Abstract
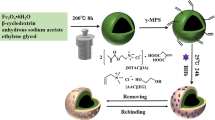
In this study, a novel kind of imprinted polymers based on metal–organic frameworks (MOF@DES-MIPs) was prepared, using bovine hemoglobin (BHb) as template molecules and deep eutectic solvents (DES) as functional monomers for selective recognition and adsorption of BHb. MOF were used as the substrates to improve the accessibility of imprinted sites and DES as the functional monomers to produce different forces for BHb to help the formation of imprinted sites. Imprinted polymer films were taken to provide analyte selectivity. The MOF@DES-MIPs prepared were characterized and evaluated by scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectrometer. We also investigated the influences of BHb concentration and adsorption time on the performance of MOF@DES-MIPs. The maximal adsorption capacity of MOF@DES-MIPs to BHb reached 151.28 mg g−1, and the MOF@DES-MIPs showed good selectivity and fast adsorption equilibrium, which might offer a novel method for the preparation and research of molecularly imprinted polymers of biomacromolecules. In addition, MOF@DES-MIPs were successfully applied in the selective recognition of BHb from a real bovine blood sample.

Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi W, Zhang S, Li K, Jia W, Han D. Integration of mixed-mode chromatography and molecular imprinting technology for double recognition and selective separation of proteins. Sep Purif Technol. 2018;202:165–73.
Xie X, Hu Q, Ke R, Zhen X, Bu Y, Wang S. Facile preparation of photonic and magnetic dual responsive protein imprinted nanomaterial for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem Eng J. 2019;371:130–7.
Zhang J, Wang Y, Lu X. Molecular imprinting technology for sensing foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413:1–18.
Han S, Yao A, Wang Y. An ionic liquid-molecularly imprinted composite based on graphene oxide for the specific recognition and extraction of cancer antigen 153. RSC Adv. 2021;11(22):13085–90.
Pichon V, Delaunay N, Combes A. Sample preparation using molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chem. 2020;92:16–33.
Dinc M, Esen C, Mizaikoff B. Recent advances on core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for biomacromolecules. Trends Anal Chem. 2019;114:202–17.
Xu W, Wang Y, Wei X, Chen J, Xu P, Ni R, et al. Fabrication of magnetic polymers based on deep eutectic solvent for separation of bovine hemoglobin via molecular imprinting technology. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1048:1–11.
Gao R, Mu X, Hao Y, Zhang L, Zhang J, Tang Y. Combination of surface imprinting and immobilized template techniques for preparation of core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers based on directly amino-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2:1733–41.
Zhang Q, Karine D, Royer S, Francois J. Deep eutectic solvents: syntheses, properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(21):7108–46.
Lyu H, Hu K, Chu Q, Su Z, Xie Z. Preparation of ionic liquid mediated molecularly imprinted polymer and specific recognition for bisphenol A from aqueous solution. Microchem J. 2020;158:105293–9.
Fu N, Li L, Liu K, Kim C, Li J, Zhu T. A choline chloride-acrylic acid deep eutectic solvent polymer based on Fe3O4 particles and MoS2 sheets (poly(ChCl-AA DES)@Fe3O4@MoS2) with specific recognition and good antibacterial properties for β-lactoglobulin in milk. Talanta. 2019;197:567–77.
Zhang Y, Cao H, Huang Q, Liu X, Zhang H. Isolation of transferrin by imprinted nanoparticles with magnetic deep eutectic solvents as monomer. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410:6237–45.
Liu Y, Wang Y, Dai Q, Zhou Y. Magnetic deep eutectic solvents molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective recognition and separation of protein. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;936:168–78.
Nadim AH, El-Aal M, Al-Ghobashy MA, El-Saharty YS. Facile imprinted polymer for label-free highly selective potentiometric sensing of proteins: case of recombinant human erythropoietin. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413:3611–23.
Li L, Chen Y, Yang L, Wang Z, Liu H. Recent advances in applications of metal-organic frameworks for sample preparation in pharmaceutical analysis. Coordin Chem Rev. 2020;411:213235.
Li Z, Xi Y, Zhao A, Jiang J, Li B, Yang X. Cobalt-imidazole metal-organic framework loaded with luminol for paper-based chemiluminescence detection of catechol with use of a smartphone. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413:3541–50.
Mirzajani R, Kardani F, Ramezani Z. Fabrication of UMCM-1 based monolithic and hollow fiber-metal-organic framework deep eutectic solvents/molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in solid phase microextraction of phthalate esters in yogurt, water and edible oil by GC-FID-ScienceDi. Food Chem. 2020;314:126179–89.
Kang Y, Zhang L, Lai Q, Lin C, Wu K, Dang L, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymer based on metal-organic frameworks: synthesis and application on determination of dibutyl phthalate. Polym-Plast Tech Mat. 2020;2:1–10.
Li J, Ma M, Zhang C, Lu R, Zhang L, Zhang W. Synthesis of a molecularly imprinted polymer using MOF-74(Ni) as matrix for selective recognition of lysozyme. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(24):7227–36.
Wu X, Chen X, Zhong G, Chen C, Cai C. A novel Wulff-type boronate acid-functionalized magnetic metal, organic framework imprinted polymer for specific recognition of glycoproteins under physiological pH. J Sep Sci. 2020;43(19):3715–824.
Han S, Ding Y, Teng F, Yao A, Leng Q. Determination of chloropropanol with an imprinted electrochemical sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes/metal-organic framework composites. RSC Adv. 2021;11:18468–75.
Zhang H, Yang C, Geng Q, Fan H, Wang B, Wu M, et al. Adsorption of hydrogen sulfide by amine-functionalized metal organic framework (MOF-199): an experimental and simulation study. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;497:143815–43.
Shadpour M, Maryam M. The effect of the coupling agents KH550 and KH570 on the nanostructure and interfacial interaction of zinc oxide/chiral poly(amide-imide) nanocomposites containing l-leucine amino acid moieties. J Mater Sci. 2014;49(14):5112–8.
Liu Z, Wang Y, Xu F, Wei X, Chen J, Li H, et al. A new magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based on deep eutectic solvents as functional monomer and cross-linker for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1129:1129–92.
Guan X, Li Q, Maimaiti T, Lan S, Ouyang P, Ouyang B, et al. Toxicity and photosynthetic inhibition of metal-organic framework MOF-199 to pea seedlings. J Hazard Mater. 2020;409:124521–52.
Chen F, Xie X, Shi Y. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective recognition of resveratrol in wine. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1300(14):112–8.
Gao R, Hao Y, Zhang L, Cui X, Liu D, Zhang M, et al. A facile method for protein imprinting on directly carboxyl-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles using non-covalent template immobilization strategy. Chem Eng J. 2016;284:139–48.
Zhang M, Wang Y, Jia X, He M, Xu M, Yang S, et al. The preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for the recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Talanta. 2014;120(4):376–85.
Sun Y, Zhong S. Nanoscale trifunctional bovine hemoglobin for fabricating molecularly imprinted polydopamine via Pickering emulsions-hydrogels polymerization. Colloid Surface B. 2017;159:131–8.
Wang P, Tang X, Hu L, Yin Y, Chen S, Xu J, et al. Preparation of bovine hemoglobin surface molecularly imprinted cotton for selective protein recognition-ScienceDirect. Process Biochem. 2020;88:31–7.
Zhao Y, Chen Y, Fang M, Tian Y, Bai G, Zhuo K. Silanized carbon dot-based thermo-sensitive molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor for bovine hemoglobin detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(23):5811–7.
Li D, He X, Chen Y, Li W, Zhang Y. Novel hybrid structure silica/CdTe/molecularly imprinted polymer: synthesis, specific recognition, and quantitative fluorescence detection of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2013;5(23):12609–16.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Heilongjiang Province Science Foundation for Youths (No. QC2018073), the Fundamental Research Funds in Heilongjiang Provincial Universities (No. 135409210), and Social Development Public Relations Project of Qiqihar Science and Technology Bureau (No. SFZD-2019151).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S., Yao, A., Ding, Y. et al. A molecularly imprinted polymer based on MOF and deep eutectic solvent for selective recognition and adsorption of bovine hemoglobin. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 5409–5417 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03520-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03520-3