Abstract
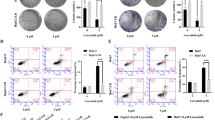
Glioblastoma is one of the most common and invasive types of primary brain malignancies in adults, accounting for 45.5% of malignancies. Its annual prevalence is low compared to other cancers. The survival rate of this disease is about 14 months after diagnosis. Temozolomide (TMZ) is a common chemotherapy drug used to treatment of glioblastoma, but drug resistance against this drug is an important barrier to successful treatment of this cancer. Today, siRNAs play a significant role in cancer treatment. SIX4 is a transcriptional regulatory molecule that can act as a transcriptional suppressor and an activator in target genes involved in differentiation, migration, and cell survival processes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of SIX4-siRNA on A-172 glioblastoma cells, its role as a tumor suppressor, and its combination with TMZ. We studied the cytotoxic effect of the SIX4-siRNA and TMZ on A-172 cells using the MTT assay investigated their effect on apoptosis and cell cycle of A-172 cells used wound healing assays to assess their effect on cell migration. Finally, we used qRT-PCR to study the mRNA expression levels of genes involved in apoptosis and migration of tumoral cells after treatments. Based on our results, silencing SIX4-siRNA expression reduced the cell viability of A-172 cells and sensitize these cells to TMZ. Furthermore, we observed an increase in apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, and a decrease in migration. Bax and caspase-9 overexpression and BCL2 and MMP9 downregulation were detected in the combination of SIX4-siRNA and TMZ. According to our results, the combination of SIX4-siRNA and TMZ can be a very useful strategy for successful glioblastoma treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The results will be available upon the reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Arora A, Somasundaram K (2019) Glioblastoma vs temozolomide: can the red queen race be won? Cancer Biol Ther 20(8):1083–1090
Bagherian A et al (2020) Combination therapy with nanomicellar-curcumin and temozolomide for in vitro therapy of glioblastoma multiforme via Wnt signaling pathways. J Mol Neurosci 70:1471–1483
Chen M et al (2020) NCK1-AS1 increases drug resistance of glioma cells to temozolomide by modulating miR-137/TRIM24. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 35(2):101–108
Doan P et al (2019) Alkylaminophenol induces G1/S phase cell cycle arrest in glioblastoma cells through p53 and cyclin-dependent kinase signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 10:330
Hanif F et al (2017) Glioblastoma multiforme: a review of its epidemiology and pathogenesis through clinical presentation and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 18(1):3
He Q et al (2020) SIX4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating YAP1 and c-MET. Oncogene 39(50):7279–7295
Hu B et al (2020) Therapeutic siRNA: state of the art. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):101
Huang C et al (2008) Small interfering RNA therapy in cancer: mechanism, potential targets, and clinical applications. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12(5):637–645
Huang W et al (2020) miR-802 inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioblastoma multiforme cells by directly targeting SIX4. Cell Biochem Funct 38(1):66–76
Kong L et al (2017) Multifunctional PEI-entrapped gold nanoparticles enable efficient delivery of therapeutic siRNA into glioblastoma cells. Biomater Sci 5(2):258–266
Lee SY (2016) Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Genes Dis 3(3):198–210
Li G et al (2017) SIX4 promotes metastasis via activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. PeerJ 5:e3394
Li X et al (2018) Effect of AQP-5 silencing by siRNA interference on chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther 11:3359–3368
Li Y et al (2019) Effects of SIRT1 silencing on viability, invasion and metastasis of human glioma cell lines. Oncol Lett 17(4):3701–3708
Li Y et al (2021) Upregulation of SIX4 indicates poor clinical outcome and promotes tumor growth and cell metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Thoracic Cancer 12(6):752–759
Louis DN et al (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131:803–820
Lozada-Delgado EL, Grafals-Ruiz N, Vivas-Mejía PE (2017) RNA interference for glioblastoma therapy: innovation ladder from the bench to clinical trials. Life Sci 188:26–36
Matias D et al (2017) Dual treatment with shikonin and temozolomide reduces glioblastoma tumor growth, migration and glial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Oncol 40:247–261
Na X et al (2019) MiR-203a functions as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer by targeting SIX4. Neoplasma 66(2):211–221
Ohka F, Natsume A, Wakabayashi T (2012) Current trends in targeted therapies for glioblastoma multiforme. Neurol Res Int 2012:878425
Oliveira KA et al (2018) Atorvastatin promotes cytotoxicity and reduces migration and proliferation of human A172 glioma cells. Mol Neurobiol 55:1509–1523
Petrenko D et al (2022) Temozolomide efficacy and metabolism: the implicit relevance of nanoscale delivery systems. Molecules 27(11):3507
Rock K et al (2012) A clinical review of treatment outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme—the validation in a non-trial population of the results of a randomised phase III clinical trial: has a more radical approach improved survival? Br J Radiol 85(1017):e729–e733
Santolini M et al (2016) MyoD reprogramming requires Six1 and Six4 homeoproteins: genome-wide cis-regulatory module analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 44(18):8621–8640
Stupp R et al (2014) High-grade glioma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 25: iii93–iii101
Sun X et al (2019) SIX4 activates Akt and promotes tumor angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res 383(1):111495
Sun X et al (2020) SIX4 promotes metastasis through STAT3 activation in breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res 10(1):224
Tamimi AF, Juweid M (2017) Epidemiology and outcome of glioblastoma. Exon Publications 143–153
Tang X et al (2019) SIX4 acts as a master regulator of oncogenes that promotes tumorigenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 516(3):851–857
Thakkar JP et al (2014) Epidemiologic and molecular prognostic review of glioblastomaGBM epidemiology and biomarkers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 23(10):1985–1996
Valtorta S et al (2017) Metformin and temozolomide, a synergic option to overcome resistance in glioblastoma multiforme models. Oncotarget 8(68):113090
Wei Q et al (2013) Expression of Six1 and Six4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their correlation with clinical prognosis. Chin J Pathol 42(7):446–450
Wick W, Platten M (2014) Understanding and targeting alkylator resistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Discov 4(10):1120–1122
Xu H-X et al (2016) Expression profile of SIX family members correlates with clinic-pathological features and prognosis of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 95(27):e4085
Yi G-Z et al (2016) Akt and β-catenin contribute to TMZ resistance and EMT of MGMT negative malignant glioma cell line. J Neurol Sci 367:101–106
Zhang D et al (2016) Inhibition of REST suppresses proliferation and migration in glioblastoma cells. Int J Mol Sci 17(5):664
Zhang X et al (2018) Synergistic anticancer effects of formononetin and temozolomide on glioma C6 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 41(8):1194–1202
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for financial support from the Immunology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zahra Jodari Mohammadpour. The first author of the manuscript, performed the experiment, contributed to the cellular and molecular assays and wrote the initial version of the manuscript. Reza Mohammadzadeh. The corresponding author of the manuscript, supervised the project, and revised the main text of the manuscript. Darya Javadrashid. and Amir Baghbanzadeh. Contributed to the cellular and molecular assays, analyzed the data, formal analysis and revised the manuscript. Mohammad Amin Doustvandi. Participate in reviewing and editing manuscript, and revised the main text of the manuscript. Nesa Barpour. Helped with the data categorization and interpreted the results. Behzad Baradaran. The corresponding author of the manuscript, supervised the project, and revised the main text of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadpour, Z.J., Mohammadzadeh, R., Javadrashid, D. et al. Combination of SIX4-siRNA and temozolomide inhibits the growth and migration of A-172 glioblastoma cancer cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 2741–2751 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02495-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02495-5