Abstract
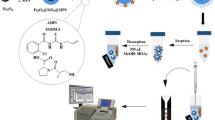
A novel deep eutectic solvent-magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer (DES-MMIP) for the specific removal of oxalic acid (OA) was prepared by an environmentally friendly deep eutectic solvent, consisting of betaine, citric acid, and glycerol, which acted as the functional monomer for polymerization. The structure and morphology of DES-MMIPs were studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, thermal gravimetric analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer. DES-MMIPs had a core–shell structure, with magnetic iron oxide as the core, and showed good thermal stability and high adsorption capacity (18.73 mg/g) for OA. The adsorption process of OA by DES-MMIPs followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm model. DES-MMIPs had significant selectivity for OA and their imprinting factor was 3.26. When applied to real samples, high performance liquid chromatography analysis showed that DES-MMIPs could remove OA from both spinach and blood serum. These findings provide potential methods for removal of OA from vegetables and for specific removal of OA in renal dialysis.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams DJ, Edwards D, Pun S, Chaliha M, Burren B, Tinggi U, et al. Organic acids in Kakadu plum (Terminalia ferdinandiana): the good (ellagic), the bad (oxalic) and the uncertain (ascorbic). Food Res Int. 2016;89(Pt 1):237–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.08.004.
Ivandini TA, Rao TN, Fujishima A, Einaga Y. Electrochemical oxidation of oxalic acid at highly boron-doped diamond electrodes. Anal Chem. 2006;78(10):3467–71. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac052029x.
Hussain S, Abbas Zaidi S, Vikraman D, Kim H-S, Jung J. Facile preparation of tungsten carbide nanoparticles for an efficient oxalic acid sensor via imprinting. Microchem J. 2020;159:105404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105404.
Judprasong K, Charoenkiatkul S, Sungpuag P, Vasanachitt K, Nakjamanong Y. Total and soluble oxalate contents in Thai vegetables, cereal grains and legume seeds and their changes after cooking. J Food Compos Anal. 2006;19(4):340–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2005.04.002.
Li F, Li X, Su J, Li Y, He X, Chen L, et al. A strategy of utilizing Cu(2+)-mediating interaction to prepare magnetic imprinted polymers for the selective detection of celastrol in traditional Chinese medicines. Talanta. 2021;231:122339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122339.
Kong X, Gao R, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y. Synthesis and characterization of the core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (Fe(3)O(4)@MIPs) adsorbents for effective extraction and determination of sulfonamides in the poultry feed. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1245:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.04.061.
Liu Z, Wang Y, Xu F, Wei X, Chen J, Li H, et al. A new magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based on deep eutectic solvents as functional monomer and cross-linker for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1129:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.06.052.
Cui Y, Kang W, Qin L, Ma J, Liu X, Yang Y. Magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymer for selective adsorption of quinoline from coking wastewater. Chem Eng J. 2020;397:125480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125480.
Cheng Y, Nie J, Liu H, Kuang L, Xu G. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for effective extraction and determination of kaempferol from apple samples. J Chromatogr A. 2020;1630:461531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461531.
Fang L, Miao Y, Wei D, Zhang Y, Zhou Y. Efficient removal of norfloxacin in water using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Chemosphere. 2021;262:128032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128032.
Fang X, Wang Z, Sun N, Deng C. Magnetic metal oxide affinity chromatography-based molecularly imprinted approach for effective separation of serous and urinary phosphoprotein biomarker. Talanta. 2021;226:122143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122143.
Wu N, Luo Z, Ge Y, Guo P, Du K, Tang W, et al. A novel surface molecularly imprinted polymer as the solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the selective determination of ampicillin sodium in milk and blood samples. J Pharm Anal. 2016;6(3):157–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2016.01.004.
Gong Y-R, Wang Y, Dong J-B, Yang J, Ren X-W, Gong B-L. Preparation of isoprocarb surface molecular-imprinted materials and its recognition character. Chin J Anal Chem. 2014;42(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-2040(13)60704-5.
Wang X, Wang L, He X, Zhang Y, Chen L. A molecularly imprinted polymer-coated nanocomposite of magnetic nanoparticles for estrone recognition. Talanta. 2009;78(2):327–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.11.024.
Sun Y, Zheng W. Surface molecular imprinting on polystyrene resin for selective adsorption of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid. Chemosphere. 2021;269:128762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128762.
Zhao M, Shao H, Ma J, Li H, He Y, Wang M, et al. Preparation of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of patulin from juice samples. J Chromatogr A. 2020;1615:460751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460751.
Zhang M, Zhang X, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y. A self-assembled polydopamine film on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for specific capture of protein. Nanoscale. 2012;4(10):3141–7. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr30316g.
Abbott AP, Boothby D, Capper G, Davies DL, Rasheed RK. Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(29):9142–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja048266j.
Kang X, Deng L, Quan T, Gao M, Zhang K, Xia Z, et al. Selective extraction of quinolizidine alkaloids from Sophora flavescens Aiton root using tailor-made deep eutectic solvents and magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. Sep Purif Technol. 2021;261:118282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118282.
Santana-Mayor Á, Rodríguez-Ramos R, Herrera-Herrera AV, Socas-Rodríguez B, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ. Deep eutectic solvents. The new generation of green solvents in analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2021;134:116108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116108.
Tan L, Zhou LD, Jiang ZF, Ma RR, He JY, Xia ZN, et al. Selective separation and inexpensive purification of paclitaxel based on molecularly imprinted polymers modified with ternary deep eutectic solvents. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021;192:113661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113661.
Fu N, Li L, Liu X, Fu N, Zhang C, Hu L, et al. Specific recognition of polyphenols by molecularly imprinted polymers based on a ternary deep eutectic solvent. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1530:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.11.011.
Husin NA, Muhamad M, Yahaya N, Miskam M, Syazni Nik Mohamed Kamal NN, Asman S, et al. Application of a new choline-imidazole based deep eutectic solvents in hybrid magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for efficient and selective removal of naproxen from aqueous samples. Mater Chem Phys. 2021;261:124228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124228.
Ling T, Yang L-L, Li Y-J, Jiang Z-F, Li Q-Y, Ma R-R, et al. Investigating two distinct dummy templates molecularly imprinted polymers as paclitaxel adsorbent in synthesis system and releaser in biological samples. Microchem J. 2021;165:106042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106042.
Wang D, Luo X, Huang Y, Wang M, Xia Z. Combined magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers with a ternary deep eutectic solvent to purify baicalein from the Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi by magnetic separation. Microchem J. 2020;157:105109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105109.
Dai L, Sun C, Li R, Mao L, Liu F, Gao Y. Structural characterization, formation mechanism and stability of curcumin in zein-lecithin composite nanoparticles fabricated by antisolvent co-precipitation. Food Chem. 2017;237:1163–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.134.
Wang SX, Ma RR, Mazzu YZ, Zhang JW, Li W, Tan L, et al. Specific adsorption of tetracycline from milk by using biocompatible magnetic molecular imprinting material and evaluation by ECD. Food Chem. 2020;326:126969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126969.
Parkinson IS, Channon SM, Tomson CRV, Adonai LR, Ward MK, Laker MF. The determination of plasma oxalate concentrations using an enzyme/bioluminescent assay. 2. Co-immobilisation of bioluminescent enzymes and studies of in vitro oxalogenesis. Clin Chim Acta. 1989;179(1):97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(89)90027-2.
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81973451); Fundamental and Frontier Research Fund of Chongqing (No. cstc2018jcyjAX0661; No. cstc2019jsyj-yzysbAX0020); the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. KJZD-K201800103); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2019CDYGYB027) and Venture & Innovation Support Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees, and Tang Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation, data curation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft: Yan-Jun Li and Jia-Yuan He; methodology: Qing-Yao Li; writing—review and editing: Li–Li Yang and Rong-Rong Ma; project administration: Chong-Zhi Wang; supervision and visualization: Lian-Di Zhou; conceptualization, validation, resources, project administration, and funding acquisition: Qi-Hui Zhang and Chun-Su Yuan. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YJ., He, JY., Li, QY. et al. An edible molecularly imprinted material prepared by a new environmentally friendly deep eutectic solvent for removing oxalic acid from vegetables and human blood. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 2481–2491 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03889-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03889-9