Abstract
Purpose
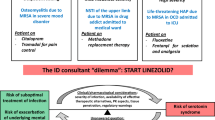
This systematic review aims to evaluate the existing evidence associating linezolid to serotonin toxicity when used as monotherapy or when co-administered with other serotonergic agents.
Methods
A systematic literature search using PubMed (till March 2023), IDWeek meetings (2003–2023), the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Annual Meetings (2001–2023), and the American College of Clinical Pharmacy (1999–2023) identified studies and abstracts related to linezolid and serotonin toxicity.
Results
A total of 84 studies were included. The data collected in retrospective/observational studies compared the incidence of serotonin toxicity with linezolid monotherapy at 0.0050% and linezolid combination therapy at 0.0134%. All cases which discontinued linezolid and serotonergic agent/s at signs and symptoms of toxicity found symptom resolution; 75% of cases reported serotonin toxicity resolution within 24–48 h after discontinuation.
Conclusion
Linezolid therapy when optimal should not be deferred due to the risk of serotonin syndrome. The data collected reveals a low prevalence of serotonin toxicity in both linezolid monotherapy and linezolid concurrent with other serotonergic agents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Diekema DJ, Jones RN (2001) Oxazolidinone antibiotics. Lancet 358:1975–1982. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06964-1
Hashemian SMR, Farhadi T, Ganjparvar M (2018) Linezolid: a review of its properties, function, and use in critical care. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:1759–1767. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S164515
Vinh DC, Rubinstein E (2009) Linezolid: a review of safety and tolerability. J Infect 59(Suppl 1):S59-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0163-4453(09)60009-8
ZYVOX®Highlights (Linezolid) | Pfizer Medical Information - US. Available online: https://www.pfizermedicalinformation.com/en-us/zyvox/highlights. Retrieved 1 September 2022
Rubinstein E, Isturiz R, Standiford HC, Smith LG, Oliphant TH, Cammarata S, Hafkin B, Le V, Remington J (2003) Worldwide assessment of linezolid’s clinical safety and tolerability: comparator-controlled phase III studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:1824–1831. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.47.6.1824-1831.2003
Butterfield JM, Lawrence KR, Reisman A, Huang DB, Thompson CA, Lodise TP (2012) Comparison of serotonin toxicity with concomitant use of either linezolid or comparators and serotonergic agents: an analysis of phase III and IV randomized clinical trial data. J Antimicrob Chemother 67:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkr467
Discotto LF, Pucci MJ, Lawrence LE, Barrett JF (1998) 38th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC), September 24–27, 1998, San Diego, CA, USA. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 7:2061–2077.https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.7.12.2061
Zhanel GG, Shroeder C, Vercaigne L, Gin AS, Embil J, Hoban DJ (2001) A critical review of oxazolidinones: an alternative or replacement for glycopeptides and streptogramins? Can J Infect Dis 12:379–390. https://doi.org/10.1155/2001/260651
Fung HB, Kirschenbaum HL, Ojofeitimi BO (2001) Linezolid: an oxazolidinone antimicrobial agent. Clin Ther 23:356–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-2918(01)80043-6
Volpi-Abadie J, Kaye AM, Kaye AD (2013) Serotonin syndrome. Ochsner J 13:533–540
Dunkley EJC, Isbister GK, Sibbritt D, Dawson AH, Whyte IM (2003) The hunter serotonin toxicity criteria: simple and accurate diagnostic decision rules for serotonin toxicity. QJM 96:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcg109
Research C (2019) for D.E. and FDA Drug Safety Communication: serious CNS reactions possible when linezolid (Zyvox) is given to patients taking certain psychiatric medications. FDA
Woytowish MR, Maynor LM (2013) Clinical relevance of linezolid-associated serotonin toxicity. Ann Pharmacother 47:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1R386
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA (2015) PRISMA-P group preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 4:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Tokuyama R, Takahashi Y, Tomita Y, Suzuki T, Yoshida T, Iwasaki N, Kado N, Okezaki E, Nagata O (2001) Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies on oxazolidinone antibacterial agents. 1. Conversion of 5-Substituent on Oxazolidinone. Chem Pharm Bull 49:347–352. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.49.347
Shi L, Yang Y, Li Z-L, Zhu Z-W, Liu C-H, Zhu H-L (2010) Design of novel nicotinamides as potent and selective monoamine oxidase a inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 18:1659–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2009.12.065
Kumar B, Sheetal S, Mantha AK, Kumar V (2016) Recent developments on the structure–activity relationship studies of MAO inhibitors and their role in different neurological disorders. RSC Adv 6:42660–42683. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA00302H
Mai A, Artico M, Valente S, Sbardella G, Turini P, Befani O, Vedova L, Agostinelli E (2005) 3-(1H-pyrrol-2-Yl)-2-oxazolidinones as novel monoamine oxidase type A inhibitors. MC 1:117–124. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573406053175247
Sutton J, Stroup J, Som M (2016) Linezolid-induced serotonin toxicity in a patient not taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors or serotonin receptor antagonists. Bayl Univ Med Cent Proc 29:214–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2016.11929423
Lv X, Alder J, Li L, O’Riordan W, Rybak MJ, Ye H, Zhang R, Zhang Z, Zhu X, Wilcox MH (2019) Efficacy and safety of tedizolid phosphate versus linezolid in a randomized phase 3 trial in patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63:e02252-e2318. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02252-18
O’Riordan W, Green S, Overcash JS, Puljiz I, Metallidis S, Gardovskis J, Garrity-Ryan L, Das AF, Tzanis E, Eckburg PB et al (2019) Omadacycline for acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections. N Engl J Med 380:528–538. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1800170
Harbarth S, von Dach E, Pagani L, Macedo-Vinas M, Huttner B, Olearo F, Emonet S, Uckay I (2015) Randomized non-inferiority trial to compare trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole plus rifampicin versus linezolid for the treatment of MRSA infection. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:264–272. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dku352
Moran GJ, Fang E, Corey GR, Das AF, De Anda C, Prokocimer P (2014) Tedizolid for 6 days versus linezolid for 10 days for acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections (ESTABLISH-2): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis 14:696–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70737-6
Prokocimer P, De Anda C, Fang E, Mehra P, Das A (2013) Tedizolid phosphate vs linezolid for treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections: the ESTABLISH-1 randomized trial. JAMA 309:559. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.241
O’Riordan W, Cardenas C, Shin E, Sirbu A, Garrity-Ryan L, Das AF, Eckburg PB, Manley A, Steenbergen JN, Tzanis E et al (2019) Once-daily oral omadacycline versus twice-daily oral linezolid for acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (OASIS-2): a phase 3, double-blind, multicentre, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis 19:1080–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30275-0
Lee J-K, Lee JY, Kim DK, Yoon HI, Jeong I, Heo EY, Park YS, Jo YS, Lee JH, Park SS et al (2019) Substitution of ethambutol with linezolid during the intensive phase of treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis: a prospective, multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis 19:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30480-8
Kingsley J, Mehra P, Lawrence LE, Henry E, Duffy E, Cammarata SK, Pullman J (2016) A Randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study to evaluate subjective and objective outcomes in patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections treated with delafloxacin, linezolid or vancomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother 71:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkv411
Boucher HW, Wilcox M, Talbot GH, Puttagunta S, Das AF, Dunne MW (2014) Once-weekly dalbavancin versus daily conventional therapy for skin infection. N Engl J Med 370:2169–2179. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1310480
Awad SS, Rodriguez AH, Chuang Y-C, Marjanek Z, Pareigis AJ, Reis G, Scheeren TWL, Sanchez AS, Zhou X, Saulay M et al (2014) A phase 3 randomized double-blind comparison of ceftobiprole medocaril versus ceftazidime plus linezolid for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis 59:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciu219
Noel GJ, Draper MP, Hait H, Tanaka SK, Arbeit RD (2012) A randomized, evaluator-blind, phase 2 study comparing the safety and efficacy of omadacycline to those of linezolid for treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:5650–5654. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00948-12
Wunderink RG, Niederman MS, Kollef MH, Shorr AF, Kunkel MJ, Baruch A, McGee WT, Reisman A, Chastre J (2012) Linezolid in methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus nosocomial pneumonia: a randomized, controlled study. Clin Infect Dis 54:621–629. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir895
Covington P, Davenport JM, Andrae D, O’Riordan W, Liverman L, McIntyre G, Almenoff J (2011) Randomized, double-blind, phase ii, multicenter study evaluating the safety/tolerability and efficacy of JNJ-Q2, a novel fluoroquinolone, compared with linezolid for treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:5790–5797. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.05044-11
Craft JC, Moriarty SR, Clark K, Scott D, Degenhardt TP, Still JG, Corey GR, Das A, Fernandes P (2011) A randomized, double-blind phase 2 study comparing the efficacy and safety of an oral fusidic acid loading-dose regimen to oral linezolid for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections. Clin Infect Dis 52:S520–S526. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir167
Karkow DC, Kauer JF, Ernst EJ (2017) Incidence of serotonin syndrome with combined use of linezolid and serotonin reuptake inhibitors compared with linezolid monotherapy. J Clin Psychopharmacol 37:518–523. https://doi.org/10.1097/JCP.0000000000000751
Lodise TP, Patel N, Rivera A, Tristani L, Lazariu V, Vandewall H, McNutt LA (2013) Comparative evaluation of serotonin toxicity among veterans affairs patients receiving linezolid and vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:5901–5911. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00921-13
Traver EC, Heil EL, Schmalzle SA (2022) A cross-sectional analysis of linezolid in combination with methadone or buprenorphine as a cause of serotonin toxicity. Open Forum Infect Dis 9:ofac331. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofac331
Bernard L, Stern R, Lew D, Hoffmeyer P (2003) Serotonin syndrome after concomitant treatment with linezolid and citalopram. Clin Infect Dis 36:1197–1197. https://doi.org/10.1086/374558
Hachem RY, Hicks K, Huen A, Raad I (2003) Myelosuppression and serotonin syndrome associated with concurrent use of linezolid and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in bone marrow transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 37:e8-11. https://doi.org/10.1086/375689
Frank C (2008) Recognition and treatment of serotonin syndrome. Can Fam Physician 54:988–992
Mckinnell JA, Eells SJ, Injean P, Whang D, Humphries R, Gregson A (2019) Linezolid versus daptomycin in the treatment of vancomycin-resistant enterococcal bloodstream infection (VRE-BSI) at a transplant center. Open Forum Infect Dis 2016:3. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofw172.1567
Li Y, Xu W (2018) Efficacy and safety of linezolid compared with other treatments for skin and soft tissue infections: a meta-analysis. Biosci Rep 38
Clarke C, Finnegan M, O’Dwyer A, Mc Donald C, O’Connell B, Cooney J (2014) Co-prescribing of linezolid and serotonergic agents in a general hospital setting. Ir J Psychol Med 31(3):191–193. https://doi.org/10.1017/ipm.2014.33
Radunz S, Juntermanns B, Kaiser GM, Treckmann J, Mathe Z, Paul A, Saner FH (2011) Efficacy and safety of linezolid in liver transplant patients. Transpl Infect Dis 13:353–358. All rights reserved
Lorenz RA, Vandenberg AM, Canepa EA (2008) Serotonergic Antidepressants and Linezolid: A Retrospective Chart Review and Presentation of Cases. Int J Psychiatry Med 38(1):81–90. https://doi.org/10.2190/PM.38.1.h
Taylor JJ, Wilson JW, Estes LL (2006) Linezolid and serotonergic drug interactions: a retrospective survey. Clin Infect Dis 43(2):180–7. https://doi.org/10.1086/504809
Bishop E, Melvani S, Howden B, Charles PG, Grayson ML (2006) Good clinical outcomes but high rates of adverse reactions during linezolid therapy for serious infections: a proposed protocol for monitoring therapy in complex patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(4):1599–602. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.50.4.1599-1602.2006
Go AC, Golightly LK, Barber GR, Barron MA (2010) Linezolid interaction with serotonin reuptake inhibitors: report of two cases and incidence assessment. 25(1–4):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1515/DMDI.2010.001
Thirot H, Briquet C, Frippiat F, Jacobs F, Holemans X, Henrard S, Tulkens PM, Spinewine A, Van Bambeke F (2021) Clinical Use and Adverse Drug Reactions of Linezolid: A Retrospective Study in Four Belgian Hospital Centers. Antibiotics 10:530. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050530
Acknowledgements
The authors of this review would like to thank Brig Turner for their initial help with study design and abstract screening.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors have made equal and substantial contributions to all of the following: (1) the conception and design of the study, acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data; (2) drafting the article and revising it critically for important intellectual content; and (3) final approval of the version to be submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Due to the nature of the systematic review, no ethical approval was required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
All authors meet the ICMJE authorship criteria
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Elbarbry, F., Moshirian, N. Linezolid-associated serotonin toxicity: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 79, 875–883 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-023-03500-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-023-03500-9