkaliphiles from soda lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:287–295. doi:10.1016/j.femsec.2005.02.012
Sorokin D, Kuenen J, Muyzer G (2011) The microbial sulfur cycle at extremely haloalkaline conditions of soda lakes. Front Microbiol 2:article 44. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2011.00044
Takabe T, Incharoensakdi A, Arakawa K, Yokota S (1988) CO2 fixation rate and RuBisCo content increase in the halotolerant cyanobacterium, Aphanothece halophytica, grown in high salinities. Plant Physiol 88:1120–1124. doi:10.1104/pp.88.4.1120
Tredici M, Rodolfi L, Sampietro G, Bassi N (2011) Low-cost photobioreactor for microalgae cultivation. Patent number: WO2011013104 A1
Ujihara T, Fujiwara K, Sazaki G, Usami N, Nakajima K (2002) New method for measurement of interdiffusion coefficient in high temperature solutions based on Fick’s first law. J Cryst Growth 241:387–394. doi:10.1016/S0022-0248(02)01316-7
Wang L, Min M, Li Y, Chen P, Chen Y, Liu Y, Wang Y, Ruan R (2010) Cultivation of green algae Chlorella sp. in different wastewaters from municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1174–1186. doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8866-7
Wang X, Nordlander E, Thorin E, Yan J (2013) Microalgal biomethane production integrated with an existing biogas plant: a case study in Sweden. Appl Energ 112:478–484. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.04.087
White D, Pagarette A, Rooks P, Ali T (2013) The effect of sodium bicarbonate supplementation on growth and biochemical composition of marine microalgae cultures. J Appl Phycol 25:153–165. doi:10.1007/s10811-012-9849-6
Wimpenny J, Manz W, Szewzyk U (2000) Heterogeneity in biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:661–671. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2000.tb00565.x
Xu L, Weathers PJ, Xiong XR, Liu CZ (2009) Microalgal bioreactors: challenges and opportunities. Eng Life Sci 9:178–189. doi:10.1002/elsc.200800111
Zamalloa C, Vulsteke E, Albrecht J, Verstraete W (2011) The techno-economic potential of renewable energy through the anaerobic digestion of microalgae. Bioresour Technol 102:1149–1158. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.017
Zavarzin G, Zhilina T, Kevbrin V (1999) The alkaliphilic microbial community and its functional diversity. Microbiology (Moscow, Russ Fed) 68:579–599
Zhu L (2015) Microalgal culture strategies for biofuel production: a review. Biofuels, Bioprod Biorefin. doi:10.1002/bbb.1576
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the University of Calgary’s Vice-President of Research, and the Campus Alberta Innovates Program Chair to Marc Strous.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 159 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canon-Rubio, K.A., Sharp, C.E., Bergerson, J. et al. Use of highly alkaline conditions to improve cost-effectiveness of algal biotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 1611–1622 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7208-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7208-7