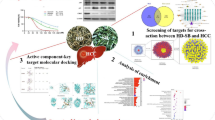
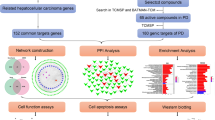
Abstract
Shuganning injection (SGNI), a TCM (traditional Chinese medicine) injection with good hepatoprotective effects, exerted therapeutic effects on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the active compounds and effects of SGNI on HCC remain unclear. The objective of this study was to investigate the active compounds and potential targets of SGNI in the treatment of HCC, and explore the molecular mechanisms of main compounds. Network pharmacology was applied to predict the active compounds and targets of SGNI on cancer. The interactions between active compounds and target proteins were validated by drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS), cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA), and pull-down assay. The in vitro test of the effects and mechanism of vanillin and baicalein was elucidated by MTT, western blot, immunofluorescence, and apoptosis analysis. According to compound characteristics, targets, etc., two typical active ingredients (vanillin and baicalein) were selected as representatives to explore the effects on HCC. Vanillin (an important food additive) bound to NF-κB1 and baicalein (a bioactive flavonoid) bound to FLT3 (FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3) were confirmed in this study. Vanillin and baicalein both inhibited cell viability and promoted apoptosis of Hep3B and Huh7 cells. In addition, both vanillin and baicalein could enhance the activation of the p38/MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signaling pathway, which may partially explain the anti-apoptosis effects of the two compounds. In conclusion, two active compounds of SGNI, vanillin and baicalein, promoted apoptosis of HCC cells via binding with NF-κB1 or FLT3, and regulating the p38/MAPK pathway. Baicalein and vanillin may be good candidates for HCC treatment on drug development.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used and analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ali M, Khan T, Fatima K, Ali QUA, Ovais M, Khalil AT, Ullah I, Raza A, Shinwari ZK, Idrees M (2018) Selected hepatoprotective herbal medicines: evidence from ethnomedicinal applications, animal models, and possible mechanism of actions. Phytotherapy Research: PTR 32:199–215. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5957
Chen Z, Ma X, Zhao Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Li J, Wang R, Zhu Y, Wang L, Xiao X (2015) Yinchenhao decoction in the treatment of cholestasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol 168:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.058
Chen X, Zhou Y, Li Z, Wang Z (2020) Mining database for the expression and clinical significance of NF-κB family in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Oncol 2020:2572048–2572048. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2572048
Coulthard LR, White DE, Jones DL, McDermott MF, Burchill SA (2009) p38(MAPK): stress responses from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Trends Mol Med 15:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2009.06.005
Daver N, Schlenk RF, Russell NH, Levis MJ (2019) Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: review of current knowledge and evidence. Leukemia 33:299–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-018-0357-9
Daver N, Venugopal S, Ravandi F (2021) FLT3 mutated acute myeloid leukemia: 2021 treatment algorithm. Blood Cancer J 11:104. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-021-00495-3
Dou W, Li J, Zhang J, Zhang Y (2013) Effect of Shuganning injection combined with reduced glutathione on liver function and serum T lymphocytes in primary liver cancer patients after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. China Medicine 13:1349–1352
Du J, Wang L, Huang X, Zhang N, Long Z, Yang Y, Zhong F, Zheng B, Lan W, Lin W, Ma W (2021) Shuganning injection, a traditional Chinese patent medicine, induces ferroptosis and suppresses tumor growth in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 85:153551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153551
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Bray F (2019) Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer 144:1941–1953. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31937
Gao H, Wang M, Chen X, Xu X (2013) Clinical observation of compound glycyrrhizin combined with SGNI on hepatoprotective effect of hepatic arterial infusion chemoembolization for primary liver cancer. Chinese Remedies & Clinics 13:1487–1488
Hoesel B, Schmid JA (2013) The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 12:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-86
Huang A, Yang XR, Chung WY, Dennison AR, Zhou J (2020) Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:146. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00264-x
Keenan BP, Fong L, Kelley RK (2019) Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: the complex interface between inflammation, fibrosis, and the immune response. J Immunother Cancer 7:267. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0749-z
Kubes P, Jenne C (2018) Immune responses in the liver. Annu Rev Immunol 36:247–277. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052415
Lam P, Cheung F, Tan HY, Wang N, Yuen MF, Feng Y (2016) Hepatoprotective effects of Chinese medicinal herbs: a focus on anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities. Int J Mol Sci 17:465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040465
Li S, Zhang B (2013) Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin J Nat Med 11:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1875-5364(13)60037-0
Mun EJ, Babiker HM, Weinberg U, Kirson ED, Von Hoff DD (2018) Tumor-treating fields: a fourth modality in cancer treatment. Clinical Cancer Research : an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 24:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-17-1117
O’Reilly LA, Putoczki TL, Mielke LA, Low JT, Lin A, Preaudet A, Herold MJ, Yaprianto K, Tai L, Kueh A, Pacini G, Ferrero RL, Gugasyan R, Hu Y, Christie M, Wilcox S, Grumont R, Griffin MDW, O’Connor L, Smyth GK, Ernst M, Waring P, Gerondakis S, Strasser A (2018) Loss of NF-κB1 causes gastric cancer with aberrant inflammation and expression of immune checkpoint regulators in a STAT-1-dependent manner. Immunity 48:570-583.e578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.003
Racanelli V, Rehermann B (2006) The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology (baltimore, MD) 43:S54-62. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21060
Sun W, Li SC, Xu L, Zhong W, Wang ZG, Pan CZ, Li J, Jin GZ, Ta N, Dong W, Liu D, Liu H, Wang HY, Ding J (2020) High FLT3 levels may predict sorafenib benefit in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research : an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 26:4302–4312. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-19-1858
Tang W, Chen Z, Zhang W, Cheng Y, Zhang B, Wu F, Wang Q, Wang S, Rong D, Reiter FP, De Toni EN, Wang X (2020) The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:87. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0187-x
Tao WW, Jiang H, Tao XM, Jiang P, Sha LY, Sun XC (2016) Effects of acupuncture, Tuina, Tai Chi, Qigong, and traditional Chinese medicine five-element music therapy on symptom management and quality of life for cancer patients: a meta-analysis. J Pain Symptom Manage 51:728–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2015.11.027
Tsimberidou AM, Fountzilas E, Nikanjam M, Kurzrock R (2020) Review of precision cancer medicine evolution of the treatment paradigm. Cancer treatment reviews 86:102019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102019
Villanueva A (2019) Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380:1450–1462. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1713263
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9:537–549. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2694
Wang W, Wei C (2020) Advances in the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes & Diseases 7:308–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2020.01.014
Wang S, Long S, Deng Z, Wu W (2020) Positive role of Chinese herbal medicine in cancer immune regulation. Am J Chin Med 48:1577–1592. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0192415x20500780
Wang K, Chen Q, Shao Y, Yin S, Liu C, Liu Y, Wang R, Wang T, Qiu Y, Yu H (2021) Anticancer activities of TCM and their active components against tumor metastasis. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy Biomedicine & pharmacotherapie 133:111044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111044
Wang X, Wang ZY, Zheng JH, Li S (2021b) TCM network pharmacology: a new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches. Chin J Nat Med 19:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1875-5364(21)60001-8
Wu D, Chen X, Hu S, Bai X (2017) Study on major antitumor components in Yinchenhao decoction in vitro and in vivo based on hollow fiber cell fishing coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr, b: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 1060:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.06.003
Xu Y (2016) Clinical observation on treating jaundice following primary hepatic carcinoma in the integrative medicine. Chinese Journal of Chinese Medicine 8:86–87
Yu Y, Wan Y, Huang C (2009) The biological functions of NF-kappaB1 (p50) and its potential as an anti-cancer target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9:566–571. https://doi.org/10.2174/156800909788486759
Zhong Y, Qiu RZ, Sun SL, Zhao C, Fan TY, Chen M, Li NG, Shi ZH (2020) Small-molecule Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors: an attractive and efficient method for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. J Med Chem 63:12403–12428. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00696
Zhou X, Menche J, Barabási AL, Sharma A (2014) Human Symptoms-Disease Network. Nature Communications 5:4212. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5212
Funding
This study was supported by The National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFE0203100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weiling Pu designed the experiments. Xiao Han conducted the experiments. Jiayan Huang and Jia Lu contributed to data acquisition and data analysis. Shuangfeng Li and Zhong Hao contributed to drafting of the paper. Feng He, Fang Wang, and Haiyang Yu reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X., Huang, J., Lu, J. et al. Active compounds and potential targets of Shuganning injection in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma by network pharmacology and in vitro validation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 1943–1955 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02432-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02432-6