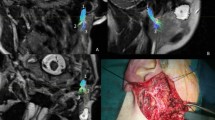
Abstract
Purpose
One of the most severe complications in surgery of parotid tumors is facial palsy. Imaging of the intra-parotid facial nerve is challenging due to small dimensions. Our aim was to assess, in patients with parotid tumors, the ability of high-resolution 3D double-echo steady-state sequence with water excitation (DE3D-WE) (1) to visualize the extracranial facial nerve and its tracts, (2) to evaluate their relationship to the parotid lesion and (3) to compare MRI and surgical findings.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted including all patients with parotid tumors, who underwent MRI from April 2022 to December 2023. Two radiologists independently reviewed DE3D-WE images, assessing quality of visualization of the facial nerve bilaterally and localizing the nerve’s divisions in relation to the tumor. MRI data were compared with surgical findings.
Results
Forty consecutive patients were included (M:F = 22:18; mean age 56.3 ± 17.4 years). DE3D-WE could excellently visualize the nerve main trunk and the temporofacial division in all cases. The cervicofacial branch was visible in 99% of cases and visibility was good. Distal divisions were displayed in 34% of cases with a higher visibility on the tumor side (p < 0.05). Interrater agreement was high (weighted kappa 0.94 ± 0.01 [95% CI 0.92–0.97]).
Compared to surgery accuracy of MRI in localizing the nerve was 100% for the main trunk, 96% for the temporofacial and 89% for the cervicofacial branches.
Conclusions
Facial nerve MR-neurography represents a reliable tool. DE3D-WE can play an important role in surgical planning of patients with parotid tumors, reducing the risk of nerve injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Upton DC, McNamar JP, Connor NP et al (2007) Parotidectomy: Ten-year review of 237 cases at a single institution. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:788–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2006.11.037
Gao M, Hao Y, Huang MX et al (2017) Salivary gland tumours in a northern Chinese population: a 50-year retrospective study of 7190 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2016.09.021
Skálová A, Hyrcza MD, Leivo I (2022) Update from the 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumors: Salivary Glands. Head Neck Pathol 16:40–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-022-01420-1
Venkatesh S, Srinivas T, Hariprasad S (2019) Parotid gland tumors: 2-year prospective clinicopathological study. Ann Maxillofac Surg 9:103–109. https://doi.org/10.4103/ams.ams_179_18
Zheng Y, mei, Li J, Liu S, et al (2021) MRI-Based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of benign and malignant lesions of the parotid gland. Eur Radiol 31:4042–4052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07483-4
Xu Z, Chen M, Zheng S et al (2022) Differential diagnosis of parotid gland tumours: Application of SWI combined with DWI and DCE-MRI. Eur J Radiol 146:110094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.110094
Yabuuchi H, Kamitani T, Sagiyama K et al (2020) Characterization of parotid gland tumors: added value of permeability MR imaging to DWI and DCE-MRI. Eur Radiol 30:6402–6412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07004-3
Huang N, Chen Y, She D et al (2022) Diffusion kurtosis imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for the differentiation of parotid gland tumors. Eur Radiol 32:2748–2759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08312-y
Guiban O, Rubini A, Fresilli D et al (2021) Preoperative Multiparametric Ultrasound and Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology evaluation of parotid gland tumors: which is the best technique? Med Ultrason 23:402–409. https://doi.org/10.11152/mu-3068
Yabuuchi H, Matsuo Y, Kamitani T et al (2008) Parotid gland tumors: Can addition of diffusion-weighted MR imaging to dynamic contrast- Enhanced MR imaging improve diagnostic accuracyin characterization? Radiology 249:909–916. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2493072045
Yabuuchi H, Fukuya T, Tajima T et al (2003) Salivary gland tumors: Diagnostic value of gadolinium-enhanced dynamic MR imaging with histopathologic correlation. Radiology 226:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2262011486
Gökçe E (2020) Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Parotid Gland Tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 52:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27061
Coudert H, Mirafzal S, Dissard A et al (2021) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of parotid tumors: A systematic review. Diagn Interv Imaging 102:121–130
Borumandi F, George KS, Cascarini L (2012) Parotid surgery for benign tumours. Oral Maxillofac Surg 16:285–290
Deschler DG, Eisele DW (2016) Surgery for Primary Malignant Parotid Neoplasms. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 78:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1159/000442128
Guntinas-Lichius O, Gabriel B, Klussmann JP (2006) Risk of facial palsy and severe Frey’s syndrome after conservative parotidectomy for benign disease: Analysis of 610 operations. Acta Otolaryngol 126:1104–1109. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480600672618
Salih AM, Baba HO, Saeed YA et al (2022) Pattern of facial nerve palsy during parotidectomy: a single-center experience. J Int Med Res 50(7). https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605221108930
Tawfik EA (2015) Sonographic characteristics of the facial nerve in healthy volunteers. Muscle Nerve 52:767–771. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.24627
Lee MK, Choi Y, Jang J et al (2021) Identification of the intraparotid facial nerve on MRI: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 31:629–639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07222-9
Qin Y, Zhang J, Li P, Wang Y (2011) 3D double-echo steady-state with water excitation MR imaging of the intraparotid facial nerve at 1.5T: A pilot study. Am J Neuroradiol 32:1167–1172. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2480
Chu J, Zhou Z, Hong G et al (2013) High-resolution MRI of the intraparotid facial nerve based on a microsurface coil and a 3d reversed fast imaging with steady-state precession DWI sequence at 3T. Am J Neuroradiol 34:1643–1648. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3472
Zhao Y, Yang B (2018) Value of visualization of the intraparotid facial nerve and parotid duct using a micro surface coil and three-dimensional reversed fast imaging with steady-state precession and diffusion-weighted imaging sequence. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 29:E754–E757. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000004704
Guenette JP, Ben-Shlomo N, Jayender J et al (2019) MR imaging of the extracranial facial nerve with the CISS sequence. Am J Neuroradiol 40:1954–1959. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A6261
van der Cruyssen F, Croonenborghs TM, Hermans R et al (2021) 3D cranial nerve imaging, a novel MR neurography technique using black-blood STIR TSE with a pseudo steady-state sweep and motion-sensitized driven equilibrium pulse for the visualization of the extraforaminal cranial nerve branches. Am J Neuroradiol 42:578–580. https://doi.org/10.3174/AJNR.A6904
Tsang JCH, Yip WH, Lau CSL et al (2009) Visualization of normal intra-parotid facial nerve on MR: BTFE or GRASS? Clin Radiol 64:1115–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2009.03.012
Takahashi N, Okamoto K, Ohkubo M, Kawana M (2005) High-resolution magnetic resonance of the extracranial facial nerve and parotid duct: Demonstration of the branches of the intraparotid facial nerve and its relation to parotid tumours by MRI with a surface coil. Clin Radiol 60:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2004.06.018
Ishibashi M, Fujii S, Kawamoto K et al (2010) The ability to identify the intraparotid facial nerve for locating parotid gland lesions in comparison to other indirect landmark methods: Evaluation by 3.0 T MR imaging with surface coils. Neuroradiology 52:1037–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0718-1
Naganawa S, Ishihara S, Satake H et al (2010) Simultaneous Three-dimensional Visualization of the Intra-parotid Facial Nerve and Parotid Duct using a Three-dimensional Reversed FISP Sequence with Diffusion Weighting. Magn Reson Med Sci 9(3):153–158. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.9.153
Li C, Li Y, Zhang D et al (2012) 3D-FIESTA MRI at 3 T demonstrating branches of the intraparotid facial nerve, parotid ducts and relation with benign parotid tumours. Clin Radiol 67:1078–1082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2012.03.014
Attyé A, Karkas A, Troprès I et al (2016) Parotid gland tumours: MR tractography to assess contact with the facial nerve. Eur Radiol 26:2233–2241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-4049-9
Kim Y, Jeong H-S, Kim H-J et al (2021) Three-dimensional double-echo steady-state with water excitation magnetic resonance imaging to localize the intraparotid facial nerve in patients with deep-seated parotid tumors. Neuroradiology 63:731–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02673-3/Published
Kwon D, Lee C, Chae YS et al (2022) Clinical validation of the 3-dimensional double-echo steady-state with water excitation sequence of MR neurography for preoperative facial and lingual nerve identification. Imaging Sci Dent 52:259–266. https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.20220035
Fujii H, Fujita A, Kanazawa H et al (2019) Localization of parotid gland tumors in relation to the intraparotid facial nerve on 3D double-echo steady-state with water excitation sequence. Am J Neuroradiol 40:1037–1042. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A6078
Thierry A, Barbe C, Labrousse M et al (2023) Intra-parotid facial nerve path by MRI tractography: radio-clinical comparison in parotid tumors. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08301-5
Saadya A, Chegini S, Morley S, McGurk M (2023) Augmented reality presentation of the extracranial facial nerve: an innovation in parotid surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:428–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2023.05.007
De Ru JA, Bleys RLAW, Van Benthem PPG, Hordijk GJ (2001) Preoperative determination of the location of parotid gland tumors by analysis of the position of the facial nerve. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:525–528. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2001.22682
De Ru JA, Van Benthem PPG, Hordijk GJ (2002) The location of parotid gland tumors in relation to the facial nerve on magnetic resonance images and computed tomography scans. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:992–994. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2002.34402
Knuesel PR, A Pfirrmann CW, Noetzli HP et al (2004) MR Arthrography of the Hip: Diagnostic Performance of a Dedicated Water-Excitation 3D Double-Echo Steady-State Sequence to Detect Cartilage Lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183(6):1729–1735. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.183.6.01831729
Eckstein F, Hudelmaier M, Wirth W et al (2006) Double echo steady state magnetic resonance imaging of knee articular cartilage at 3 Tesla: A pilot study for the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 65:433–441. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2005.039370
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no conflicts of interest and no competing interests. The authors declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gaudino, C., Cassoni, A., Pisciotti, M.L. et al. MR-Neurography of the facial nerve in parotid tumors: intra-parotid nerve visualization and surgical correlation. Neuroradiology (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-024-03372-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-024-03372-5