Abstract
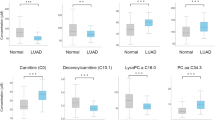
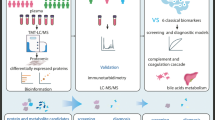
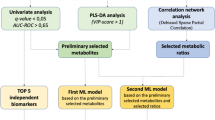
Metabolic markers, offering sensitive information on biological dysfunction, play important roles in diagnosing and treating cancers. However, the discovery of effective markers is limited by the lack of well-established metabolite selection approaches. Here, we propose a network-based strategy to uncover the metabolic markers with potential clinical availability for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). First, an integrated mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics was used to profile the plasma samples from 43 NSCLC patients and 43 healthy controls. We found that a series of 39 metabolites were altered significantly. Relying on the human metabolic network assembled from Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database, we mapped these differential metabolites to the network and constructed an NSCLC-related disease module containing 23 putative metabolic markers. By measuring the PageRank centrality of molecules in this module, we computationally evaluated the network-based importance of the 23 metabolites and demonstrated that the metabolism pathways of aromatic amino acids and long-chain fatty acids provided potential molecular targets of NSCLC (i.e., IL4l1 and ACOT2). Combining network-based ranking and support-vector machine modeling, we further found a panel of eight metabolites (i.e., pyruvate, tryptophan, and palmitic acid) that showed a high capability to differentiate patients from controls (accuracy > 97.7%). In summary, we present a meaningful network method for metabolic marker discovery and have identified eight strong candidate metabolites for NSCLC diagnosis.
Graphic abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wishart DS. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15:473–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.32.
Rinschen MM, Ivanisevic J, Giera M, Siuzdak G. Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2019;20:353–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0108-4.
Hu Q, Tang H, Wang Y. Challenges in Analysis of Hydrophilic Metabolites Using Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. J Analysis Test. 2020;4:140–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-020-00126-z.
Tolstikov V, Moser AJ, Sarangarajan R, Narain NR, Kiebish MA. Current Status of Metabolomic Biomarker Discovery: Impact of Study Design and Demographic Characteristics. Metabolites. 2020;10:224. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060224.
Kennedy AD, Wittmann BM, Evans AM, Miller LAD, Toal DR, Lonergan S, Elsea SH, Pappan KL. Metabolomics in the clinic: A review of the shared and unique features of untargeted metabolomics for clinical research and clinical testing. J Mass Spectrom. 2018;53:1143–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.4292.
Date Y, Kikuchi J. Application of a Deep Neural Network to Metabolomics Studies and Its Performance in Determining Important Variables. Anal Chem. 2018;90:1805–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03795.
Alakwaa FM, Chaudhary K, Garmire LX. Deep Learning Accurately Predicts Estrogen Receptor Status in Breast Cancer Metabolomics Data. J Proteome Res. 2017;17:337–47. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00595.
Shen X, Wang R, Xiong X, Yin Y, Cai Y, Ma Z, Liu N, Zhu Z-J. Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1516. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09550-x.
Rudin C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead. Nat Mach Intell. 2019;1:206–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-019-0048-x.
Lee MY, Hu T. Computational Methods for the Discovery of Metabolic Markers of Complex Traits. Metabolites. 2019;9:66. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9040066.
Xu J, Zhang P, Huang Y, Zhou Y, Hou Y, Bekris L, Lathia J, Chiang C-W, Li L, Pieper A, Leverenz J, Cummings J, Cheng F (2021) Multimodal single-cell/nucleus RNA sequencing data analysis uncovers molecular networks between disease-associated microglia and astrocytes with implications for drug repurposing in Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Res gr.272484.120. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.272484.120
Barabási A-L, Gulbahce N, Loscalzo J. Network medicine: a network-based approach to human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2918.
Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94:1623–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.01.013.
Cancer IA, of LCE and R (INTEGRAL) C for ED of L, Guida F, Sun N, Bantis LE, Muller DC, Li P, Taguchi A, Dhillon D, Kundnani DL, Patel NJ, Yan Q, Byrnes G, Moons KGM, Tjønneland A, Panico S, Agnoli C, Vineis P, Palli D, Bueno-de-Mesquita B, Peeters PH, Agudo A, Huerta JM, Dorronsoro M, Barranco MR, Ardanaz E, Travis RC, Byrne KS, Boeing H, Steffen A, Kaaks R, Hüsing A, Trichopoulou A, Lagiou P, Vecchia CL, Severi G, Boutron-Ruault M-C, Sandanger TM, Weiderpass E, Nøst TH, Tsilidis K, Riboli E, Grankvist K, Johansson M, Goodman GE, Feng Z, Brennan P, Johansson M, Hanash SM, . Assessment of Lung Cancer Risk on the Basis of a Biomarker Panel of Circulating Proteins. Jama Oncol. 2018;4:e182078–e182078. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2078.
Seijo LM, Peled N, Ajona D, Boeri M, Field JK, Sozzi G, Pio R, Zulueta JJ, Spira A, Massion PP, Mazzone PJ, Montuenga LM. Biomarkers in lung cancer screening: achievements, promises and challenges. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;14:343–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.11.023.
Hensley CT, Faubert B, Yuan Q, Lev-Cohain N, Jin E, Kim J, Jiang L, Ko B, Skelton R, Loudat L, Wodzak M, Klimko C, McMillan E, Butt Y, Ni M, Oliver D, Torrealba J, Malloy CR, Kernstine K, Lenkinski RE, DeBerardinis RJ. Metabolic Heterogeneity in Human Lung Tumors. Cell. 2016;164:681–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.034.
Ruiying C, Zeyun L, Yongliang Y, Zijia Z, Ji Z, Xin T, Xiaojian Z. A comprehensive analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE. 2020;15: e0232272. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232272.
Seow WJ, Shu X-O, Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Walker DI, Hu W, Cai Q, Gao Y-T, Xiang Y-B, Moore SC, Bassig BA, Wong JYY, Zhang J, Ji B-T, Boulangé CL, Kaluarachchi M, Wijeyesekera A, Zheng W, Elliott P, Rothman N, Lan Q. Association of Untargeted Urinary Metabolomics and Lung Cancer Risk Among Never-Smoking Women in China. Jama Netw Open. 2019;2: e1911970. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.11970.
Liu P, Li R, Antonov AA, Wang L, Li W, Hua Y, Guo H, Wang L, Liu P, Chen L, Tian Y, Xu F, Zhang Z, Zhu Y, Huang Y. Discovery of Metabolite Biomarkers for Acute Ischemic Stroke Progression. J Proteome Res. 2017;16:773–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00779.
Hua Y, Yang X, Li R, Liu P, Liu P, Li L, Yuan X, Hua X, Tian Y, Zhang Z, Huang Y. Quantitative characterization of glutaminolysis in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:2045–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01626-3.
Luan H, Ji F, Chen Y, Cai Z. statTarget: A streamlined tool for signal drift correction and interpretations of quantitative mass spectrometry-based omics data. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1036:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.08.002.
Sumner LW, Amberg A, Barrett D, Beale MH, Beger R, Daykin CA, Fan TW-M, Fiehn O, Goodacre R, Griffin JL, Hankemeier T, Hardy N, Harnly J, Higashi R, Kopka J, Lane AN, Lindon JC, Marriott P, Nicholls AW, Reily MD, Thaden JJ, Viant MR. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics. 2007;3:211–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2.
Liu C, Ma Y, Zhao J, Nussinov R, Zhang Y-C, Cheng F, Zhang Z-K. Computational network biology: Data, model, and applications. Phys Reports. 2019;846:1–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2019.12.004.
Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27.
Lv L, Zhang K, Zhang T, Bardou D, Zhang J, Cai Y. PageRank centrality for temporal networks. Phys Lett A. 2019;383:1215–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2019.01.041.
Chong J, Wishart DS, Xia J (2019) Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr Protoc Bioinform 68:e86. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.86
Snaebjornsson MT, Janaki-Raman S, Schulze A. Greasing the Wheels of the Cancer Machine: The Role of Lipid Metabolism in Cancer. Cell Metab. 2019;31:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.010.
Olson KA, Schell JC, Rutter J. Pyruvate and Metabolic Flexibility: Illuminating a Path Toward Selective Cancer Therapies. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41:219–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.01.002.
Sadik A, Patterson LFS, Öztürk S, Mohapatra SR, Panitz V, Secker PF, Pfänder P, Loth S, Salem H, Prentzell MT, Berdel B, Iskar M, Faessler E, Reuter F, Kirst I, Kalter V, Foerster KI, Jäger E, Guevara CR, Sobeh M, Hielscher T, Poschet G, Reinhardt A, Hassel JC, Zapatka M, Hahn U, von Deimling A, Hopf C, Schlichting R, Escher BI, Burhenne J, Haefeli WE, Ishaque N, Böhme A, Schäuble S, Thedieck K, Trump S, Seiffert M, Opitz CA. IL4I1 Is a Metabolic Immune Checkpoint that Activates the AHR and Promotes Tumor Progression. Cell. 2020;182:1252-1270.e34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.038.
Huang B, Song B, Xu C. Cholesterol metabolism in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Metabolism. 2020;2:132–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-020-0174-0.
Bai D, Wu Y, Deol P, Nobumori Y, Zhou Q, Sladek FM, Liu X. Palmitic acid negatively regulates tumor suppressor PTEN through T366 phosphorylation and protein degradation. Cancer Lett. 2021;496:127–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.007.
Zou KH, O’Malley AJ, Mauri L. Receiver-Operating Characteristic Analysis for Evaluating Diagnostic Tests and Predictive Models. Circulation. 2007;115:654–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.105.594929.
Huttlin EL, Bruckner RJ, Paulo JA, Cannon JR, Ting L, Baltier K, Colby G, Gebreab F, Gygi MP, Parzen H, Szpyt J, Tam S, Zarraga G, Pontano-Vaites L, Swarup S, White AE, Schweppe DK, Rad R, Erickson BK, Obar RA, Guruharsha KG, Li K, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Gygi SP, Harper JW. Architecture of the human interactome defines protein communities and disease networks. Nature. 2017;545:505–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22366.
Cheng F, Zhao J, Wang Y, Lu W, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Martin WR, Wang R, Huang J, Hao T, Yue H, Ma J, Hou Y, Castrillon JA, Fang J, Lathia JD, Keri RA, Lightstone FC, Antman EM, Rabadan R, Hill DE, Eng C, Vidal M, Loscalzo J. Comprehensive characterization of protein–protein interactions perturbed by disease mutations. Nat Genet. 2021;53:342–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-00774-y.
Ruiz C, Zitnik M, Leskovec J. Identification of disease treatment mechanisms through the multiscale interactome. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1796. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21770-8.
Oldham S, Fulcher B, Parkes L, Arnatkevic̆iūtė A, Suo C, Fornito A, . Consistency and differences between centrality measures across distinct classes of networks. PLoS ONE. 2019;14: e0220061. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220061.
Sellers K, Fox MP, Bousamra M, Slone SP, Higashi RM, Miller DM, Wang Y, Yan J, Yuneva MO, Deshpande R, Lane AN, Fan TW-M. Pyruvate carboxylase is critical for non–small-cell lung cancer proliferation. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:687–98. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci72873.
Wang Z, Li T, Mao C, Liu W, Tao Y. IL4I1-driven AHR signature: a new avenue for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00529-z.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Prof. Wei Jiang at Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics for his valued suggestions and guidance of TCGA data analysis.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81903992), the Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Commission of Health (No. Q2017004), and the Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent (No. QNRC2016656).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committees of the Cancer Hospital of Jiangsu Province and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were following the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, L., Li, L., Xu, Z. et al. Metabolic network-based identification of plasma markers for non-small cell lung cancer. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 7421–7430 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03699-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03699-5