Abstract
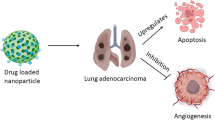
This study explored the potential of poly-(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) nanoparticles to enhance the effectiveness of anticancer treatments through combination therapy with phytol and α-bisabolol. The encapsulation efficiency of the nanoparticles was investigated, highlighting the role of ionic interactions between the drugs and the polymer. Characterization of PLGA-Phy+Bis nanoparticles was carried out using DLS with zeta potential and HR-TEM for size determination. Spectrophotometric measurements evaluated the encapsulation efficiency, loading efficiency, and in vitro drug release. FTIR analysis assessed the chemical interactions between PLGA and the drug actives, ensuring nanoparticle stability. GC-MS was employed to analyze the chemical composition of drug-loaded PLGA nanocarriers. Cytotoxicity was evaluated via the MTT assay, while Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and western blot analysis confirmed apoptotic cell death. Additionally, toxicity tests were performed on L-132 cells and in vivo zebrafish embryos. The study demonstrates high encapsulation efficiency of PLGA-Phy+Bis nanoparticles, which exhibit monodispersity and sizes of 189.3±5nm (DLS) and 268±54 nm (HR-TEM). Spectrophotometric analysis confirmed efficient drug encapsulation and release control. FTIR analysis revealed nanoparticle structural stability without chemical interactions. MTT assay results demonstrated the promising anticancer potential of all the three nanoparticle types (PLGA-Phy, PLGA-Bis, and PLGA-Phy+Bis) against lung cancer cells. Apoptosis was confirmed through Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and western blot analysis, which also revealed changes in Bax and Bcl-2 protein expression. Furthermore, the nanoparticles exhibited non-toxicity in L-132 cells and zebrafish embryo toxicity tests. PLGA-Phy+Bis nanoparticles exhibited efficient encapsulation, controlled release, and low toxicity. Apoptosis induction in A549 cells and non-toxicity in healthy cells highlight their clinical potential.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The article contains all relevant data from the study. The original contributions are available upon request to the corresponding author for further inquiries.
References
Anwer K, Mohammad M, Ezzeldin E et al (2019) Preparation of sustained release apremilast-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: in vitro characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study in rats. Int J Nanomed 14:1587–1595. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S195048
Asal HA, Shoueir KR, El-Hagrasy MA, Toson EA (2022) Controlled synthesis of in-situ gold nanoparticles onto chitosan functionalized PLGA nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Int J Biol Macromol 209:2188–2196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.200
Babos G, Biró E, Meiczinger M, Feczkó T (2018) Dual drug delivery of sorafenib and doxorubicin from PLGA and PEG-PLGA polymeric nanoparticles. Polymers (Basel) 10:895. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080895
Bala I, Hariharan S, Kumar MR (2004) PLGA nanoparticles in drug delivery: the state of the art. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 21:387–422. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.v21.i5.20
Balan DJ, Rajavel T, Das M et al (2021) Thymol induces mitochondrial pathway-mediated apoptosis via ROS generation, macromolecular damage and SOD diminution in A549 cells. Pharmacol Reports 73:240–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-020-00171-6
Cavalieri E, Mariotto S, Fabrizi C et al (2004) α-Bisabolol, a nontoxic natural compound, strongly induces apoptosis in glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.088
Chirumbolo S, Bjørklund G, Lysiuk R et al (2018) Targeting cancer with phytochemicals via their fine tuning of the cell survival signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci 19:3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113568
Clogston JD, Patri AK (2011) Zeta potential measurement. In: Methods in Molecular Biology. pp 63–70
Fornaguera C, Feiner-Gracia N, Calderó G et al (2015) Galantamine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles, from nano-emulsion templating, as novel advanced drug delivery systems to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Nanoscale 7:12076–12084. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR03474D
Gavas S, Quazi S, Karpiński TM (2021) Nanoparticles for cancer therapy: current progress and challenges. Nanoscale Res Lett 16:173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-021-03628-6
Hadjiivanov KI, Panayotov DA, Mihaylov MY et al (2021) Power of infrared and raman spectroscopies to characterize metal-organic frameworks and investigate their interaction with guest molecules. Chem Rev 121:1286–1424. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00487
Hanahan D, Robert A W (2017) Biological Hallmarks of cancer. Holland-Frei cancer Med 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119000822.hfcm002
Harrison S, Judd J, Chin S, Ragin C (2022) Disparities in lung cancer treatment. Curr Oncol Rep 24:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-022-01193-4
Huang W-C, Chen S-H, Chiang W-H et al (2016) Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoparticle delivery of chemotherapy for enhanced selective cellular uptake and transportation within tumor. Biomacromolecules 17:3883–3892. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00956
Ibrahim WN, Rosli LMBMR, Doolaanea AA (2020) Formulation, Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of thymoquinone-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in malignant melanoma cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine 15:8059–8074. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S269340
Kiruthiga C, Balan DJ, Jafni S, Anandan DP, Devi KP (2024) Phytol and (−)-α-bisabolol Synergistically trigger intrinsic apoptosis through redox and Ca2+ imbalance in non-small cell lung cancer. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 103005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2023.103005
Komiya T, Kyohkon M, Ohwaki S et al (1999) Phytol induces programmed cell death in human lymphoid leukemia Molt 4B cells. Int J Mol Med 4:377–380. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.4.4.377
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K et al (2009) Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 149:196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.11.006
Lee JH, Yeo Y (2016) Controlled drug release from pharmaceutical nanocarriers Jinhyun. Chem Eng Sci 24:75–84
Makadia HK, Siegel SJ (2011) Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers (Basel) 3:1377–1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3031377
Marongiu L, Donini M, Bovi M et al (2014) The inclusion into PLGA nanoparticles enables α-bisabolol to efficiently inhibit the human dendritic cell pro-inflammatory activity. J Nanoparticle Res 16:2554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2554-4
Mathew A, Fukuda T, Nagaoka Y et al (2012) Curcumin loaded-PLGA nanoparticles conjugated with Tet-1 peptide for potential use in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 7:e32616. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032616
Murata Y, Kokuryo T, Yokoyama Y et al (2017) The anticancer effects of novel α-bisabolol derivatives against pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res. 37:589–598
Norouzi M, Hardy P (2021) Clinical applications of nanomedicines in lung cancer treatment. Acta Biomater 121:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.009
Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF et al (2018) Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnology 16:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8
Picquart M, Lefèvre T (2003) Raman and Fourier transform infrared study of phytol effects on saturated and unsaturated lipid multibilayers. J Raman Spectrosc 34:4–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.927
Rajavel T, Mohankumar R, Archunan G et al (2017) Beta sitosterol and Daucosterol (phytosterols identified in Grewia tiliaefolia) perturbs cell cycle and induces apoptotic cell death in A549 cells. Sci Rep 7:3418. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03511-4
Rajavel T, Packiyaraj P, Suryanarayanan V et al (2018) β-Sitosterol targets Trx/Trx1 reductase to induce apoptosis in A549 cells via ROS mediated mitochondrial dysregulation and p53 activation. Sci Rep 8:2071. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20311-6
Ray S, Ghosh RS, Mandal S (2017) Development of bicalutamide-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and in-vitro evaluation for the treatment of prostate cancer. Artif Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol 45:944–954. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1196457
Rezvantalab S, Drude NI, Moraveji MK et al (2018) PLGA-based nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol 9:1260. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01260
Ruirui Z, He J, Xu X et al (2021) PLGA-based drug delivery system for combined therapy of cancer: research progress. Mater Res Express 8:122002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ac3f5e
Sah AK, Suresh PK, Verma VK (2017) PLGA nanoparticles for ocular delivery of loteprednol etabonate: a corneal penetration study. Artif Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol 45:1156–1164. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1203794
Sakthivel R, Malar DS, Devi KP (2018) Phytol shows anti-angiogenic activity and induces apoptosis in A549 cells by depolarizing the mitochondrial membrane potential. Biomed Pharmacother 105:742–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.035
Singh V, Tiwari M (2010) Structure-processing-property relationship of poly(glycolic acid) for drug delivery systems 1: synthesis and catalysis. Int J Polym Sci 2010:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/652719
Soni S, Gupta H, Kumar N et al (2010) Biodegradable biomaterials. Recent Patents. Biomed Eng 3:30–40. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874764711003010030
Thakor P, Subramanian RB, Thakkar SS et al (2017) Phytol induces ROS mediated apoptosis by induction of caspase 9 and 3 through activation of TRAIL, FAS and TNF receptors and inhibits tumor progression factor Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase in lung carcinoma cell line (A549). Biomed Pharmacother 92:491–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.066
Varani M, Galli F, Capriotti G et al (2020) Theranostic designed near-infrared fluorescent poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles and preliminary studies with functionalized VEGF-nanoparticles. J Clin Med 9:1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061750
Wang Y, Li P, Kong L (2013) Chitosan-modified PLGA nanoparticles with versatile surface for improved drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 14:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9943-3
Wei W, Zhang X, Chen X et al (2016) Smart surface coating of drug nanoparticles with cross-linkable polyethylene glycol for bio-responsive and highly efficient drug delivery. Nanoscale 8:8118–8125. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR09167E
Wen Y-H, Lee T-Y, Fu P-C et al (2017) Multifunctional polymer nanoparticles for dual drug release and cancer cell targeting. Polymers (Basel) 9:213. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060213
Weng J, Tong HHY, Chow SF (2020) In vitro release study of the polymeric drug nanoparticles: development and validation of a novel method. Pharmaceutics 12:732. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080732
Wu S, Peng L, Sang H et al (2018) Anticancer effects of α-Bisabolol in human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells are mediated via apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest, inhibition of cell migration and invasion and upregulation of P13K/AKT signalling pathway. J BUON 23:1407–1412
Xie B, Liu T, Chen S et al (2021) Combination of DNA demethylation and chemotherapy to trigger cell pyroptosis for inhalation treatment of lung cancer. Nanoscale 13:18608–18615. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR05001J
Yao Y, Zang Y, Qu J et al (2019) The toxicity of metallic nanoparticles on liver: the subcellular damages, mechanisms, and outcomes. Int J Nanomedicine 14:8787–8804
Acknowledgements
The authors thankfully acknowledge DST-FIST (Grant No. SR/FST/LSI-639/2015(C)), UGC-SAP (Grant No.F.5-1/2018/DRSII (SAP-II)), DST-PURSE (Grant No. SR/PURSE Phase 2/38 (G)), and ICMR Ad-hoc project (ISRM/Ad-hoc/31/2020-21), for providing Instrumentations and lab facilities. The authors also thank RUSA 2.0 (F. 24-51/2014-U, Policy (TNMulti-Gen), Dept of Edn, GoI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CK designed and conducted the experiments, with assistance from DJB in developing the methodology. SKP and NHP provided support in interpreting FTIR and GC-MS results. KPD encouraged CK to explore the topic and supervised the research findings. SJ contributed to sample preparation, while NMP and MM aided in assessing embryo toxicity. CK and KPD thoroughly reviewed the findings and jointly approved the final version of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The zebrafish embryo acute toxicity test was conducted following the guidelines and regulations of the Institutional Ethics Committee of Alagappa University, Karaikudi, India. The study was approved under the ethical approval number IAEC/AU/OCT/2021/Fish-6.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kiruthiga, C., Balan, D.J., Prasath, N.H. et al. Synergistic induction of apoptosis in lung cancer cells through co-delivery of PLGA phytol/α-bisabolol nanoparticles. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02935-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02935-2