Abstract
Purpose
The Centiloid project helps calibrate the quantitative amyloid-β (Aβ) load into a unified Centiloid (CL) scale that allows data comparison across multi-site. How the smaller regional amyloid converted into CL has not been attempted. We first aimed to express regional Aβ deposition in CL using [18F]Flutemetamol and evaluate regional Aβ deposition in CL with that in standardized uptake value ratio (SUVr). Second, we aimed to determine the presence or absence of focal Aβ deposition by measuring regional CL in equivocal cases showing negative global CL.
Methods
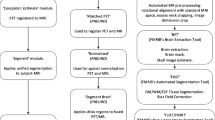
Following the Centiloid project pipeline, Level-1 replication, Level-2 calibration, and quality control were completed to generate corresponding Centiloid conversion equations to convert SUVr into Centiloid at regional levels. In equivocal cases, the regional CL was compared with visual inspection to evaluate regional Aβ positivity.
Results
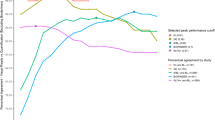
14 out of 16 regional conversions from [18F]Flutemetamol SUVr to Centiloid successfully passed the quality control, showing good reliability and relative variance, especially precuneus/posterior cingulate and prefrontal regions with good stability for Centiloid scaling. The absence of focal Aβ deposition could be detected by measuring regional CL, showing a high agreement rate with visual inspection. The regional Aβ positivity in the bilateral anterior cingulate cortex was most prevalent in equivocal cases.
Conclusion
The expression of regional brain Aβ deposition in CL with [18F]Flutemetamol has been attempted in this study. Equivocal cases had focal Aβ deposition that can be detected by measuring regional CL.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
04 June 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-024-03394-z
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid-β
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s Disease
- APOE e4:
-
Apolipoprotein E allele 4
- AIBL:
-
Australian Imaging Biomarkers and Lifestyle Study
- AUC:
-
Area under ROC
- CL:
-
Centiloid
- CTX:
-
Global cortical target
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- FWHM:
-
Full width half maximum
- GAAIN:
-
Global Alzheimer’s Association Interactive Network
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- OHC:
-
Older healthy control
- SPM 8:
-
Statistical Parametric Mapping 8
- SUV:
-
Standardized uptake value
- SUVr:
-
Standardized uptake value ratio
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- VOI:
-
Volume of interest
- WC:
-
Whole cerebellum
References
Jack C, Knopman D, Jagust W, Shaw L, Aisen P, Weiner M, Petersen R, Trojanowski J (2010) Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer’s pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol 9:119–128
Chételat G (2018) Multimodal neuroimaging in alzheimer’s disease: early diagnosis, physiopathological mechanisms, and impact of lifestyle. J Alzheimers Dis 64:S199-s211
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the national institute on aging-alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7:263–269
Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, Iwatsubo T, Jack CR Jr, Kaye J, Montine TJ, Park DC, Reiman EM, Rowe CC, Siemers E, Stern Y, Yaffe K, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Morrison-Bogorad M, Wagster MV, Phelps CH (2011) Toward defining the preclinical stages of alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the national institute on aging-alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7:280–292
Dubois B, Hampel H, Feldman HH, Scheltens P, Aisen P, Andrieu S, Bakardjian H, Benali H, Bertram L, Blennow K, Broich K, Cavedo E, Crutch S, Dartigues JF, Duyckaerts C, Epelbaum S, Frisoni GB, Gauthier S, Genthon R, Gouw AA, Habert MO, Holtzman DM, Kivipelto M, Lista S, Molinuevo JL, O’Bryant SE, Rabinovici GD, Rowe C, Salloway S, Schneider LS, Sperling R, Teichmann M, Carrillo MC, Cummings J, Jack CR Jr (2016) Preclinical alzheimer’s disease: definition, natural history, and diagnostic criteria. Alzheimers Dement 12:292–323
Palmqvist S, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Vestberg S, Andreasson U, Brooks DJ, Owenius R, Hägerström D, Wollmer P, Minthon L, Hansson O (2014) Accuracy of brain amyloid detection in clinical practice using cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid 42: a cross-validation study against amyloid positron emission tomography. JAMA Neurol 71:1282–1289
Ozlen H, Pichet Binette A, Köbe T, Meyer PF, Gonneaud J, St-Onge F, Provost K, Soucy JP, Rosa-Neto P, Breitner J, Poirier J, Villeneuve S (2022) Spatial extent of amyloid-β levels and associations with tau-pet and cognition. JAMA Neurol 79:1025–1035
Ishii K, Yamada T, Hanaoka K, Kaida H, Miyazaki K, Ueda M, Hanada K, Saigoh K, Sauerbeck J, Rominger A, Bartenstein P, Kimura Y (2020) Regional gray matter-dedicated SUVR with 3D-MRI detects positive amyloid deposits in equivocal amyloid PET images. Ann Nucl Med 34:856–863
Klunk WE, Koeppe RA, Price JC, Benzinger TL, Devous MD, Jagust WJ, Johnson KA, Mathis CA, Minhas D, Pontecorvo MJ, Rowe CC, Skovronsky DM, Mintun MA (2015) The centiloid project: standardizing quantitative amyloid plaque estimation by PET. Alzheimers Dement 11:1–15.e11–14.
Battle MR, Pillay LC, Lowe VJ, Knopman D, Kemp B, Rowe CC, Doré V, Villemagne VL, Buckley CJ (2018) Centiloid scaling for quantification of brain amyloid with [18F]flutemetamol using multiple processing methods. EJNMMI Res 8:107
Navitsky M, Joshi AD, Kennedy I, Klunk WE, Rowe CC, Wong DF, Pontecorvo MJ, Mintun MA, Devous MD Sr (2018) Standardization of amyloid quantitation with florbetapir standardized uptake value ratios to the Centiloid scale. Alzheimers Dement 14:1565–1571
Rowe CC, Jones G, Doré V, Pejoska S, Margison L, Mulligan RS, Chan JG, Young K, Villemagne VL (2016) Standardized Expression of 18F-NAV4694 and 11C-PiB β-Amyloid PET Results with the Centiloid Scale. J Nucl Med 57:1233–1237
Rowe CC, Doré V, Jones G, Baxendale D, Mulligan RS, Bullich S, Stephens AW, De Santi S, Masters CL, Dinkelborg L, Villemagne VL (2017) (18)F-Florbetaben PET beta-amyloid binding expressed in Centiloids. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44:2053–2059
Amadoru S, Doré V, McLean CA, Hinton F, Shepherd CE, Halliday GM, Leyton CE, Yates PA, Hodges JR, Masters CL, Villemagne VL, Rowe CC (2020) Comparison of amyloid PET measured in Centiloid units with neuropathological findings in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 12:22
Su Y, Flores S, Hornbeck RC, Speidel B, Vlassenko AG, Gordon BA, Koeppe RA, Klunk WE, Xiong C, Morris JC, Benzinger TLS (2018) Utilizing the centiloid scale in cross-sectional and longitudinal PiB PET studies. Neuroimage Clin 19:406–416
Hanseeuw BJ, Malotaux V, Dricot L, Quenon L, Sznajer Y, Cerman J, Woodard JL, Buckley C, Farrar G, Ivanoiu A, Lhommel R (2021) Defining a centiloid scale threshold predicting long-term progression to dementia in patients attending the memory clinic: an [18 F] flutemetamol amyloid PET study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48:302–310
Nelissen N, Van Laere K, Thurfjell L, Owenius R, Vandenbulcke M, Koole M, Bormans G, Brooks D, Vandenberghe R (2009) Phase 1 study of the pittsburgh compound b derivative ^sup 18^F-flutemetamol in healthy volunteers and patients with probable alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med 50:1251–1259
Vandenberghe R, Van Laere K, Ivanoiu A, Salmon E, Bastin C, Triau E, Hasselbalch S, Law I, Andersen A, Korner A, Minthon L, Garraux G, Nelissen N, Bormans G, Buckley C, Owenius R, Thurfjell L, Farrar G, Brooks DJ (2010) 18F-flutemetamol amyloid imaging in alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: a phase 2 trial. Ann Neurol 68:319–329
Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Kraft RA, Burdette JH (2003) An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. Neuroimage 19:1233–1239
Palmqvist S, Schöll M, Strandberg O, Mattsson N, Stomrud E, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Landau S, Jagust W, Hansson O (2017) Earliest accumulation of β-amyloid occurs within the default-mode network and concurrently affects brain connectivity. Nat Commun 8:1214
Grothe JM, Barthel JH, Sepulcre JJ, Dyrba JM, Sabri JO, Teipel JS (2017) In vivo staging of regional amyloid deposition. Neurology 89:2031–2038
Song X-W, Dong Z-Y, Long X-Y, Li S-F, Zuo X-N, Zhu C-Z, He Y, Yan C-G, Zang Y-F (2011) REST: A Toolkit for Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data Processing. PLoS ONE 6:e25031
Flutemetamol F 18 Injection, GE Healthcare. https://www.gehealthcare.co.uk/-/jssmedia/widen/gehealthcarecom/migrated/er-clinical-product-info-vizamyl-203-8c17d992a0aa9aadb2e446d7f5580a8b_43-1067c_vizamyl_pdf.pdf?rev=f0b80c4c7a0440ebaf7fb2f92883cfbb&hash=6C5B978AB8A1A17937F3FB8A3733687A,
Tudorascu DL, Minhas DS, Lao PJ, Betthauser TJ, Yu Z, Laymon CM, Lopresti BJ, Mathis CA, Klunk WE, Handen BL, Christian BT, Cohen AD (2018) The use of Centiloids for applying [11C]PiB classification cutoffs across region-of-interest delineation methods. Alzheimers Dement 10:332–339
Jack CR Jr, Bennett DA, Blennow K, Carrillo MC, Feldman HH, Frisoni GB, Hampel H, Jagust WJ, Johnson KA, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Scheltens P, Sperling RA, Dubois B (2016) A/T/N: An unbiased descriptive classification scheme for alzheimer disease biomarkers. Neurology 87:539–547
Cho H, Choi JY, Hwang MS, Kim YJ, Lee HM, Lee HS, Lee JH, Ryu YH, Lee MS, Lyoo CH (2016) In vivo cortical spreading pattern of tau and amyloid in the alzheimer disease spectrum. Ann Neurol 80:247–258
Thal DR, Rüb U, Orantes M, Braak H (2002) Phases of A beta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 58:1791–1800
Wang P, Chen K, Yao L, Hu B, Wu X, Zhang J, Ye Q, Guo X (2016) Multimodal classification of mild cognitive impairment based on partial least squares. J Alzheimer’s Dis: JAD 54:359–371
Bao YW, Chau ACM, Chiu PK, Shea YF, Kwan JSK, Chan FHW, Mak HK (2021) Heterogeneity of amyloid binding in cognitively impaired patients consecutively recruited from a memory clinic: evaluating the utility of quantitative 18F-Flutemetamol PET-CT in discrimination of mild cognitive impairment from alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. J Alzheimers Dis 79:819–832
Royse SK, Minhas DS, Lopresti BJ, Murphy A, Ward T, Koeppe RA, Bullich S, DeSanti S, Jagust WJ, Landau SM (2021) Validation of amyloid PET positivity thresholds in centiloids: a multisite PET study approach. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 13:99–99
Doré V, Bullich S, Rowe CC, Bourgeat P, Konate S, Sabri O, Stephens AW, Barthel H, Fripp J, Masters CL, Dinkelborg L, Salvado O, Villemagne VL, De Santi S (2019) Comparison of (18)F-florbetaben quantification results using the standard Centiloid, MR-based, and MR-less CapAIBL(®) approaches: validation against histopathology. Alzheimers Dement 15:807–816
La Joie R, Ayakta N, Seeley WW, Borys E, Boxer AL, DeCarli C, Doré V, Grinberg LT, Huang E, Hwang JH, Ikonomovic MD, Jack C Jr, Jagust WJ, Jin LW, Klunk WE, Kofler J, Lesman-Segev OH, Lockhart SN, Lowe VJ, Masters CL, Mathis CA, McLean CL, Miller BL, Mungas D, O’Neil JP, Olichney JM, Parisi JE, Petersen RC, Rosen HJ, Rowe CC, Spina S, Vemuri P, Villemagne VL, Murray ME, Rabinovici GD (2019) Multisite study of the relationships between antemortem [(11)C]PIB-PET Centiloid values and postmortem measures of Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. Alzheimers Dement 15:205–216
Rodrigue KM, Kennedy KM, Devous MD Sr, Rieck JR, Hebrank AC, Diaz-Arrastia R, Mathews D, Park DC (2012) β-Amyloid burden in healthy aging: regional distribution and cognitive consequences. Neurology 78:387–395
Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Kelly JF, Aggarwal NT, Shah RC, Wilson RS (2006) Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology 66:1837–1844
Jansen WJ, Ossenkoppele R, Knol DL, Tijms BM, Scheltens P, Verhey FRJ, Visser PJ, Aalten P, Aarsland D, Alcolea D, Alexander M, Almdahl IS, Arnold SE, Baldeiras I, Barthel H, van Berckel BNM, Bibeau K, Blennow K, Brooks DJ, van Buchem MA, Camus V, Cavedo E, Chen K, Chetelat G, Cohen AD, Drzezga A, Engelborghs S, Fagan AM, Fladby T, Fleisher AS, van der Flier WM, Ford L, Förster S, Fortea J, Foskett N, Frederiksen KS, Freund-Levi Y, Frisoni GB, Froelich L, Gabryelewicz T, Gill KD, Gkatzima O, Gómez-Tortosa E, Gordon MF, Grimmer T, Hampel H, Hausner L, Hellwig S, Herukka S-K, Hildebrandt H, Ishihara L, Ivanoiu A, Jagust WJ, Johannsen P, Kandimalla R, Kapaki E, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A, Klunk WE, Köhler S, Koglin N, Kornhuber J, Kramberger MG, Van Laere K, Landau SM, Lee DY, de Leon M, Lisetti V, Lleó A, Madsen K, Maier W, Marcusson J, Mattsson N, de Mendonça A, Meulenbroek O, Meyer PT, Mintun MA, Mok V, Molinuevo JL, Møllergård HM, Morris JC, Mroczko B, Van der Mussele S, Na DL, Newberg A, Nordberg A, Nordlund A, Novak GP, Paraskevas GP, Parnetti L, Perera G, Peters O, Popp J, Prabhakar S, Rabinovici GD, Ramakers IHGB, Rami L, Resende de Oliveira C, Rinne JO, Rodrigue KM, Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Roe CM, Rot U, Rowe CC, Rüther E, Sabri O, Sanchez-Juan P, Santana I, Sarazin M, Schröder J, Schütte C, Seo SW, Soetewey F, Soininen H, Spiru L, Struyfs H, Teunissen CE, Tsolaki M, Vandenberghe R, Verbeek MM, Villemagne VL, Vos SJB, van Waalwijk van Doorn LJC, Waldemar G, Wallin A, Wallin Å, Wiltfang J, Wolk DA, Zboch M, Zetterberg H (2015) Prevalence of cerebral amyloid pathology in persons without dementia: a meta-analysis. JAMA 313:1924–1938
Albrecht MA, Szoeke C, Maruff P, Savage G, Lautenschlager NT, Ellis KA, Taddei K, Martins R, Masters CL, Ames D, Foster JK (2015) Longitudinal cognitive decline in the AIBL cohort: the role of APOE ε4 status. Neuropsychologia 75:411–419
Villeneuve S, Rabinovici GD, Cohn-Sheehy BI, Madison C, Ayakta N, Ghosh PM, La Joie R, Arthur-Bentil SK, Vogel JW, Marks SM, Lehmann M, Rosen HJ, Reed B, Olichney J, Boxer AL, Miller BL, Borys E, Jin LW, Huang EJ, Grinberg LT, DeCarli C, Seeley WW, Jagust W (2015) Existing Pittsburgh Compound-B positron emission tomography thresholds are too high: statistical and pathological evaluation. Brain 138:2020–2033
Mesulam MM, Rogalski EJ, Wieneke C, Hurley RS, Geula C, Bigio EH, Thompson CK, Weintraub S (2014) Primary progressive aphasia and the evolving neurology of the language network. Nat Rev Neurol 10:554–569
Acknowledgements
The authors thanked Dr. Henry KF Mak, Clinical Associate Professor, School of Clinical Medicine, the University of Hong Kong for supporting this work by sharing local data. The contribution (including local data collection, data validation, and suggestions for this work) of Prof. Mak is invaluable and should be included as the senior author.
Apology note
We would like to sincerely apologize to our senior author Prof. Henry KF Mak. Due to our negligence, the information of the senior author was not included in the author list during submission. The alteration of the author list is not allowed after online publication. Therefore, we would like to express our apology under this section.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the special funds for the Science and Technology Programs of Huai'an (HABL202235) and the Science and Technology Development Programs of Nanjing Medical University (NMUB20220204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approval of the research protocols had official authorization. The protocol of the AIBL study was approved by the institutional human research ethics committees of Austin Health, St Vincent’s Health, Hollywood Private Hospital and Edith Cowan University. The GAAIN cohort used in the current work involves several datasets collected from different studies, which were approved by Washington University's Human Research Protection Office and the Ethical Committees of the participating centers or the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Medical Center Institutional Review Boards. The study logistics of our local memory clinical complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and ethical approval of the research protocol had been obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants or, if participants are under 16, from a parent and/or legal guardian.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The original article requires updates to the Acknowledgement and Funding sections. Additionally, an apology note has been added.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, YW., Wang, ZJ., Guo, LL. et al. Expression of regional brain amyloid-β deposition with [18F]Flutemetamol in Centiloid scale -a multi-site study. Neuroradiology (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-024-03364-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-024-03364-5