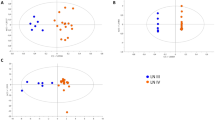
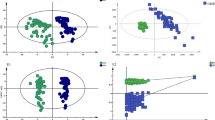
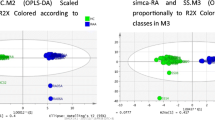
Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease which leads to the formation of immune complex deposits in multiple organs and has heterogeneous clinical manifestations. Currently, exosomes for liquid biopsy have been applied in diagnosis and monitoring of diseases, whereas SLE discrimination based on exosomes at the metabolic level is rarely reported. Herein, we constructed a protocol for metabolomic study of urinary exosomes from SLE patients and healthy controls (HCs) with high efficiency and throughput. Exosomes were first obtained by high-performance liquid size-exclusion chromatography (HPL-SEC), and then metabolic fingerprints of urinary exosomes were extracted by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) with high throughput and high efficency. With the statistical analysis by orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model, SLE patients were efficiently distinguished from HCs, the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver characteristic curve (ROC) was 1.00, and the accuracy of the unsupervised clustering heatmap was 90.32%. In addition, potential biomarkers and related metabolic pathways were analyzed. This method, with the characteristics of high throughput, high efficiency, and high accuracy, will provide the broad prospect of exosome-driven precision medicine and large-scale screening in clinical applications.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andonopoulos AP, Constantopoulos SH, Galanopoulou V, Drosos AA, Acritidis NC, Moutsopoulos HM. Pulmonary function of nonsmoking patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chest. 1988;94(2):312–5.
Basta F, Fasola F, Triantafyllias K, Schwarting A. Systemic lupus erythematosus (sle) therapy: the old and the new. Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(3):433–46.
Almaani S, Meara A, Rovin BH. Update on lupus nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(5):825–35.
Perez-Hernandez J, Cortes R. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of systemic lupus erythematosus. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:613536.
Mok CC, Lau CS. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Pathol. 2003;56(7):481.
Lisnevskaia L, Murphy G, Isenberg D. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2014;384(9957):1878–88.
Ippolito A, Petri M. An update on mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26(5):S72–9.
Drug, Therapeutics B. Systemic lupus erythematosus — an update. Drug Ther Bull. 2011;49(7):81–4.
Zhang B, Zhao M, Lu Q. Extracellular vesicles in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: functions and applications. Front Immunol. 2020;11:575712.
Ponticelli C, Moroni G. Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017;16(3):411–9.
Parikh SV, Almaani S, Brodsky S, Rovin BH. Update on lupus nephritis: core curriculum 2020. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76(2):265–81.
Frodlund M, Reid S, Wetterö J, Dahlström Ö, Sjöwall C, Leonard D. The majority of Swedish systemic lupus erythematosus patients are still affected by irreversible organ impairment: factors related to damage accrual in two regional cohorts. Lupus. 2019;28(10):1261–72.
Bajaj S, Albert L, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Hallett DC, Ritchie S. Serial renal biopsy in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(12):2822–6.
Hsieh YP, Wen YK, Chen ML. The value of early renal biopsy in systemic lupus erythematosus patients presenting with renal involvement. Clin Nephrol. 2012;77(1):18–24.
Kang ES, Ahn SM, Oh JS, Kim H, Yang WS, Kim Y-G, et al. Risk of bleeding-related complications after kidney biopsy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2023;42(3):751–9.
Chen TK, Estrella MM, Fine DM. Predictors of kidney biopsy complication among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2012;21(8):848–54.
van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213–28.
Dieker J, Tel J, Pieterse E, Thielen A, Rother N, Bakker M, et al. Circulating apoptotic microparticles in systemic lupus erythematosus patients drive the activation of dendritic cell subsets and prime neutrophils for netosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(2):462–72.
Yang C, Sun J, Tian Y, Li H, Zhang L, Yang J, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of mscs and mscs-derived extracellular vesicles in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2021;12:714832.
Arima Y, Liu W, Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, Takakura Y. Effects of localization of antigen proteins in antigen-loaded exosomes on efficiency of antigen presentation. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(6):2309–14.
Dong C, Zhou Q, Fu T, Zhao R, Yang J, Kong X, et al. Circulating exosomes derived-miR-146a from systemic lupus erythematosus patients regulates senescence of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019.
Bruschi M, Ravera S, Santucci L, Candiano G, Bartolucci M, Calzia D, et al. The human urinary exosome as a potential metabolic effector cargo. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015;12(4):425–32.
Henderson M, Azorsa D. The genomic and proteomic content of cancer cell-derived exosomes. Front Oncol. 2012;2.
Huang X, Luu LDW, Jia N, Zhu J, Fu J, Xiao F, et al. Multi-platform omics analysis reveals molecular signatures for pathogenesis and activity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2022;13.
Du Y, Chen L, Li X-S, Li X-L, Xu X-D, Tai S-B, et al. Metabolomic identification of exosome-derived biomarkers for schizophrenia: a large multicenter study. Schizophr Bull. 2021;47(3):615–23.
Hadizadeh N, Bagheri D, Shamsara M, Hamblin MR, Farmany A, Xu M, et al. Extracellular vesicles biogenesis, isolation, manipulation and genetic engineering for potential in vitro and in vivo therapeutics: an overview. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10.
Chen H, Huang C, Wu Y, Sun N, Deng C. Exosome metabolic patterns on aptamer-coupled polymorphic carbon for precise detection of early gastric cancer. ACS Nano. 2022;16(8):12952–63.
Yan B, Huang J, Zhang C, Hu X, Gao M, Shi A, et al. Serum metabolomic profiling in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by GC/MS. Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(6):914–22.
Chen J, Deng J, Zhou J, Xie Z-j, Gan J, Wen C-p. Metabonomic study of traditional Chinese herb pair, Qinghao-Biejia in treating systemic lupus erythematosus mice. Chin Pharmacol Bull. 2016;32(5):727–31,32.
Mendoza-Pinto C, Garcia-Carrasco M, Mendez-Martinez S, Munguia-Realpozo P, Etchegaray-Morales I, Diaz-Merino G, et al. Insulin resistance metabolomic profile in non-diabetic women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Gac Med Mex. 2021;157(6):613–7.
Xue J, Liu H, Chen S, Xiong C, Zhan L, Sun J, et al. Mass spectrometry imaging of the in situ drug release from nanocarriers. Sci Adv. 4(10):eaat9039.
Zhao D, Ma C, Gao M, Li Y, Yang B, Li H, et al. Super-assembled sandwich-like Au@MSN@Ag nanomatrices for high-throughput and efficient detection of small biomolecules. Nano Res. 2022;15(3):2722–33.
Sun X, Huang L, Zhang R, Xu W, Huang J, Gurav DD, et al. Metabolic fingerprinting on a plasmonic gold chip for mass spectrometry based in vitro diagnostics. ACS Cent Sci. 2018;4(2):223–9.
Guan S, Yu H, Yan G, Gao M, Sun W, Zhang X. Size-dependent sub-proteome analysis of urinary exosomes. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(18):4141–9.
Guan S, Yu H, Yan G, Gao M, Sun W, Zhang X. Characterization of urinary exosomes purified with size exclusion chromatography and ultracentrifugation. J Proteome Res. 2020;19(6):2217–25.
Zheng H, Guan S, Wang X, Zhao J, Gao M, Zhang X. Deconstruction of heterogeneity of size-dependent exosome subpopulations from human urine by profiling n-glycoproteomics and phosphoproteomics simultaneously. Anal Chem. 2020;92(13):9239–46.
Zhang N, Sun N, Deng C. Rapid isolation and proteome analysis of urinary exosome based on double interactions of Fe3O4@TiO2-DNA aptamer. Talanta. 2021;221:121571.
Rossetti FF, Bally M, Michel R, Textor M, Reviakine I. Interactions between titanium dioxide and phosphatidyl serine-containing liposomes: formation and patterning of supported phospholipid bilayers on the surface of a medically relevant material. Langmuir. 2005;21(14):6443–50.
Gao F, Jiao F, Xia C, Zhao Y, Ying W, Xie Y, et al. A novel strategy for facile serum exosome isolation based on specific interactions between phospholipid bilayers and TiO2. Chem Sci. 2019;10(6):1579–88.
Chen H, Zhang N, Wu Y, Yang C, Xie Q, Deng C, et al. Investigation of urinary exosome metabolic patterns in membranous nephropathy by titania‐assisted intact exosome mass spectrometry. Small Science. 2022;2(5).
Zhu Y, Gasilova N, Jovic M, Qiao L, Liu B, Lovey LT, et al. Detection of antimicrobial resistance-associated proteins by titanium dioxide-facilitated intact bacteria mass spectrometry. Chem Sci. 2018;9(8):2212–21.
Yin X, Yang J, Zhang M, Wang X, Xu W, Price CH, et al. Serum metabolic fingerprints on bowl-shaped submicroreactor chip for chemotherapy monitoring. ACS Nano. 2022;16(2):2852–65.
Gibb S, Strimmer K. Mass spectrometry analysis using MALDIquant. In: Datta S, Mertens BJA, editors. Statistical analysis of proteomics, metabolomics, and lipidomics data using mass spectrometry. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2017. p. 101–24.
Wu T, Xie C, Han J, Ye Y, Weiel J, Li Q, et al. Metabolic disturbances associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Plos One. 2012;7(6).
Ouyang X, Dai Y, Wen JL, Wang LX. 1H NMR-based metabolomic study of metabolic profiling for systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2011;20(13):1411–20.
Cao Z, Wang J, Weng Z, Tao X, Xu Y, Li X, et al. Metabolomic analysis of serum from pure coronary artery ectasia patients based on UPLC-QE/MS technique. Clin Chim Acta. 2022;534:93–105.
Tam LS, Li EK, Leung VYF, Griffith JF, Benzie IFF, Um PL, et al. The effects of vitamins C and E on oxidative stress markers and endothelial function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:212–3.
Moori M, Ghafoori H, Sariri R. Nonenzymatic antioxidants in saliva of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2016;25(3):265–71.
Wang Q, Sun Z, Cao S, Lin X, Wu M, Li Y, et al. Reduced immunity regulator MAVS contributes to non-hypertrophic cardiac dysfunction by disturbing energy metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:919038.
Kang J, Zhu L, Lu J, Zhang X. Application of metabolomics in autoimmune diseases: insight into biomarkers and pathology. J Neuroimmunol. 2015;279:25–32.
Rodriguez-Carrio J, Lopez P, Sanchez B, Gonzalez S, Gueimonde M, Margolles A, et al. Intestinal dysbiosis is associated with altered short-chain fatty acids and serum-free fatty acids in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2017;8.
Yan R, Jiang H, Gu S, Feng N, Zhang N, Lv L, et al. Fecal metabolites were altered, identified as biomarkers and correlated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in a GC-MS-based metabolomics study. Front Immunol. 2020;11.
Xie Y, Liu B, Wu Z. Identification of serum biomarkers and pathways of systemic lupus erythematosus with skin involvement through GC/MS-based metabolomics analysis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:77–86.
Duarte-Delgado NP, Cala MP, Barreto A, Rodríguez CL-S. Metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Transl Autoimmun. 2022;5:100150.
Wen M, Liu T, Zhao M, Dang X, Feng S, Ding X, et al. Correlation analysis between gut microbiota and metabolites in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:5579608.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project: 22274027 and 21974023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All of the urine samples in this work were collected in compliance with the ethical standards. This study was approved by the Review Board and Ethical Committee of Fudan University, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Huang, Z., Chen, X. et al. Metabolic profiling of urinary exosomes for systemic lupus erythematosus discrimination based on HPL-SEC/MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 6411–6420 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04916-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04916-z