Abstract
Impaired insulin and growth factor functions are thought to drive many alterations in neurodegenerative diseases like dementia and seem to contribute to oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Recent studies revealed that nasal growth factor therapy could induce neuronal and oligodendroglia protection in rodent brain damage induction models. Impairment of several growth factors signaling was reported in neurodegenerative diseases. So, in the present study, we examined the effects of intranasal co-treatment of insulin and a pool of growth factor-rich serum (GFRS) which separated from activated platelets on memory, and behavioral defects induced by intracerebroventricular streptozotocin (icv-STZ) rat model also investigated changes in the hippocampal oxidative-nitrosative state and histology. We found that icv-STZ injection (3 mg/kg bilaterally) impairs spatial learning and memory in Morris Water Maze, leads to anxiogenic-like behavior in the open field arena, and induces oxidative-nitrosative stress, neuroinflammation, and neuronal/oligodendroglia death in the hippocampus. GFRS (1µl/kg, each other day, 9 doses) and regular insulin (4 U/40 µl, daily, 18 doses) treatments improved learning, memory, and anxiogenic behaviors. The present study showed that co-treatment (GFRS + insulin with respective dose) has more robust protection against hippocampal oxidative-nitrosative stress, neuroinflammation, and neuronal/oligodendroglia survival in comparison with the single therapy. Memory and behavioral improvements in the co-treatment of insulin and GFRS could be attributed to their effects on neuronal/oligodendroglia survival and reduction of neuroinflammation in the hippocampus.
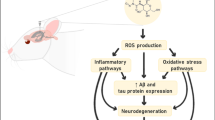
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Study data and analysis are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP/PS1:
-
A mutant amyloid precursor protein and presenilin 1 gene
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- CA:
-
Cornu Ammonis
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- CREB:
-
CAMP response element-binding protein
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- FGF2:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GABA:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- GFRS:
-
Growth factor-rich serum
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- ICV:
-
Intracerebroventricular
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- OCT:
-
Optimal cutting temperature compound
- PRP:
-
Platelet-rich plasma
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- sAD:
-
Elderly sporadic Alzheimer’s disease
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- TGF-B1:
-
Transforming growth factor beta 1
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Aksu I, Ates M, Baykara B, Kiray M, Sisman AR, Buyuk E, Baykara B, Cetinkaya C, Gumus H, Uysal N (2012) Anxiety correlates to decreased blood and prefrontal cortex IGF-1 levels in streptozotocin induced diabetes. Neurosci Lett 531:176–181
Alberini CM (2009) Transcription factors in long-term memory and synaptic plasticity. Physiol Rev 89:121–145
Altman R, Rutledge JC (2010) The vascular contribution to Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Sci 119:407–421
Anitua E, Prado R, Sánchez M, Orive G (2012) Platelet-rich plasma: preparation and formulation. Oper Tech Orthop 22:25–32
Anitua E, Pascual C, Antequera D, Bolos M, Padilla S, Orive G, Carro E (2014) Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) reduces neuropathologic hallmarks and improves cognitive functions in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 35:1582–1595
Anitua E, Prado R, Troya M, Zalduendo M, de la Fuente M, Pino A, Muruzabal F, Orive G (2016) Implementation of a more physiological plasma rich in growth factor (PRGF) protocol: Anticoagulant removal and reduction in activator concentration. Platelets 27:459–466
Arnold SE, Arvanitakis Z, Macauley-Rambach SL, Koenig AM, Wang H-Y, Ahima RS, Craft S, Gandy S, Buettner C, Stoeckel LE (2018) Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: concepts and conundrums. Nat Rev Neurol 14:168–181
Becker E, Rios CLO, Lahmann C, Ruecker G, Bauer J, Boeker M (2018) Anxiety as a risk factor of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Br J Psychiatry 213:654–660
Bedse G, Di Domenico F, Serviddio G, Cassano T (2015) Aberrant insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease: current knowledge. Front Neurosci 9:204
Bisht K, Sharma K, Tremblay M-È (2018) Chronic stress as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: roles of microglia-mediated synaptic remodeling, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Neurobiol Stress 9:9–21
Bouvier DS, Murai KK (2015) Synergistic actions of microglia and astrocytes in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 45:1001–1014
Bruehl H, Wolf OT, Convit A (2009) A blunted cortisol awakening response and hippocampal atrophy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Psychoneuroendocrinology 34:815–821
Burnouf T, Walker TL (2022) The multifaceted role of platelets in mediating brain function. Blood 140:815–827
Cai Z, Fan L-W, Lin S, Pang Y, Rhodes PG (2011) Intranasal administration of insulin-like growth factor-1 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in the developing rat brain. Neuroscience 194:195–207
Casadesus G, Smith MA, Basu S, Hua J, Capobianco DE, Siedlak SL, Zhu X, Perry G (2007) Increased isoprostane and prostaglandin are prominent in neurons in Alzheimer disease. Mol Neurodegener 2:1–8
Chen Y, Guo Z, Mao Y-F, Zheng T, Zhang B (2018) Intranasal insulin ameliorates cerebral hypometabolism, neuronal loss, and astrogliosis in streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s rat model. Neurotox Res 33:716–724
Correia CS, Santos XR, Santos SM, Casadesus G, LaManna CJ, Perry G, Smith AM, Moreira IP (2013) Mitochondrial abnormalities in a streptozotocin-induced rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 10:406–419
Costantino HR, Illum L, Brandt G, Johnson PH, Quay SC (2007) Intranasal delivery: physicochemical and therapeutic aspects. Int J Pharm 337:1–24
España J, Giménez-Llort L, Valero J, Miñano A, Rábano A, Rodriguez-Alvarez J, LaFerla FM, Saura CA (2010) Intraneuronal β-amyloid accumulation in the amygdala enhances fear and anxiety in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Biol Psychiat 67:513–521
Fadool D, Tucker K, Phillips J, Simmen J (2000) Brain insulin receptor causes activity-dependent current suppression in the olfactory bulb through multiple phosphorylation of Kv1. 3. J Neurophysiol 83:2332–2348
Faesel N, Schünemann M, Koch M, Fendt M (2021) Angiotensin II-induced drinking behavior as a method to verify cannula placement into the cerebral ventricles of mice: an evaluation of its accuracy. Physiol Behav 232:113339
Fukunaga K, Kawano T (2003) Akt is a molecular target for signal transduction therapy in brain ischemic insult. J Pharmacol Sci 92:317–327
García-Cabezas MÁ, John YJ, Barbas H, Zikopoulos B (2016) Distinction of neurons, glia and endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex: an algorithm based on cytological features. Front Neuroanat 10:107
García-Cabezas MÁ, Barbas H, Zikopoulos B (2018) Parallel development of chromatin patterns, neuron morphology, and connections: potential for disruption in autism. Front Neuroanat 12:70
García-Robledo E, Corzo A, Papaspyrou S (2014) A fast and direct spectrophotometric method for the sequential determination of nitrate and nitrite at low concentrations in small volumes. Mar Chem 162:30–36
Grieb P (2016) Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin injections as a model of Alzheimer’s disease: in search of a relevant mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 53:1741–1752
Gundersen H, Jensen E, Kiêu K, Nielsen J (1999) The efficiency of systematic sampling in stereology—reconsidered. J Microsc 193:199–211
Gutierres JM, Carvalho FB, Schetinger MRC, Marisco P, Agostinho P, Rodrigues M, Rubin MA, Schmatz R, da Silva CR, Cognato GdP (2014) Anthocyanins restore behavioral and biochemical changes caused by streptozotocin-induced sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Life Sci 96:7–17
Hashemi-Firouzi N, Komaki A, Asl SS, Shahidi S (2017) The effects of the 5-HT7 receptor on hippocampal long-term potentiation and apoptosis in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Bull 135:85–91
Henneman W, Sluimer J, Barnes J, Van Der Flier W, Sluimer I, Fox N, Scheltens P, Vrenken H, Barkhof F (2009) Hippocampal atrophy rates in Alzheimer disease: added value over whole brain volume measures. Neurology 72:999–1007
Higaki A, Mogi M, Iwanami J, Min L-J, Bai H-Y, Shan B-S, Kan-No H, Ikeda S, Higaki J, Horiuchi M (2018) Recognition of early stage thigmotaxis in Morris water maze test with convolutional neural network. PLoS ONE 13:e0197003
Howard V, Reed M (2005) Unbiased stereology: three-dimensional measurement in microscopy, Second edn. Garland Science
Illouz T, Madar R, Louzon Y, Griffioen KJ, Okun E (2016) Unraveling cognitive traits using the Morris water maze unbiased strategy classification (MUST-C) algorithm. Brain Behav Immun 52:132–144
Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Sun Y, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) Cerebral neurogenesis is induced by intranasal administration of growth factors. Ann Neurol 53:405–409
Kamat PK, Kalani A, Rai S, Tota SK, Kumar A, Ahmad AS (2016) Streptozotocin intracerebroventricular-induced neurotoxicity and brain insulin resistance: a therapeutic intervention for treatment of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (sAD)-like pathology. Mol Neurobiol 53:4548–4562
Kruger NJ (2009) The Bradford method for protein quantitation. The protein protocols handbook: 17–24
Krupinski J, Issa R, Bujny T, Slevin M, Kumar P, Kumar S, Kaluza J (1997) A putative role for platelet-derived growth factor in angiogenesis and neuroprotection after ischemic stroke in humans. Stroke 28:564–573
Leiter O, Walker TL (2020) Platelets in neurodegenerative conditions—Friend or foe? Front Immunol 11
Lester-Coll N, Rivera EJ, Soscia SJ, Doiron K, Wands JR, de la Monte SM (2006) Intracerebral streptozotocin model of type 3 diabetes: relevance to sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 9:13–33
Lochhead JJ, Thorne RG (2012) Intranasal delivery of biologics to the central nervous system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:614–628
Mah L, Binns MA, Steffens DC, AsDN I (2015) Anxiety symptoms in amnestic mild cognitive impairment are associated with medial temporal atrophy and predict conversion to Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 23:466–476
Majno G, Joris I (1995) Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am J Pathol 146:3
Manolopoulos K, Klotz L, Korsten P, Bornstein S, Barthel A (2010) Linking Alzheimer’s disease to insulin resistance: the FoxO response to oxidative stress. Mol Psychiatry 15:1046–1052
Mansouri MT, Naghizadeh B, Ghorbanzadeh B, Farbood Y, Sarkaki A, Bavarsad K (2013) Gallic acid prevents memory deficits and oxidative stress induced by intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 111:90–96
Marcus DL, Thomas C, Rodriguez C, Simberkoff K, Tsai JS, Strafaci JA, Freedman ML (1998) Increased peroxidation and reduced antioxidant enzyme activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 150:40–44
Marks DR, Tucker K, Cavallin MA, Mast TG, Fadool DA (2009) Awake intranasal insulin delivery modifies protein complexes and alters memory, anxiety, and olfactory behaviors. J Neurosci 29:6734–6751
Meraz-Ríos MA, Toral-Rios D, Franco-Bocanegra D, Villeda-Hernández J, Campos-Peña V (2013) Inflammatory process in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Integr Neurosci 7:59
Mishra SK, Singh S, Shukla S, Shukla R (2018) Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin impairs adult neurogenesis and cognitive functions via regulating neuroinflammation and insulin signaling in adult rats. Neurochem Int 113:56–68
Moloney AM, Griffin RJ, Timmons S, O’Connor R, Ravid R, O’Neill C (2010) Defects in IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and IRS-1/2 in Alzheimer’s disease indicate possible resistance to IGF-1 and insulin signalling. Neurobiol Aging 31:224–243
Moreira PI, Duarte AI, Santos MS, Rego AC, Oliveira CR (2009) An integrative view of the role of oxidative stress, mitochondria and insulin in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 16:741–761
Nguyen TTL, Chan LC, Borreginne K, Kale RP, Hu C, Tye SJ (2018) A review of brain insulin signaling in mood disorders: from biomarker to clinical target. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 92:7–15
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Patterson MA, Szatmari EM, Yasuda R (2010) AMPA receptors are exocytosed in stimulated spines and adjacent dendrites in a Ras-ERK–dependent manner during long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:15951–15956
Paxinos G, Watson C (2006) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates: hard, cover. Elsevier
Prut L, Belzung C (2003) The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol 463:3–33
Rajasekar N, Nath C, Hanif K, Shukla R (2017) Intranasal insulin administration ameliorates streptozotocin (ICV)-induced insulin receptor dysfunction, neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis, and memory impairment in rats. Mol Neurobiol 54:6507–6522
Rivera EJ, Goldin A, Fulmer N, Tavares R, Wands JR, de la Monte SM (2005) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and function deteriorate with progression of Alzheimer’s disease: link to brain reductions in acetylcholine. J Alzheimers Dis 8:247–268
Rostami F, Javan M, Moghimi A, Haddad-Mashadrizeh A, Fereidoni M (2017) Streptozotocin-induced hippocampal astrogliosis and insulin signaling malfunction as experimental scales for subclinical sporadic Alzheimer model. Life Sci 188:172–185
Salmaso N, Stevens HE, McNeill J, ElSayed M, Ren Q, Maragnoli ME, Schwartz ML, Tomasi S, Sapolsky RM, Duman R (2016) Fibroblast growth factor 2 modulates hypothalamic pituitary axis activity and anxiety behavior through glucocorticoid receptors. Biol Psychiat 80:479–489
Sartorius T, Peter A, Heni M, Maetzler W, Fritsche A, Häring H-U, Hennige AM (2015) The brain response to peripheral insulin declines with age: a contribution of the blood-brain barrier? PLoS ONE 10:e0126804
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Preibisch S, Rueden C, Saalfeld S, Schmid B (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9:676–682
Schubert M, Brazil DP, Burks DJ, Kushner JA, Ye J, Flint CL, Farhang-Fallah J, Dikkes P, Warot XM, Rio C (2003) Insulin receptor substrate-2 deficiency impairs brain growth and promotes tau phosphorylation. J Neurosci 23:7084–7092
Shen Y-X, Fan Z-H, Zhao J-G, Zhang P (2009) The application of platelet-rich plasma may be a novel treatment for central nervous system diseases. Med Hypotheses 73:1038–1040
Shoham S, Bejar C, Kovalev E, Weinstock M (2003) Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin causes neurotoxicity to myelin that contributes to spatial memory deficits in rats. Exp Neurol 184:1043–1052
Simon DI, Mullins ME, Jia L, Gaston B, Singel DJ, Stamler JS (1996) Polynitrosylated proteins: characterization, bioactivity, and functional consequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:4736–4741
Sparling JE, Baker SL, Bielajew C (2018) Effects of combined pre-and post-natal enrichment on anxiety-like, social, and cognitive behaviours in juvenile and adult rat offspring. Behav Brain Res 353:40–50
Su L, Hayes L, Soteriades S, Williams G, Brain SA, Firbank MJ, Longoni G, Arnold RJ, Rowe JB, O’Brien JT (2018) Hippocampal stratum radiatum, lacunosum, and moleculare sparing in mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 61:415–424
Takeuchi D, Sato N, Shimamura M, Kurinami H, Takeda S, Shinohara M, Suzuki S, Kojima M, Ogihara T, Morishita R (2008) Alleviation of Aβ-induced cognitive impairment by ultrasound-mediated gene transfer of HGF in a mouse model. Gene Ther 15:561–571
Tiwari V, Kuhad A, Bishnoi M, Chopra K (2009) Chronic treatment with tocotrienol, an isoform of vitamin E, prevents intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative–nitrosative stress in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93:183–189
Tohidi M, Ghasemi A, Hadaegh F, Derakhshan A, Chary A, Azizi F (2014) Age-and sex-specific reference values for fasting serum insulin levels and insulin resistance/sensitivity indices in healthy Iranian adults: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Clin Biochem 47:432–438
Unsicker K, Krieglstein K (2000) Co-activation of TGF-ss and cytokine signaling pathways are required for neurotrophic functions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 11:97–102
Upton Z, Yandell CA, Degger BG, Chan SJ, Moriyama S, Francis GL, Ballard FJ (1998) Evolution of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) action: in vitro characterization of vertebrate IGF-I proteins. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 121:35–41
Uysal N, Sisman AR, Dayi A, Aksu I, Cetin F, Gencoglu C, Tas A, Buyuk E (2011) Maternal exercise decreases maternal deprivation induced anxiety of pups and correlates to increased prefrontal cortex BDNF and VEGF. Neurosci Lett 505:273–278
Wang P, Xie Z-H, Guo Y-J, Zhao C-P, Jiang H, Song Y, Zhu Z-Y, Lai C, Xu S-L, Bi J-Z (2011) VEGF-induced angiogenesis ameliorates the memory impairment in APP transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 411:620–626
Westwood AJ, Beiser A, DeCarli C, Harris TB, Chen TC, He X-m, Roubenoff R, Pikula A, Au R, Braverman LE (2014) Insulin-like growth factor-1 and risk of Alzheimer dementia and brain atrophy. Neurology 82:1613–1619
Winblad B, Amouyel P, Andrieu S, Ballard C, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Cedazo-Minguez A, Dubois B, Edvardsson D, Feldman H (2016) Defeating Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: a priority for European science and society. Lancet Neurol 15:455–532
Yuan Z, Zhou H, Zhou N, Dong D, Chu Y, Shen J, Han Y, Chu X-P, Zhu K (2019) Dynamic evaluation indices in spatial learning and memory of rat vascular dementia in the Morris water maze. Sci Rep 9:7224
Yuliani T, Lobentanzer S, Klein J (2021) Central cholinergic function and metabolic changes in streptozotocin-induced rat brain injury. J Neurochem 158:1307–1319
Zappa Villar MF, López Hanotte J, Falomir Lockhart E, Trípodi LS, Morel GR, Reggiani PC (2018) Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induces impaired Barnes maze spatial memory and reduces astrocyte branching in the CA1 and CA3 hippocampal regions. J Neural Transm 125:1787–1803
Zhao W-Q, Chen H, Quon MJ, Alkon DL (2004) Insulin and the insulin receptor in experimental models of learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 490:71–81
Zheng L, Ishii Y, Tokunaga A, Hamashima T, Shen J, Zhao QL, Ishizawa S, Fujimori T, Yi N, Mori H (2010) Neuroprotective effects of PDGF against oxidative stress and the signaling pathway involved. J Neurosci Res 88:1273–1284
Acknowledgements
The present article is part of a Master of Sciences thesis written by Mahdi Khorsand Ghaffari.
Funding
This research was financed by grant number SUMS-97–01-01018475, awarded to Dr. Ali Rafati from the Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mahdi Khorsand Ghaffari: designing the study, performing laboratory work, data collection, and writing the manuscript draft. Ali Rafati: supervising laboratory works, conceptualization, methodology, and data analysis. Narges Karbalaei: conceptualization, methodology. Masoud Haghani: conceptualization, methodology. Marzieh Nemati: methodology, laboratory assistance, data analysis. Niloofar Sefati: methodology, laboratory assistance, graphical design. Mohammad Reza Namavar: conceptualization, methodology, data analysis, editing, and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures in the study were based on the National Institutes of Health’s Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the Animal Research: Reporting in Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) Guidelines and approved by the local Ethical Committee of the Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (approval number: IR.SUMS.REC.1398.168).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaffari, M.K., Rafati, A., Karbalaei, N. et al. The effect of intra-nasal co-treatment with insulin and growth factor-rich serum on behavioral defects, hippocampal oxidative-nitrosative stress, and histological changes induced by icv-STZ in a rat model. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02899-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02899-3